There are n cities in Bearland, numbered 1 through n. Cities are arranged in one long row. The distance between cities i and j is equal to |i - j|.
Limak is a police officer. He lives in a city a. His job is to catch criminals. It's hard because he doesn't know in which cities criminals are. Though, he knows that there is at most one criminal in each city.
Limak is going to use a BCD (Bear Criminal Detector). The BCD will tell Limak how many criminals there are for every distance from a city a. After that, Limak can catch a criminal in each city for which he is sure that there must be a criminal.
You know in which cities criminals are. Count the number of criminals Limak will catch, after he uses the BCD.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and a (1 ≤ a ≤ n ≤ 100) — the number of cities and the index of city where Limak lives.
The second line contains n integers t1, t2, ..., tn (0 ≤ ti ≤ 1). There are ti criminals in the i-th city.
Print the number of criminals Limak will catch.
6 3
1 1 1 0 1 0
3
5 2
0 0 0 1 0
1
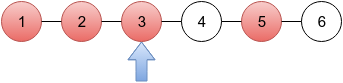
In the first sample, there are six cities and Limak lives in the third one (blue arrow below). Criminals are in cities marked red.
Using the BCD gives Limak the following information:
- There is one criminal at distance 0 from the third city — Limak is sure that this criminal is exactly in the third city.
- There is one criminal at distance 1 from the third city — Limak doesn't know if a criminal is in the second or fourth city.
- There are two criminals at distance 2 from the third city — Limak is sure that there is one criminal in the first city and one in the fifth city.
- There are zero criminals for every greater distance.
So, Limak will catch criminals in cities 1, 3 and 5, that is 3 criminals in total.
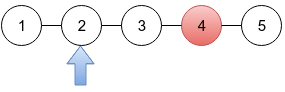
In the second sample (drawing below), the BCD gives Limak the information that there is one criminal at distance 2 from Limak's city. There is only one city at distance 2 so Limak is sure where a criminal is.
题意:
给出小偷的位置p, 然后开始偷跑,
分2种情况。
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[105];
int main()
{
int n, p, ans;
while(cin >> n >> p)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
ans = 0, p--;
if(a[p])
ans++;
for(int i = 1 ;i < n ; i++)
{
if(p + i >= n && p - i < 0)
break;
if(p + i >= n && a[p-i])
ans++;
else if(p - i < 0 && a[p+i])
ans++;
else if(p + i < n && p - i >= 0 && a[p-i] && a[p+i])
ans += 2;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}




















 384
384











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








