一、同步操作过程:
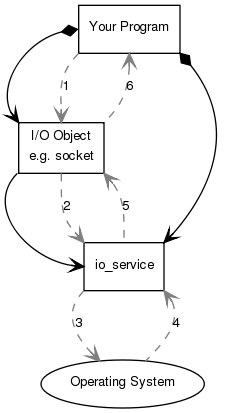
Your program will have at least one io_service object. The io_service represents your program's link to the operating system's I/O services.
asio::io_service io_service;
To perform I/O operations your program will need an I/O object such as a TCP socket:
asio::ip::tcp::socket socket(io_service);
When a synchronous connect operation is performed, the following sequence of events occurs:
1. Your program initiates the connect operation by calling the I/O object:
socket.connect(server_endpoint);
2. The I/O object forwards the request to the io_service.
3. The io_service calls on the operating system to perform the connect operation.
4. The operating system returns the result of the operation to the io_service.
5. The io_service translates any error resulting from the operation into an object of typeasio::error_code. An error_code may be compared with specific values, or tested as a boolean (where afalse result means that no error occurred). The result is then forwarded back up to the I/O object.
6. The I/O object throws an exception of type asio::system_error if the operation failed. If the code to initiate the operation had instead been written as:
asio::error_code ec;
socket.connect(server_endpoint, ec);
then the error_code variable ec would be set to the result of the operation, and no exception would be thrown.
二、异步操作过程:
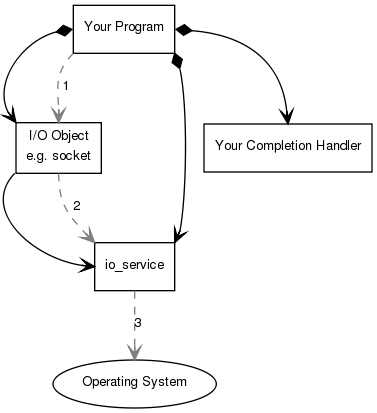
1. Your program initiates the connect operation by calling the I/O object:
socket.async_connect(server_endpoint, your_completion_handler);
where your_completion_handler is a function or function object with the signature:
void your_completion_handler(const asio::error_code& ec);
The exact signature required depends on the asynchronous operation being performed. The reference documentation indicates the appropriate form for each operation.
2. The I/O object forwards the request to the io_service.
3. The io_service signals to the operating system that it should start an asynchronous connect.
Time passes. (In the synchronous case this wait would have been contained entirely within the duration of the connect operation.)
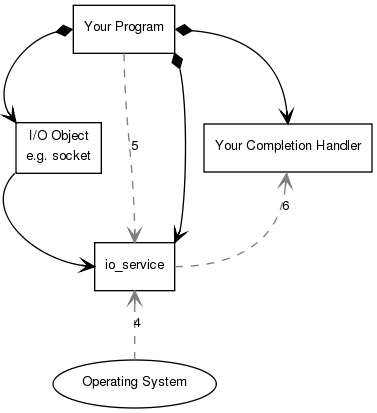
4. The operating system indicates that the connect operation has completed by placing the result on a queue, ready to be picked up by the io_service.
5. Your program must make a call to io_service::run() (or to one of the similar io_service member functions) in order for the result to be retrieved. A call to io_service::run() blocks while there are unfinished asynchronous operations, so you would typically call it as soon as you have started your first asynchronous operation.
6. While inside the call to io_service::run(), the io_service dequeues the result of the operation, translates it into an error_code, and then passes it to your completion handler.
This is a simplified picture of how Asio operates. You will want to delve further into the documentation if your needs are more advanced, such as extending Asio to perform other types of asynchronous operations.




















 632
632











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








