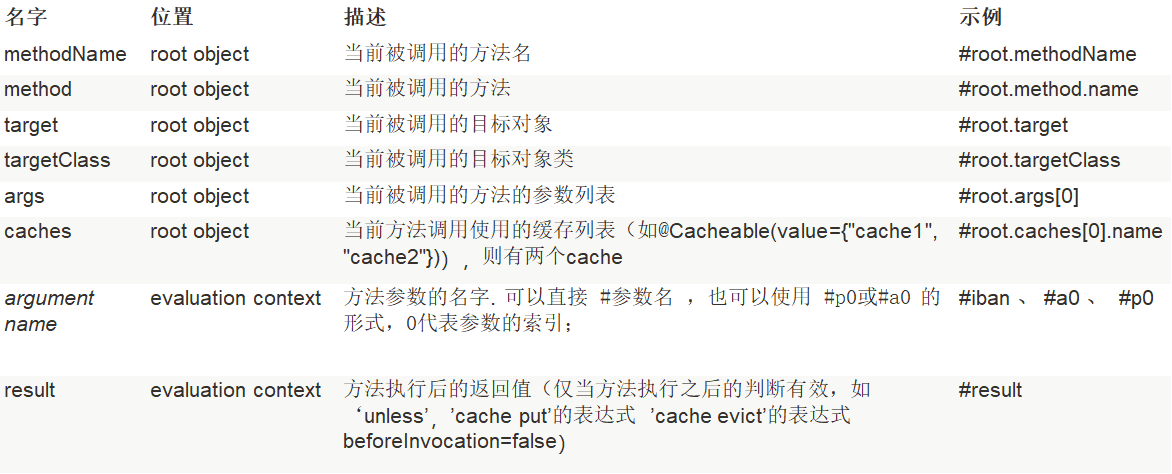
1.理论介绍
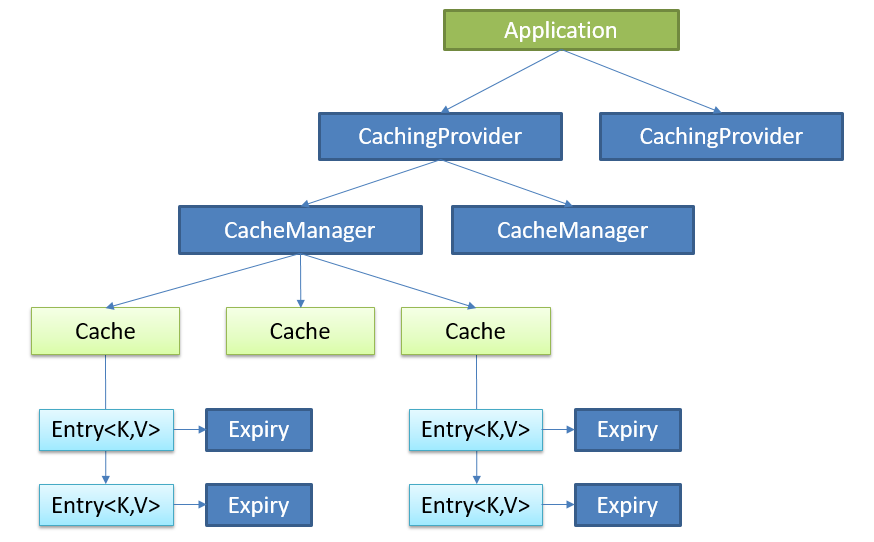
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
Expiry 每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
Spring缓存抽象
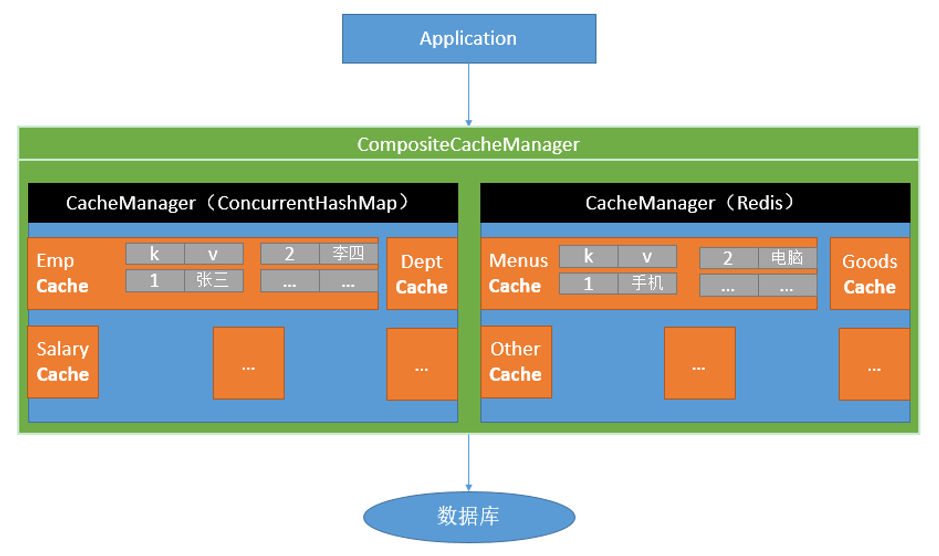
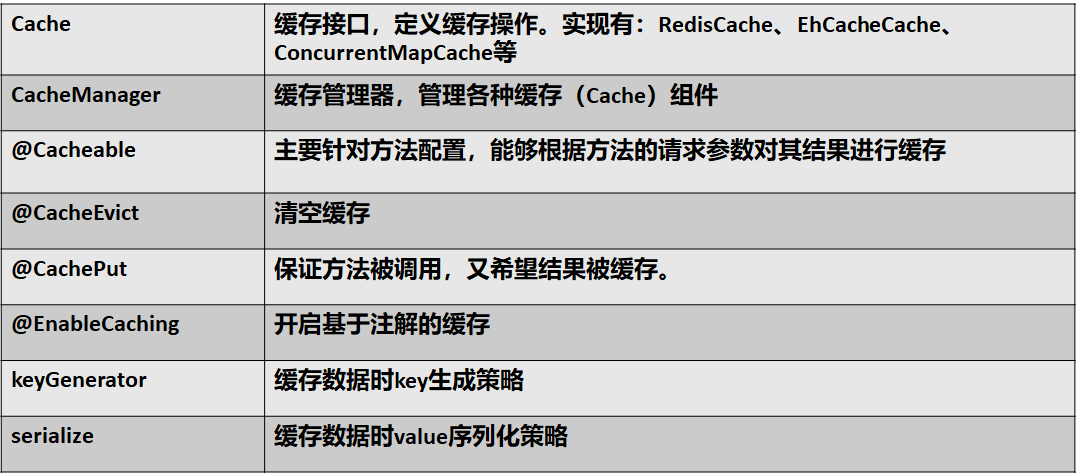
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache
和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;
并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache等;
每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
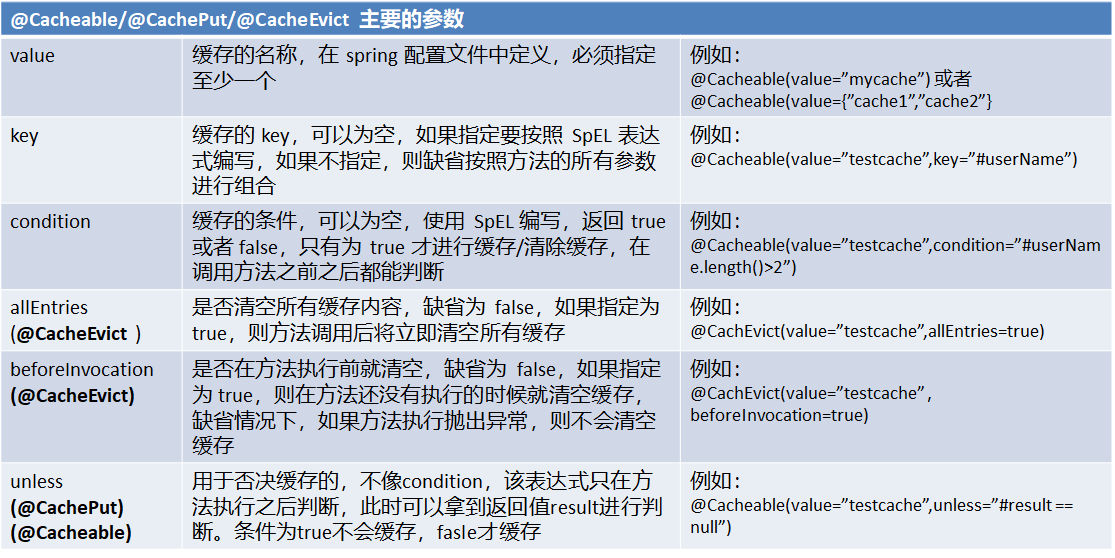
使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
1、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
2、从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
![]()
2.代码结构及pom文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.zy</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-cache</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>spring-boot-cache</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.14.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <lombok.version>1.16.10</lombok.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency> <!-- 引入redis的starter,这里面有jedis客户端 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <!--<scope>test</scope>--> </dependency> <!-- 引入lombok的依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>${lombok.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- 引入caffeine缓存Jar包 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId> <artifactId>caffeine</artifactId> <version>2.6.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
3.启动类
package com.zy; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching; /** * 一、搭建基本环境 * 1、导入数据库文件 创建出department和employee表 * 2、创建javaBean封装数据 * 3、整合MyBatis操作数据库 * 1.配置数据源信息 * 2.使用注解版的MyBatis; * 1)、@MapperScan指定需要扫描的mapper接口所在的包 * 二、快速体验缓存 * 步骤: * 1、开启基于注解的缓存 @EnableCaching * 2、标注缓存注解即可 * @Cacheable * @CacheEvict * @CachePut * 默认使用的是ConcurrentMapCacheManager==ConcurrentMapCache;将数据保存在 ConcurrentMap<Object, Object>中 * 开发中使用缓存中间件;redis、memcached、ehcache; * 三、整合redis作为缓存 * Redis 是一个开源(BSD许可)的,内存中的数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库、缓存和消息中间件。 * 1、安装redis:使用docker; * 2、引入redis的starter * 3、配置redis * 4、测试缓存 * 原理:CacheManager===Cache 缓存组件来实际给缓存中存取数据 * 1)、引入redis的starter,容器中保存的是 RedisCacheManager; * 2)、RedisCacheManager 帮我们创建 RedisCache 来作为缓存组件;RedisCache通过操作redis缓存数据的 * 3)、默认保存数据 k-v 都是Object;利用序列化保存;如何保存为json * 1、引入了redis的starter,cacheManager变为 RedisCacheManager; * 2、默认创建的 RedisCacheManager 操作redis的时候使用的是 RedisTemplate<Object, Object> * 3、RedisTemplate<Object, Object> 是 默认使用jdk的序列化机制 * 4)、自定义CacheManager; * */ @SpringBootApplication // 扫描mapper,支持mybatis @MapperScan("com.zy.mapper") // 开启缓存注解,此外,还要在service层加上缓存注解@Cacheable才能生效 @EnableCaching public class SpringBootCacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootCacheApplication.class, args); } }
4.model层对象
package com.zy.model; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties; import lombok.*; import java.io.Serializable; @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Builder @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public class Employee implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String lastName; private String email; //1 male, 0 female private Integer gender; private Integer dId; } package com.zy.model; /** * * 部门的实体类 */ import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Builder; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import java.io.Serializable; @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Builder @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public class Department implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String departmentName; }
5.mapper层
package com.zy.mapper; import com.zy.model.Employee; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update; import java.util.List; /** * * employee是xml配置文件版的mapper */ // 此处@Mapper也可以不写,但是要在springboot启动类出加上注解@MapperScan // @Mapper public interface EmployeeMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE id = #{id}") public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); @Update("UPDATE employee SET lastName=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender},dId=#{dId} WHERE id=#{id}") public void updateEmp(Employee employee); @Delete("DELETE FROM employee WHERE id=#{id}") public void deleteEmpById(Integer id); @Insert("INSERT INTO employee(lastName,email,gender,dId) VALUES(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{dId})") public void insertEmployee(Employee employee); @Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE lastName = #{lastName}") Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName); } package com.zy.mapper; /** * * department是注解版的mybatis */ import com.zy.model.Department; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*; // 此处@Mapper也可以不写,但是要在springboot启动类出加上注解@MapperScan // @Mapper public interface DepartmentMapper { @Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "id") @Insert("insert into department(departmentName) values(#{departmentName})") public int addDept(Department department); @Delete("delete from department where id=#{id}") public void deleteDeptById(Integer id); @Update("update department set departmentName=#{departmentName} where id=#{id}") public void updateDeptById(Integer id); @Select("select * from department where id=#{id}") public Department getDeptById(Integer id); }
6.service层实现类
package com.zy.service; import com.zy.mapper.EmployeeMapper; import com.zy.model.Employee; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; // 抽取公共配置-->到类上 @CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp") @Service("employeeService") public class EmployeeServiceImpl { @Autowired private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; /** * 将方法的运行结果进行缓存;以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法; * CacheManager管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件有自己唯一一个名字; * * * 原理: * 1、自动配置类;CacheAutoConfiguration * 2、缓存的配置类 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration【默认】 * org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration * 3、哪个配置类默认生效:SimpleCacheConfiguration; * * 4、给容器中注册了一个CacheManager:ConcurrentMapCacheManager * 5、可以获取和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件;他的作用将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中; * * 运行流程: * @Cacheable: * 1、方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取; * (CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建。 * 2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数; * key是按照某种策略生成的;默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key; * SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略; * 如果没有参数;key=new SimpleKey(); * 如果有一个参数:key=参数的值 * 如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params); * 3、没有查到缓存就调用目标方法; * 4、将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中 * * @Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存, * 如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据; * * 核心: * 1)、使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】组件 * 2)、key使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator * * * 几个属性: * cacheNames或者value:指定缓存组件的名字;将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存; * * key:缓存数据使用的key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 1-方法的返回值 * 编写SpEL; #id;参数id的值 #a0 #p0 #root.args[0] * getEmp[2] * * keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id * key和keyGenerator:二选一使用; * * * cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;或者cacheResolver指定获取解析器;二选一使用; * * condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存; * ,condition = "#id>0" * condition = "#a0>1":第一个参数的值》1的时候才进行缓存 * * unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;可以获取到结果进行判断 * unless = "#result == null" * unless = "#a0==2":如果第一个参数的值是2,结果不缓存; * sync:是否使用异步模式 * @param id * @return * */ // 此处与启动类的@EnableCaching注解连用才能生效 @Cacheable(value = "{emp}") public Employee getEmpById(Integer id){ Employee employee = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); return employee; } /** * @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存 * 修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存; * 运行时机: * 1、先调用目标方法 * 2、将目标方法的结果缓存起来 * * 测试步骤: * 1、查询1号员工;查到的结果会放在缓存中; * key:1 value:lastName:张三 * 2、以后查询还是之前的结果 * 3、更新1号员工;【lastName:zhangsan;gender:0】 * 将方法的返回值也放进缓存了; * key:传入的employee对象 值:返回的employee对象; * 4、查询1号员工? * 应该是更新后的员工; * key = "#employee.id":使用传入的参数的员工id; * key = "#result.id":使用返回后的id * @Cacheable的key是不能用#result * 为什么是没更新前的?【1号员工没有在缓存中更新】 * */ @CachePut(/*value = "emp",*/key = "#result.id") public void updateEmp(Employee employee){ employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee); } /** * @CacheEvict:缓存清除 * key:指定要清除的数据 * allEntries = true:指定清除这个缓存中所有的数据 * beforeInvocation = false:缓存的清除是否在方法之前执行 * 默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行;如果出现异常缓存就不会清除 * * beforeInvocation = true: * 代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都清除 */ @CacheEvict public void deleteEmp(Integer id){ employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id); } // @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则 @Caching( cacheable = { @Cacheable(/*value="emp",*/key = "#lastName") }, put = { @CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.id"), @CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.email") } ) public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){ return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName); } }
7.controller层
package com.zy.controller; import com.zy.model.Employee; import com.zy.service.EmployeeServiceImpl; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController @RequestMapping("/emps") public class EmployeeController { @Autowired private EmployeeServiceImpl employeeService; @GetMapping("/getEmpById/{id}") public Employee getEmpById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ Employee employee = employeeService.getEmpById(id); return employee; } @GetMapping("/updateEmp") public void updateEmp(Employee employee){ employeeService.updateEmp(employee); } @GetMapping("/delemp") public String deleteEmp(Integer id){ employeeService.deleteEmp(id); return "success"; } @GetMapping("/emp/lastname/{lastName}") public Employee getEmpByLastName(@PathVariable("lastName") String lastName){ return employeeService.getEmpByLastName(lastName); } }
8.application.yml文件
spring:
# 这里指定数据源即配置
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_boot
username: root
password: 123456
# 这里指定cache的类型即配置
cache:
type: caffeine
caffeine:
spec: initialCapacity=100,maximumSize=500,expireAfterWrite=30s
# Caffeine配置说明:
# initialCapacity=[integer]: 初始的缓存空间大小
# maximumSize=[long]: 缓存的最大条数
# maximumWeight=[long]: 缓存的最大权重
# expireAfterAccess=[duration]: 最后一次写入或访问后经过固定时间过期
# expireAfterWrite=[duration]: 最后一次写入后经过固定时间过期
# refreshAfterWrite=[duration]: 创建缓存或者最近一次更新缓存后经过固定的时间间隔,刷新缓存
# weakKeys: 打开key的弱引用
# weakValues:打开value的弱引用
# softValues:打开value的软引用
# recordStats:开发统计功能
# 连接redis缓存主机:这里是redis的配置
# redis:
# host: 192.168.0.100
logging:
level:
com.zy.mapper: debug
# 打印所有详情
debug: true
9.当使用redis进行缓存时,若需要更改默认的序列化规则,则可以添加:
# docker中国镜像加速http://www.docker-cn.com/registry-mirror
# docker安装redis
docker pull registry.docker-cn.com/library/redis
# docker 运行redis
docker run --name redis01 -p 6379:6379 -d --rm registry.docker-cn.com/library/redis
报错解决:
报错1: WARNING: IPv4 forwarding is disabled. Networking will not work.
解决办法: # vi /etc/sysctl.conf 或者 # vi /usr/lib/sysctl.d/00-system.conf 添加如下代码: net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 重启network服务 # systemctl restart network 查看是否修改成功 # sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward 如果返回为“net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1”则表示成功了
报错2: /usr/bin/docker-current: Error response from daemon: driver failed programming external connectivity on endpoint redis01 (19c4784b08511fa716aea4d0eb3da402e648f409afa3e532b178ff3c2d95a92d): exec: "docker-proxy": executable file not found in $PATH.
ln -s /usr/libexec/docker/docker-proxy-current /usr/bin/docker-proxy
报错3: /usr/bin/docker-current: Error response from daemon: shim error: docker-runc not installed on system.
ln -s /usr/libexec/docker/docker-runc-current /usr/libexec/docker/docker-runc
9.1MyRedisConfig
package com.zy.config; import com.zy.model.Department; import com.zy.model.Employee; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import java.net.UnknownHostException; @Configuration public class MyRedisConfig { @Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate( RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException { RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee>(Employee.class); template.setDefaultSerializer(ser); return template; } @Bean public RedisTemplate<Object, Department> deptRedisTemplate( RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException { RedisTemplate<Object, Department> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Department>(); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Department> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Department>(Department.class); template.setDefaultSerializer(ser); return template; } //CacheManagerCustomizers可以来定制缓存的一些规则 @Primary //将某个缓存管理器作为默认的 @Bean public RedisCacheManager employeeCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate){ RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(empRedisTemplate); //key多了一个前缀 //使用前缀,默认会将CacheName作为key的前缀 cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true); return cacheManager; } @Bean public RedisCacheManager deptCacheManager(RedisTemplate<Object, Department> deptRedisTemplate){ RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(deptRedisTemplate); //key多了一个前缀 //使用前缀,默认会将CacheName作为key的前缀 cacheManager.setUsePrefix(true); return cacheManager; } }
9.2RedisDemo
package com.zy;
import com.zy.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.zy.model.Employee;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Redis常见的五大数据类型
* String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、ZSet(有序集合)
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()[String(字符串)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForList()[List(列表)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet()[Set(集合)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash()[Hash(散列)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet()[ZSet(有序集合)]
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBootCacheApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
// 自定义的redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
/*employeeMapper*/
System.out.println(employeeMapper.getEmpById(2));
}
@Test
public void fn01(){
// 1.向redis中放置数据,并取出
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().append("good", "morning");
String good = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("good");
System.out.println(good);
// 2.放置其他类型的数据
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("mylist", "zx");
RedisOperations<String, String> operations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().getOperations();
Set<String> mylist = operations.keys("mylist");
}
@Test
// 测试保存对象
public void fn02(){
Employee employee = employeeMapper.getEmpById(1);
/*
官方自带的方式
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("emp01", employee);
*/
//1、将数据以json的方式保存
//(1)自己将对象转为json
//(2)redisTemplate默认的序列化规则;改变默认的序列化规则;
empRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("emp01", employee);
}
}
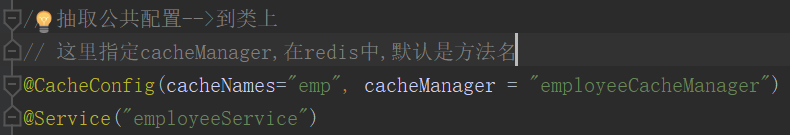
9.3分别在对应的service实现类上加上对应的cacheManager




















 558
558











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








