linux-rdma为Linux内核Infiniband子系统drivers/infiniband对应的用户态库,提供了Infiniband Verbs API和RDMA Verbs API.
基本概念
Queue Pair(QP)
为了进行RDMA操作,需要在两端建立连接,这通过Queue Pair (QP)来完成,QP相当于socket。通信的两端都需要进行QP的初始化,Communication Manager (CM)
在双方真正建立连接前交换QP信息。
Once a QP is established, the verbs API can be used to perform RDMA reads, RDMA writes, and atomic operations.
Serialized send/receive operations, which are similar to socket reads/writes, can be performed as well.
/**
* ibv_create_qp - Create a queue pair.
*/
struct ibv_qp *ibv_create_qp(struct ibv_pd *pd,
struct ibv_qp_init_attr *qp_init_attr);
Completion Queue(CQ)
A Completion Queue is an object which contains the completed work requests which were posted to the Work Queues (WQ). Every completion says that a specific WR was completed (both successfully completed WRs and unsuccessfully completed WRs).
A Completion Queue is a mechanism to notify the application about information of ended Work Requests (status, opcode, size, source).
/**
* ibv_create_cq - Create a completion queue
* @context - Context CQ will be attached to
* @cqe - Minimum number of entries required for CQ
* @cq_context - Consumer-supplied context returned for completion events
* @channel - Completion channel where completion events will be queued.
* May be NULL if completion events will not be used.
* @comp_vector - Completion vector used to signal completion events.
* Must be >= 0 and < context->num_comp_vectors.
*/
struct ibv_cq *ibv_create_cq(struct ibv_context *context, int cqe,
void *cq_context,
struct ibv_comp_channel *channel,
int comp_vector);
Memory Registration (MR)
Memory Registration is a mechanism that allows an application to describe a set of virtually con- tiguous memory locations or a set of physically contiguous memory locations to the network adapter as a virtually contiguous buffer using Virtual Addresses.
struct ibv_mr {
struct ibv_context *context;
struct ibv_pd *pd;
void *addr;
size_tlength;
uint32_thandle;
uint32_tlkey;
uint32_trkey;
};
Every MR has a remote and a local key (rkey, lkey).
Local keys are used by the local HCA to access local memory, such as during a receive operation.
Remote keys are given to the remote HCA to allow a remote process access to system memory during RDMA operations.
ibv_reg_mr registers a memory region (MR), associates it with a protection domain (PD), and assigns it local and remote keys (lkey, rkey).
/**
* ibv_reg_mr - Register a memory region
*/
struct ibv_mr *ibv_reg_mr(struct ibv_pd *pd, void *addr,
size_t length, int access);
Protection Domain (PD)
Object whose components can interact with only each other. These components can be AH, QP, MR, and SRQ.
A protection domain is used to associate Queue Pairs with Memory Regions and Memory Windows , as a means for enabling and controlling network adapter access to Host System memory.
struct ibv_pd is used to implement protection domains:
struct ibv_pd {
struct ibv_context *context;
uint32_thandle;
};
ibv_alloc_pd creates a protection domain (PD). PDs limit which memory regions can be accessed by which queue pairs (QP) providing a degree of protection from unauthorized access.
/**
* ibv_alloc_pd - Allocate a protection domain
*/
struct ibv_pd *ibv_alloc_pd(struct ibv_context *context);
Send Request (SR)
An SR defines how much data will be sent, from where, how and, with RDMA, to where.
struct ibv_send_wr is used to implement SRs.参考struct ibv_send_wr
示例(IB Verbs API example)
RDMA应用可以使用librdmacm或者libibverbs API编程。前者是对后者的进一步封装。
一般来说,使用IB Verbs API的基本流程如下:
(1) Get the device list
First you must retrieve the list of available IB devices on the local host. Every device in this list contains both a name and a GUID. For example the device names can be: mthca0, mlx4_1.参考这里.
IB devices对应数据结构struct ibv_device:
struct ibv_device {
struct _ibv_device_ops_ops;
enum ibv_node_typenode_type;
enum ibv_transport_typetransport_type;
/* Name of underlying kernel IB device, eg "mthca0" */
charname[IBV_SYSFS_NAME_MAX];
/* Name of uverbs device, eg "uverbs0" */
chardev_name[IBV_SYSFS_NAME_MAX];
/* Path to infiniband_verbs class device in sysfs */
chardev_path[IBV_SYSFS_PATH_MAX];
/* Path to infiniband class device in sysfs */
charibdev_path[IBV_SYSFS_PATH_MAX];
};
/**
* ibv_get_device_list - Get list of IB devices currently available
* @num_devices: optional. if non-NULL, set to the number of devices
* returned in the array.
*
* Return a NULL-terminated array of IB devices. The array can be
* released with ibv_free_device_list().
*/
struct ibv_device **ibv_get_device_list(int *num_devices);
(2) Open the requested device
Iterate over the device list, choose a device according to its GUID or name and open it.参考这里.
/**
* ibv_open_device - Initialize device for use
*/
struct ibv_context *ibv_open_device(struct ibv_device *device);
struct ibv_context {
struct ibv_device *device;
struct ibv_context_opsops;
intcmd_fd;
intasync_fd;
intnum_comp_vectors;
pthread_mutex_tmutex;
void *abi_compat;
};
(3) Allocate a Protection Domain
分配一个PD,参考这里
A Protection Domain (PD) allows the user to restrict which components can interact with only each other.
These components can be AH, QP, MR, MW, and SRQ.
(4) Register a memory region
注册一个MR,参考这里.
Any memory buffer which is valid in the process’s virtual space can be registered.
During the registration process the user sets memory permissions and receives local and remote keys (lkey/rkey) which will later be used to refer to this memory buffer.
(5) Create a Completion Queue(CQ)
创建一个CQ,参考这里.
A CQ contains completed work requests (WR). Each WR will generate a completion queue entry (CQE) that is placed on the CQ.
The CQE will specify if the WR was completed successfully or not.
(6) Create a Queue Pair(QP)
创建QP,参考这里.
Creating a QP will also create an associated send queue and receive queue.
(7) Bring up a QP
启动QP,参考这里.
A created QP still cannot be used until it is transitioned through several states, eventually getting to Ready To Send (RTS).
This provides needed information used by the QP to be able send / receive data.
/**
* ibv_modify_qp - Modify a queue pair.
*/
int ibv_modify_qp(struct ibv_qp *qp, struct ibv_qp_attr *attr,
int attr_mask);
例如,对于client/server,需要将QP设置为RTS状态,参考rc_pingpong@pp_connect_ctx.
QP有如下一些状态:
RESET Newly created, queues empty.
INIT Basic information set. Ready for posting to receive queue.
RTR Ready to Receive. Remote address info set for connected QPs, QP may now receive packets.
RTS Ready to Send. Timeout and retry parameters set, QP may now send packets.
(8) Post work requests and poll for completion
Use the created QP for communication operations.
(9) Cleanup
Destroy objects in the reverse order you created them:
Delete QP
Delete CQ
Deregister MR
Deallocate PD
Close device
测试
server
# ibv_rc_pingpong -d rxe0 -g 0 -s 128 -r 1 -n 1
local address: LID 0x0000, QPN 0x000011, PSN 0x626753, GID fe80::5054:61ff:fe57:1211
remote address: LID 0x0000, QPN 0x000011, PSN 0x849753, GID fe80::5054:61ff:fe56:1211
256 bytes in 0.00 seconds = 11.38 Mbit/sec
1 iters in 0.00 seconds = 180.00 usec/iter
client
# ibv_rc_pingpong -d rxe0 -g 0 172.18.42.162 -s 128 -r 1 -n 1
local address: LID 0x0000, QPN 0x000011, PSN 0x849753, GID fe80::5054:61ff:fe56:1211
remote address: LID 0x0000, QPN 0x000011, PSN 0x626753, GID fe80::5054:61ff:fe57:1211
256 bytes in 0.00 seconds = 16.13 Mbit/sec
1 iters in 0.00 seconds = 127.00 usec/iter
抓包可以查看client与server端的通信流程:
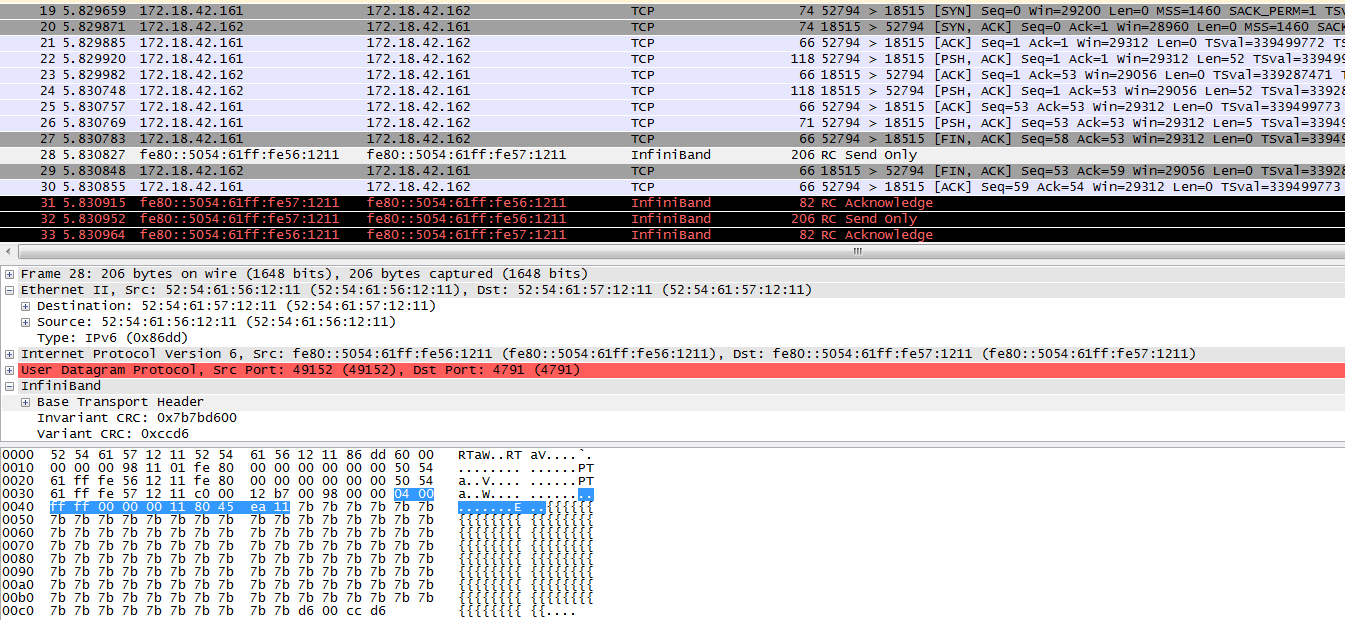
其中,第一个RC Send only为client发送给server的包,参考这里.
然后server回了一个RC Ack,并给client发送了一个RC Send only,参考这里.
前面的一些TCP包为client与server交互的控制信息,参考这里.
Refs





















 769
769











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








