什么是bucket
bucket的英文解释:
Hash table lookup operations are often O(n/m) (where n is the number of objects in the table and m is the number of buckets), which is close to O(1), especially when the hash function has spread the hashed objects evenly through the hash table, and there are more hash buckets than objects to be stored.
可以这样理解:
一个HASH的结果所对应的地址可存放两个BUCKET。可解决HASH冲突。
- 要存数据时,第一次HASH到这里,在第一个BUCKET存放一个数据。
- 要存数据时,当第二次因某些原因HASH到这里时,在第二个BUCKET存放另一个数据。
一个由5个buckets组成的哈希表,里面有7个元素:
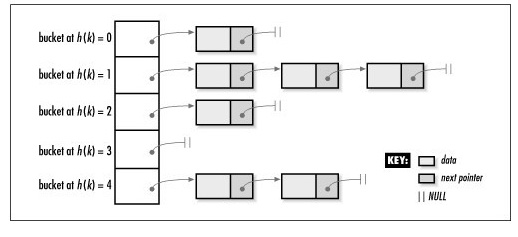
linux的hash函数hash_long等,用了golden ratio来计算。因为桶(bits)的数量需要由hash函数和对冲突的期望来决定,那么对于hash_long这样的hash函数,我们怎么确定桶的数量呢?
一般情况下都是自己根据数据特性来考虑使用的 hash 算法,不是千篇一律咬死一个不放。
比如存放 IP 地址的 hash table,用一个 65536 的桶就很好,把 IP 的后 16bit 作为 key。这种方法绝对比 hash_long、jhash 等函数的碰撞率低。
其实就是这个界和性能的折中。我可以取我问题空间的最大值。这样肯定能保证键值分散。但是这样会浪费很多空间。然而取得太小,又影响查找效率。感觉还是要在试验中进行测试。而且个人觉得,hash比其他搜索的数据结构灵活的地方就是它的可定制性。可以根据具体情况调整,以达到最优的效果。
大致的思路是这样的:
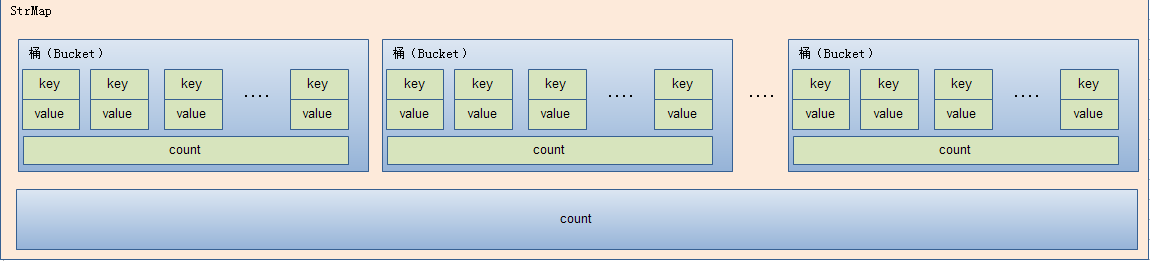
首先哈希桶的个数是固定的,有用户构建的时候输入,一旦构建,个数就已经固定;查找的时候首先将key值通过哈希函数获取哈希值,根据哈希值获取到对应的哈希桶,然后遍历哈希桶内的pairs数组获取;
这两种实现方法看似比较类似,但也有差异:
基于哈希桶的情况下,由于Hash桶容量的限制,所以,有可能发生Hash表填不满的情况,也就是,虽然Hash表里面还有空位,但是新建的表项由于冲突过多,而不能装入Hash表中。不过,这样的实现也有其好处,就是查表的最大开销是可以确定的,因为最多处理的冲突数是确定的,所以算法的时间复杂度为O(1)+O(m),其中m为Hash桶容量。
而另一种通过链表的实现,由于Hash桶的容量是无限的,因此,只要没有超出Hash表的最大容量,就能够容纳新建的表项。但是,一旦发生了Hash冲突严重的情况,就会造成Hash桶的链表过长,大大降低查找效率。在最坏的情况下,时间复杂度退化为O(n),其中n为Hash表的总容量。当然,这种情况的概率小之又小,几乎是可以忽略的。




 本文围绕哈希表中的bucket展开,介绍了bucket的英文解释及作用,可解决HASH冲突。探讨了如何确定桶的数量,需在空间和性能间折中。还对比了基于哈希桶和链表实现的差异,前者查表开销可确定,后者可能因冲突严重降低查找效率。
本文围绕哈希表中的bucket展开,介绍了bucket的英文解释及作用,可解决HASH冲突。探讨了如何确定桶的数量,需在空间和性能间折中。还对比了基于哈希桶和链表实现的差异,前者查表开销可确定,后者可能因冲突严重降低查找效率。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








