16.10 编程练习
6.使用STL queue模板类而不是第12章的Queue类,重新编写程序清单12.12所示的示例。
程序清单12.12:
Test.h
//
// Test.h
// HelloWorld
//
// Created by feiyin001 on 16/12/21.
// Copyright (c) 2016年 FableGame. All rights reserved.
//
#ifndef _Test_H_
#define _Test_H_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace FableGame
{
class Customer
{
private:
long arrive;//到达的时间
int processtime;//处理业务的时间
public:
Customer() { arrive = processtime = 0; }
void set(long when);
long when() const { return arrive; }
int ptime() const { return processtime; }
};
typedef Customer Item;
class Queue
{
private:
struct Node
{
Item item;
struct Node * next;
};
enum{ Q_SIZE = 10 };
Node* front;
Node* rear;
int items;
const int qsize;
Queue(const Queue& q) :qsize(0) {}
Queue& operator=(const Queue& q) { return *this; }
public:
Queue(int qs = Q_SIZE);
~Queue();
bool isempty() const;
bool isfull()const;
int queuecount() const;
bool enqueue(const Item& item);
bool dequeue(Item& item);
};
}
#endif //
// Test.cpp
// HelloWorld
//
// Created by feiyin001 on 16/12/21.
// Copyright (c) 2016年 FableGame. All rights reserved.
//
#include "Test.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
using namespace FableGame;
Queue::Queue(int qs) : qsize(qs)
{
front = rear = nullptr;
items = 0;
}
Queue::~Queue()
{
Node * temp;
while (front != nullptr) {
temp = front;
front = front->next;
delete temp;
}
}
bool Queue::isempty()const
{
return items == 0;
}
bool Queue::isfull() const
{
return items == qsize;
}
int Queue::queuecount()const
{
return items;
}
bool Queue::enqueue(const Item &item)
{
if (isfull()) {
return false;
}
Node* add = new Node;
add->item = item;
add->next = nullptr;
items++;
if (front == nullptr) {
front = add;
}
else
{
rear->next = add;
}
rear = add;
return true;
}
bool Queue::dequeue(Item &item)
{
if (front == nullptr) {
return false;
}
item = front->item;
items--;
Node* temp = front;
front = front->next;
delete temp;
if (items == 0) {
rear = nullptr;
}
return true;
}
void Customer::set(long when)
{
processtime = std::rand() % 3 + 1;
arrive = when;
}#include <iostream>
#include "Test.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
using namespace FableGame;
const int MIN_PER_HR = 60;//每小时的分钟数
bool newcustomer(double x);
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
srand((int)time(0));//随机数种子
cout << "Case Study: Bank of Heather Automatic Teller\n";
cout << "Enter maximum size of queue: ";
int qs;//队列最大长度
cin >> qs;
Queue line(qs);
cout << "Enter the number of simulation hours: ";
int hours;//模拟的小时数
cin >> hours;
int cyclelimit = MIN_PER_HR * hours;//总分钟数限制
cout << "Enter the average number of customers per hour: ";
double perhour;//每小时接收的客人
cin >> perhour;
double min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / perhour;
Item temp;
int turnaways = 0;//来了没处理就离开的人
int customers = 0;//客户数
int served = 0;//已经服务过的客户数
int sum_line = 0;//队列总长度
int wait_time = 0;//正在处理业务时间
int line_wait = 0;//总的等待时间
for (int cycle = 0; cycle < cyclelimit; ++cycle)
{
if (newcustomer(min_per_cust))
{
//有客户来了
if (line.isfull())
{
turnaways++;//队伍满了,离开
}
else
{
customers++; //增加客户
temp.set(cycle);
line.enqueue(temp);//加入队列
}
}
if (wait_time <= 0 && !line.isempty())
{
line.dequeue(temp);//处理客户
wait_time = temp.ptime();
line_wait += cycle - temp.when();//等待时间
served++;//服务的客户加1
}
if (wait_time > 0)
{
wait_time--;//每分钟减1
}
sum_line += line.queuecount();//这分钟正在等待的人数
}
if (customers > 0)
{
cout << "customers accepted: " << customers << endl;
cout << "customers served: " << served << endl;
cout << "turnsways: " << turnaways << endl;
cout << "average queue size: ";
cout.precision(2);
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
cout << (double)sum_line / cyclelimit << endl;
cout << "average wait time: " << (double)line_wait / served << " minutes\n";
}
else
{
cout << "No customers!\n";
}
cout << "Done!\n";
return 0;
}
//判断客户是否到来
bool newcustomer(double x)
{
return (rand() * x / RAND_MAX < 1);
}Test.h
//
// Test.h
// HelloWorld
//
// Created by feiyin001 on 16/12/21.
// Copyright (c) 2016年 FableGame. All rights reserved.
//
#ifndef _Test_H_
#define _Test_H_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace FableGame
{
class Customer
{
private:
long arrive;//到达的时间
int processtime;//处理业务的时间
public:
Customer() { arrive = processtime = 0; }
void set(long when);
long when() const { return arrive; }
int ptime() const { return processtime; }
};
}
#endif //
// Test.cpp
// HelloWorld
//
// Created by feiyin001 on 16/12/21.
// Copyright (c) 2016年 FableGame. All rights reserved.
//
#include "Test.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
using namespace FableGame;
void Customer::set(long when)
{
processtime = std::rand() % 3 + 1;
arrive = when;
}#include <iostream>
#include "Test.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
using namespace FableGame;
const int MIN_PER_HR = 60;//每小时的分钟数
bool newcustomer(double x);
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
srand((int)time(0));//随机数种子
cout << "Case Study: Bank of Heather Automatic Teller\n";
cout << "Enter maximum size of queue: ";
size_t qs;//队列最大长度
cin >> qs;
queue<Customer> line;
cout << "Enter the number of simulation hours: ";
int hours;//模拟的小时数
cin >> hours;
int cyclelimit = MIN_PER_HR * hours;//总分钟数限制
cout << "Enter the average number of customers per hour: ";
double perhour;//每小时接收的客人
cin >> perhour;
double min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / perhour;
Customer temp;
int turnaways = 0;//来了没处理就离开的人
int customers = 0;//客户数
int served = 0;//已经服务过的客户数
size_t sum_line = 0;//队列总长度
int wait_time = 0;//正在处理业务时间
int line_wait = 0;//总的等待时间
for (int cycle = 0; cycle < cyclelimit; ++cycle)
{
if (newcustomer(min_per_cust))
{
//有客户来了
if (line.size() >= qs)
{
turnaways++;//队伍满了,离开
}
else
{
customers++; //增加客户
temp.set(cycle);
line.push(temp);//加入队列
}
}
if (wait_time <= 0 && !line.empty())
{
temp = line.front();
line.pop();//处理客户
wait_time = temp.ptime();
line_wait += cycle - temp.when();//等待时间
served++;//服务的客户加1
}
if (wait_time > 0)
{
wait_time--;//每分钟减1
}
sum_line += line.size();//这分钟正在等待的人数
}
if (customers > 0)
{
cout << "customers accepted: " << customers << endl;
cout << "customers served: " << served << endl;
cout << "turnsways: " << turnaways << endl;
cout << "average queue size: ";
cout.precision(2);
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
cout << (double)sum_line / cyclelimit << endl;
cout << "average wait time: " << (double)line_wait / served << " minutes\n";
}
else
{
cout << "No customers!\n";
}
cout << "Done!\n";
return 0;
}
//判断客户是否到来
bool newcustomer(double x)
{
return (rand() * x / RAND_MAX < 1);
}7.彩票卡是一个常见的游戏。卡片上是带编号的圆点,其中一些圆点被随机选中。编写一个lotto()函数,它接受两个参数。第一个参数是彩票卡上圆点的个数,第二个参数是随机选择的圆点个数。该函数返回一个vector<int> 对象,其中包含(安排列后的顺序)随机选择的号码。例如,可以这样使用该函数:
vector<int > winners;
winners = lotto(51, 6);
这样将一个矢量赋给winner,该矢量包含1~51中随机选定的6歌数字。注意,仅仅使用rand()无法完成这项任务,因它会生成重复的值。提示:让函数创建一个包含所有可能值的矢量,使用random_shuffle(),然后通过打乱后的矢量的第一个值来获取值。编写一个小程序来测试这个函数。
#include <iostream>
#include "Test.h"
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
using namespace FableGame;
vector<int> lotto(int x, int y)
{
vector<int> a;
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++)
{
a.push_back(i);
}
random_shuffle(a.begin(), a.end());
a.resize(y);
return a;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
srand((int)time(0));//随机数种子
vector<int> a = lotto(51, 6);
for (size_t i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
8.Mat和Pat希望邀请他们的朋友参加派对。他们要编写一个程序完成下面的任务。
·让Mat输入他朋友的姓名列表。姓名存储在一个容器中,然后按排列后的顺序显示出来。
·让Pat输入她朋友的姓名列表。姓名存储在另一个容器中,然后按排列后的顺序显示出来。
·创建第三个容器,将两个列表合并,删除重复的部分,并显示这个容器的内容。
#include <iostream>
#include "Test.h"
#include <ctime>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
using namespace FableGame;
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
set<string> friends1;
set<string> friends2;
string str;
cout << "enter Mat's friend name(q to quit):" << endl;
while (cin && getline(cin, str))
{
if (str == "q")
{
break;
}
friends1.insert(str);
}
cout << "enter Pat's friend name(q to quit):"<< endl;
while (cin && getline(cin, str))
{
if (str == "q")
{
break;
}
friends2.insert(str);
}
set<string> friend3;
friend3.insert( friends1.begin(), friends1.end());
friend3.insert( friends2.begin(), friends2.end());
cout << "Mat's friends: ";
for(string s: friends1)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "Pat's friends: ";
for (string s : friends2)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "All friends: ";
for (string s : friend3)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}9.相对于数组,在链表中添加和删除元素更容易,但排序速度更慢。这就引出了一个可能性:相对于使用链表算法进行排序,将链表复制到数组中,对数组进行排序,再将排序后的结果复制到链表中的速度可能更快;但这也可能占用了更多的内存。请使用如下方法检验上述假设。
a.创建大型vector<int>对象vi0,并使用rand()给它提供初始值。
b.创建vector<int>对象vi和list<int>对象li,他们的长度都和初始值与vi0相同。
c.计算使用STL算法sort()对vi进行排序所需的时间,再计算使用list的方法sort()对li进行排序所需的时间。
d.将li重置为排序的vi0的内容,并计算执行如下操作所需的时间:将li的内容复制到vi中,对vi进行排序,并将结果复制到li中。
要计算这些操作所需的时间,可使用ctime库中的clock()。正如程序清单5.14演示的,可使用下面的语句来获取开始时间:
clock_t start= clock();
再再操作结果后使用下面的语句获取经过了多长时间:
clock_t end = clock();
cout << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
这种测试并非绝对可靠,因为结果取决于很多因素,如可用内存量、是否支持多处理以及数组(列表)的长度(随着要排序的元素数增加,数组对于列表的效率将更明显)。另外,如果编译器提供了默认生成方式和发布生成方式,请使用发布生成方式。鉴于当今计算机的速度非常快,要获取有意义的结果,可能需要使用尽可能大的数组。例如,可尝试包含100000、1000000和10000000个元素。
#include <iostream>
#include "Test.h"
#include <ctime>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <list>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
using namespace FableGame;
const int num = 1000000;
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
vector<int> vi0;
vector<int> vi;
list<int> li;
srand(int(time(nullptr)));
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
int temp = rand() * rand();
vi0.push_back(temp);
vi.push_back(temp);
li.push_back(temp);
}
{
time_t t1 = time(nullptr);
cout << "sort vi, begin time: " << t1 << endl;
sort(vi.begin(), vi.end());
time_t t2 = time(nullptr);
cout << "sort vi, end time: " << t2 << " use " << t2 - t1 << " seconds" << endl;
}
{
time_t t1 = time(nullptr);
cout << "sort li, begin time: " << t1 << endl;
li.sort();
time_t t2 = time(nullptr);
cout << "sort li, end time: " << t2 << " use " << t2 - t1 << " seconds" << endl;
}
{
li.clear();
copy(vi0.begin(), vi0.end(), std::back_inserter(li));
vi0.clear();
time_t t1 = time(nullptr);
cout << "li to vector, sort, begin time: " << t1 << endl;
copy(li.begin(), li.end(), std::back_inserter(vi0));//复制到vector
sort(vi.begin(), vi.end());//排序
li.clear();
copy(vi0.begin(), vi0.end(), std::back_inserter(li));//再复制回来
time_t t2 = time(nullptr);
cout << "li to vector, sort, end time: " << t2 << " use " << t2 - t1 << " seconds" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
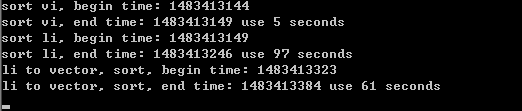
好像真的是转成vector快很多,如果足够大的数组。
不过除了消耗内存,转换成vector,然后再转回来,也是有消耗时间的。
vector排序只用了5秒,
list排序用了97秒,
通过list复制到vector,排序,再复制回来,用了61秒。证明其中用在复制的时间是50多秒。
10.请按如下方式修改程序清单16.9(vect3.cpp)。
a.在结构Review中添加成员price。
b.不使用vector<Review>来存储输入,而使用vector<shared_ptr<Review>>。别忘了,必须使用new返回的指针来初始化shared_ptr。
c. 在输入阶段结束后,使用一个循环让用户选择如下方式之一显示书籍:按原始顺序显示、按字母表顺序显示、按评级升序显示、按评级降序显示、按价格升序显示、按价格降序显示、退出。
下面是一种可能的解决方案:获取输入后,在创建一个shared_ptr矢量,并用原始数组初始化它。定义一个队指向结构的指针进行比较的operator<()函数,并使用它对第二个矢量进行排序,让其中的shared_ptr按其指向的对象中的书名排序。重复上述过程,创建按rating和price排序的shared_ptr矢量。请注意,通过使用rbegin()和end(),可避免创建按相反的顺序排序的share_ptr矢量。
先看看原来的代码先:程序清单16.9
//
// main.cpp
// HelloWorld
//
// Created by feiyin001 on 16/12/30.
// Copyright (c) 2016年 FableGame. All rights reserved.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include "Test.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace FableGame;
struct Review
{
string title;
int rating;
};
bool operator<(const Review& r1, const Review& r2);
bool worseThan(const Review& r1, const Review& r2);
bool fillReview(Review& rr);
void showReview(const Review& rr);
int main()
{
vector<Review> books;
Review temp;
while (fillReview(temp))
{
books.push_back(temp);
}
if (books.size() > 0) {
cout << "Thank you. You entered the following " << books.size() << " ratings:\n" << "Rating\tBook\n";
for_each(books.begin(), books.end(), showReview);
sort(books.begin(), books.end());
cout << "Sorted by title:\nRating\tBook\n";
for_each(books.begin(), books.end(), showReview);
sort(books.begin(), books.end(), worseThan);
cout << "Sorted by rating:\nRating\tBook\n";
for_each(books.begin(), books.end(), showReview);
random_shuffle(books.begin(), books.end());
cout << "After shuffling:\nRating\tBook\n";
for_each(books.begin(), books.end(), showReview);
}
else{
cout << "No entries.";
}
cout << "bye.\n";
return 0;
}
bool operator<(const Review& r1, const Review& r2)
{
if (r1.title < r2.title) {
return true;
}
else if (r1.title == r2.title && r1.rating < r2.rating)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool worseThan(const Review& r1, const Review& r2)
{
if (r1.rating < r2.rating) {
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool fillReview(Review& rr)
{
cout << "Enter book title (quit to quit): ";
getline(cin, rr.title);
if (rr.title == "quit" || rr.title == "q") {
return false;
}
cout << "Enter book rating: ";
cin >> rr.rating;
if (!cin) {
return false;
}
while (cin.get() != '\n') {
continue;
}
return true;
}
void showReview(const Review& rr)
{
cout << rr.rating << "\t" << rr.title << endl;
}//
// main.cpp
// HelloWorld
//
// Created by feiyin001 on 16/12/30.
// Copyright (c) 2016年 FableGame. All rights reserved.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include "Test.h"
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
using namespace FableGame;
struct Review
{
string title;
int rating;
int price;
};
bool operator<(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2);
bool worseThan(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2);
bool betterThan(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2);
bool cheaperThan(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2);
bool valuerThan(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2);
bool fillReview(Review& rr);
void showReview(const shared_ptr<Review>& rr);
int main()
{
vector<shared_ptr<Review>> books;
while (true)
{
shared_ptr<Review> temp(new Review);
if (!fillReview(*temp))
{
break;
}
books.push_back(temp);
}
cout << "Enter show type: 0.原始顺序, 1.按字母表顺序显示," << endl<<
"2.按评级升序显示, 3.按评级降序显示" << endl <<
"4.按价格升序显示, 5.按价格降序显示, 6.退出" << endl;
int orderType = 0;
while (cin >> orderType && orderType != 6)
{
switch (orderType)
{
case 0:
break;
case 1:
sort(books.begin(), books.end());
break;
case 2:
sort(books.begin(), books.end(), worseThan);
break;
case 3:
sort(books.begin(), books.end(), betterThan);
break;
case 4:
sort(books.begin(), books.end(), cheaperThan);
break;
case 5:
sort(books.begin(), books.end(), valuerThan);
break;
}
for_each(books.begin(), books.end(), showReview);
cout << "Enter show type: 0.原始顺序, 1.按字母表顺序显示," << endl <<
"2.按评级升序显示, 3.按评级降序显示" << endl <<
"4.按价格升序显示, 5.按价格降序显示, 6.退出" << endl;
}
cout << "bye.\n";
return 0;
}
bool operator<(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2)
{
if (r1->title < r2->title) {
return true;
}
else if (r1->title == r2->title && r1->rating < r2->rating)
{
return true;
}
else if (r1->rating == r2->rating && r1->price < r2->price)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool worseThan(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2)
{
if (r1->rating < r2->rating) {
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool betterThan(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2)
{
if (r1->rating > r2->rating) {
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool cheaperThan(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2)
{
if (r1->price < r2->price) {
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool valuerThan(const shared_ptr<Review>& r1, const shared_ptr<Review>& r2)
{
if (r1->price > r2->price) {
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool fillReview(Review& rr)
{
cout << "Enter book title (quit to quit): ";
getline(cin, rr.title);
if (rr.title == "quit" || rr.title == "q") {
return false;
}
cout << "Enter book rating: ";
cin >> rr.rating;
if (!cin) {
return false;
}
cout << "Enter book price: ";
cin >> rr.price;
if (!cin) {
return false;
}
while (cin.get() != '\n') {
continue;
}
return true;
}
void showReview(const shared_ptr<Review>& rr)
{
cout << rr->rating << "\t" << rr->title << "\t" << rr->price << endl;
}




















 1257
1257

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








