一,Fork-Join
1,定义:
Fork-Join框架:就是在必要的情况下,将一个大任务,进行拆分(fork)成若干个小任务(拆到不能再拆时),再将一个个的小任务运算的结果进行join汇总。
2,,Fork-Join体现了分而治之。什么是分而治之?
规模为N的问题, 当N < 阈值,直接解决。当 N > 阈值, 将N分解为k个小规模子问题,子问题互相独立,与原问题形式相同。将子问题的解合并得到原问题大的解。
3,工作密取(workStealing)
4,Fork-Join实战
4.1,Fork/Join的同步调用同时演示返回值结果: 统计整型数组中所有元素的和
/** * 产生整型数组工具类 */ public class MakeArray { //数组长度 public static final int ARRAY_LENGTH = 4000; public static int[] makeArray(){ //new一个随机数发生器 Random rd = new Random(); int[] result = new int[ARRAY_LENGTH]; for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_LENGTH;i++){ //用随机数填充数组 result[i] = rd.nextInt(ARRAY_LENGTH*3); } return result; } }
/** * 使用Fork-Join框架进行计算 */ public class SumArray { private static class SumTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{ private final static int THRESHOLD = MakeArray.ARRAY_LENGTH/10; private int[] src;//要实际应用的数组 private int fromIndex;//开始统计的下标 private int toIndex;//统计到哪里结束的下标 public SumTask(int[] src,int fromIndex,int toIndex){ this.src = src; this.fromIndex = fromIndex; this.toIndex = toIndex; } @Override protected Integer compute() { if(toIndex - fromIndex < THRESHOLD){ int count = 0; for(int i = fromIndex;i <= toIndex;i++){ try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } count = count + src[i]; } return count; }else { //fromIndex ..... mid....... toIndex。这里我们自己定义的算法:大于阈值就平均分为两部分 int mid = (fromIndex + toIndex)/2; SumTask left = new SumTask(src,fromIndex,mid); SumTask right = new SumTask(src,mid,toIndex); invokeAll(left,right); return left.join() + right.join(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); int[] src = MakeArray.makeArray(); SumTask innerFind = new SumTask(src,0,src.length-1); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); pool.invoke(innerFind);//同步调用 System.out.println("Task is Running......."); System.out.println("the count is "+ innerFind.join()+" spend time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms"); } /** * 注意: * 对于这种简单的相加操作,其实单线程处理的速度更快。 * 使用forkjoin后,使用多线程进行处理。由于需要线程间的切换(上下文切换),导致forkjoin的处理方式花的时间更多。 * 所以使用forkjoin一定要注意场合。 * 这也是redis虽然使用单进程单线程模式,但是处理能力非常强的原因,就是因为redis处理的数据比较简单(String)。 * 并且使用单线程处理避免了进程间的切换。 */ }
4.2,Fork/Join的异步调用同时演示不要求返回值:遍历指定目录(含子目录),寻找指定类型文件
/** * 遍历指定目录(含子目录),找寻指定类型文件 * 不需要返回值的的Fork/Join */ public class FindDirsFiles extends RecursiveAction{ //当前任务需要搜寻的目录 private File path; public FindDirsFiles(File path){ this.path = path; } @Override protected void compute() { List<FindDirsFiles> subTasks = new ArrayList<>(); File[] files = path.listFiles();//拿到目录下文件 if (files != null){ for (File file : files){ if (file.isDirectory()){ //对每一个子目录都新建一个子任务 subTasks.add(new FindDirsFiles(file)); }else { //遇到文件,检查 if (file.getAbsolutePath().endsWith("txt")){ System.out.println("文件:"+ file.getAbsolutePath()); } } } if (!subTasks.isEmpty()){ for (FindDirsFiles subTask:invokeAll(subTasks)){ //上面的invlkeAll():用来递交子任务 subTask.join();//等待子任务 } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { try { //用一个ForkJoinPool 实例调度总任务 ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool(); FindDirsFiles task = new FindDirsFiles(new File("D:\\yishang")); pool.execute(task); System.out.println("task is running........"); //主线程做一些自己的事情 try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } int otherWork = 0; for (int i = 0; i<100;i++){ otherWork = otherWork + i; } System.out.println("main Thread done sth ....., otherWork = "+otherWork); task.join();//阻塞方法, System.out.println("task end"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
二,CountDownLatch:计数器
1,方法:
latch.countDown():调用该方法,计数器的数量减一
latch.await():调用该方法,如果计数器的数量没有减为0,那么就该方法会阻塞,知道计数器的数量为0才继续执行后面的代码
2,示例代码:当初始化工作完成以后,才执行业务逻辑代码
/** * 演示CountDownLatch,有5个初始化的线程,6个扣除点。 * 扣除完毕以后,主线程和业务线程才能继续自己的工作 */ public class UseCountDownLatch { static CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(6); /** * 初始化线程 */ private static class InitThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("InitThread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+ " ready init work ......."); latch.countDown();//初始化线程完成工作了 //初始化线程调用了countDown()以后,还是可以继续走自己的逻辑的 for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { System.out.println("InitThread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+ ".....continue to its work"); } } } /** * 业务线程 * 等所有的初始化线程的初始化工作做完了,业务线程才能执行 */ private static class BusiThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { try { //业务线程阻塞,直到countDown减为0,才往下执行 latch.await();//阻塞方法 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { System.out.println("BusiThread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+ " do business"); } } } public static void main(String[] args)throws InterruptedException { //单独的初始化线程,初始化分为2,需要扣减2次 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"ready init work step 1st...."); latch.countDown();//每完成一步初始化工作,扣减一次 System.out.println("begin step 2nd......."); try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"ready init work step 2nd...."); latch.countDown();//每完成一步初始化工作,扣减一次 } }).start(); new Thread(new BusiThread()).start(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { Thread thread = new Thread(new InitThread()); thread.start(); } //主线程阻塞,必须等countDown减为0,才往下执行 latch.await(); System.out.println("main do its work ........."); } }
三,CyclicBarrier:栅栏
1,方法:
barrier.await():等所有线程执行到该方法时,才能继续向前执行。否则,一直阻塞在这里
2,示例代码:
/** * 演示:CyclicBarrier,当所有的线程都来到了barrier.await();线程才继续往下执行。不然就一直阻塞在这个方法前 * 可以类比人员到指定的集合场地,然后在一起出发的场景。比如出去旅游,等所有的人都来到集合地点,然后大家才一起出发。 */ public class UseCyslicBarrier { private static CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(5); //工作线程 private static class SubThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { long id = Thread.currentThread().getId(); //为了模拟真实环境,每个线程到达barrier.await()方法的时间不一样。随即决定工作线程是否睡眠 Random random = new Random(); try { if (random.nextBoolean()){ Thread.sleep(1000+id); System.out.println("Thread_"+id+" 在来的路上堵车了,堵车时间 "+(1000+id)+"ms"); } System.out.println("Thread_"+id+" 在来的路上没有堵车,提前到达集合地点,然后在集合地点等待其他人员.... "); //当5个线程都执行到了这个地方,然后所有的线程继续往下执行。 barrier.await(); Thread.sleep(1000+id); System.out.println("Thread_"+id+"开始上车"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Thread thread = new Thread(new SubThread()); thread.start(); } } }
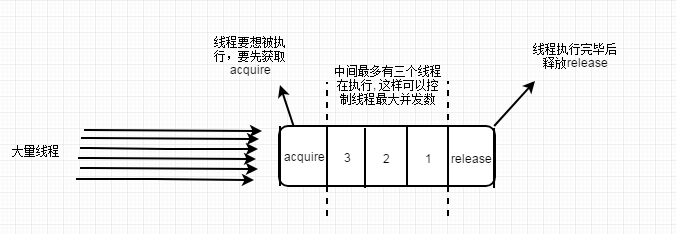
四,Semaphore:信号灯(控制并发执行的线程个数)
1,方法:
sp.acquire():获得信号灯
sp.release():释放信号灯
2,图示理解:
3,示例代码:
/** * 信号灯:控制并发执行的线程个数 */ public class SemaphoreTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //最多运行3个线程并发执行 final Semaphore sp=new Semaphore(3); Runnable runnable=new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { sp.acquire();//获得信号灯 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进入,还有"+(3-sp.availablePermits())+"个线程"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"离开,还有"+(3-sp.availablePermits())+"个线程"); //释放信号灯 sp.release(); } }; //开启20个线程 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { Thread thread = new Thread(runnable); thread.start(); } } }
五,Exchanger(两个线程之间做数据交换)
1,方法:
exchanger.exchange(data):该方法一直阻塞到另外一个线程过来交换数据
2,示例代码:
public class ExchangerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { final Exchanger exchanger = new Exchanger(); //线程1 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { String data1 = "aaa"; System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+":当前的数据是"+data1+ ",该线程正在准备把 "+data1+"换出去"); String data2 = (String) exchanger.exchange(data1); System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "换回的数据为"+data2); }catch (InterruptedException e){ } } }).start(); //线程二 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(3000)); String data1 = "bbb"; System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+":当前的数据是"+data1+ ",该线程正在准备把 "+data1+"换出去"); String data2 = (String) exchanger.exchange(data1); System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "换回的数据为"+data2); }catch (InterruptedException e){ } } }).start(); } }





















 122
122











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








