In statistics, Moran's I is a measure of spatial autocorrelation developed by Patrick A.P. Moran.[1] Like autocorrelation, spatial autocorrelation means that adjacent observations of the same phenomenon are correlated. However, autocorrelation is about proximity in time. Spatial autocorrelation is about proximity in (two-dimensional) space. Spatial autocorrelation is more complex than autocorrelation because the correlation is two-dimensional and bi-directional.
Moran's I is defined as
where N is the number of spatial units indexed by i and j; X is the variable of interest;  is the mean of X; and wij is a matrix of spatial weights.
is the mean of X; and wij is a matrix of spatial weights.
The expected value of Moran's I under hypothesis of no spatial autocorrelation is
Its variance equals
where
Negative (positive) values indicate negative (positive) spatial autocorrelation. Values range from −1 (indicating perfect dispersion) to +1 (perfect correlation). A zero values indicates a random spatial pattern. For statistical hypothesis testing, Moran's I values can be transformed to Z-scores in which values greater than 1.96 or smaller than −1.96 indicate spatial autocorrelation that is significant at the 5% level.
The significance of ![]()
![]() I can be judged by calculating the variance of
I can be judged by calculating the variance of ![]()
![]() I and then comparing the following statistic to the standard normal distribution
I and then comparing the following statistic to the standard normal distribution

![]()
![]()
![]() . (关于置信度的计算)
. (关于置信度的计算)
Moran's I is inversely related to Geary's C, but it is not identical. Moran's I is a measure of global spatial autocorrelation, while Geary's C is more sensitive to local spatial autocorrelation.
可以看出Moran’s I的相关特点。














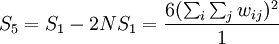














 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








