1.关于二叉树的定义
2.二叉树的类型
3.二叉树所解决的问题
在链表中,插入、删除速度很快,但查找速度较慢。
在数组中,查找速度很快,但插入删除速度很慢。
为了解决这个问题,找寻一种能够在插入、删除、查找、遍历等操作都相对快的容器,于是人们发明了二叉树。
值得注意的是,无特征的二叉树在工业上是没啥用处的,一般都是用的bst、avl(平衡二叉树)等具有特殊特征的二叉树。
比如在bst(二叉搜索树)中,中序遍历可以得到顺序输出,插入查找删除的速度都相当快速(logn).
在工业界用到较多的红黑树,相比hash table来说也有一定的优势:
咋一看,hashtable的优势是很明显的:
查找、插入、删除速度都为O(1)
而红黑树的查找、插入、删除速度为O(logn)
但红黑树有很重要的特征是hashtable所不具备的:有序的特征。
1 红黑树遍历可以得出有序输出,但hashtable是无序输出。
2 如果需要求某一范围的输出,红黑树可以完美解决
3 hashtable的最恶劣的情况是效率很低的(比如需要resize时),而红黑树不存在这种情况。
总结:每种数据结构都相当于一种容器,我们需要把数据存放在里面后供我们高效地操作这些数据。二叉树(带有特征的)就是这种在各个操作上兼容了高效的容器。
4.二叉查找树
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),也称二叉搜索树,是指一棵空树或者具有下列性质的二叉树:
- 任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
- 没有键值相等的节点。
二叉查找树相比于其他数据结构的优势在于查找、插入的时间复杂度较低。为O(log n)。二叉查找树是基础性数据结构,用于构建更为抽象的数据结构,如集合、multiset、关联数组等。(摘自维基百科)
下面 4 张 GIF 动图,是 penjee 官博制作分享。正好伯小乐最近看到,分享给大家。
图1:查找 BST 中的某个元素
在二叉搜索树b中查找x的过程为:
- 若b是空树,则搜索失败,否则:
- 若x等于b的根节点的数据域之值,则查找成功;否则:
- 若x小于b的根节点的数据域之值,则搜索左子树;否则:
- 查找右子树。

图2 ↓ :从有序数组构造一个二叉查找树

图3 ↓:往 BST 中插入元素
向一个二叉搜索树b中插入一个节点s的算法,过程为:
- 若b是空树,则将s所指结点作为根节点插入,否则:
- 若s->data等于b的根节点的数据域之值,则返回,否则:
- 若s->data小于b的根节点的数据域之值,则把s所指节点插入到左子树中,否则:
- 把s所指节点插入到右子树中。(新插入节点总是叶子节点)

图4 ↓:BST 转成有序数组

5.Java中二叉树操作
引言
二叉查找树是一种能将链表插入的灵活性和有序数组查找的高效性结合起来的一种重要的数据结构,它是我们后面学习红黑树和AVL树的基础,本文我们就先来看一下二叉查找树的实现原理。
二叉查找树的定义
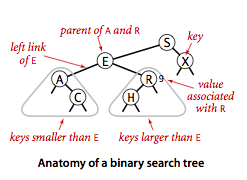
二叉查找树最重要的一个特征就是:每个结点都含有一个Comparable的键及其相关联的值,该结点的键要大于左子树中所有结点的键,而小于右子树中所有结点的键。
下图就是一个典型的二叉查找树,我们以结点E为例,可以观察到,左子树中的所有结点A和C都要小于E,而右子树中所有的结点R和H都要大于结点E。
二叉查找树
在实现二叉查找树中相关操作之前我们先要来定义一个二叉查找树,由于Java中不支持指针操作,我们可以用内部类Node来替代以表示树中的结点,每个Node对象都含有一对键值(key和val),两条链接(left和right),和子节点计数器(size)。另外我们还提前实现了size(), isEmpty()和contains()这几个基础方法,三种分别用来计算二叉树中的结点数目,判断二叉树是否为空,判断二叉树中是否含有包含指定键的结点。
1 public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> { 2 private Node root; // root of BST 3 private class Node { 4 private Key key; // sorted by key 5 private Value val; // associated data 6 private Node left, right; // left and right subtrees 7 private int size; // number of nodes in subtree 8 public Node(Key key, Value val, int size) { 9 this.key = key; 10 this.val = val; 11 this.size = size; 12 } 13 } 14 // Returns the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table. 15 public int size() { 16 return size(root); 17 } 18 // Returns number of key-value pairs in BST rooted at x. 19 private int size(Node x) { 20 if(x == null) { 21 return 0; 22 } else { 23 return x.size; 24 } 25 } 26 // Returns true if this symbol table is empty. 27 public boolean isEmpty() { 28 return size() == 0; 29 } 30 // Returns true if this symbol table contains key and false otherwise. 31 public boolean contains(Key key) { 32 if(key == null) { 33 throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null"); 34 } else { 35 return get(key) != null; 36 } 37 } 38 }
查找和插入操作的实现
查找操作
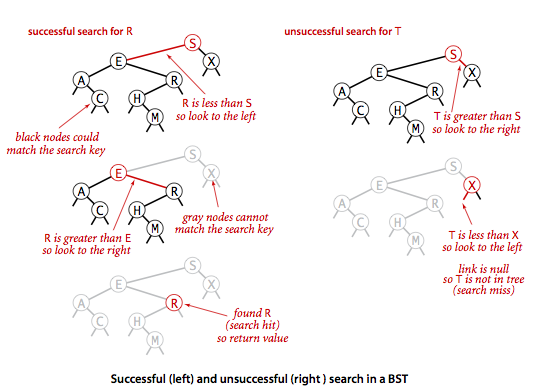
我们先来看一下如何在二叉树中根据指定的键查找到它相关联的结点。查找会有两种结果:查找成功或者不成功,我们以查找成功的情形来分析一下整个查找的过程。前面我们提到了二叉查找树的一个重要特征就是:左子树的结点都要小于根结点,右子树的结点都要大于根结点。根据这一性质,我们从根结点开始遍历二叉树,遍历的过程中会出现3种情况:
- 如果查找的键key小于根结点的key,说明我们要查找的键如果存在的话肯定在左子树,因为左子树中的结点都要小于根结点,接下来我们继续递归遍历左子树。
- 如果要查找的键key大于根结点的key,说明我们要查找的键如果存在的话肯定在右子树中,因为右子树中的结点都要大于根节点,接下来我们继续递归遍历右子树。
- 如果要查找的键key等于根结点的key,那么我们就直接返回根结点的val。
二叉树查找流程图
上面的操作我们利用递归可以非常容易的实现,代码如下:
1 /** 2 * Returns the value associated with the given key. 3 * 4 * @param key the key 5 * @return the value associated with the given key if the key is in the symbol table 6 * and null if the key is not in the symbol table 7 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if key is null 8 */ 9 public Value get(Key key) { 10 if(key == null) { 11 throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to put() is null"); 12 } else { 13 return get(root, key); 14 } 15 } 16 private Value get(Node x, Key key) { 17 if(x == null) { 18 return null; 19 } else { 20 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 21 if(cmp < 0) { 22 return get(x.left, key); 23 } else if(cmp > 0) { 24 return get(x.right, key); 25 } else { 26 return x.val; 27 } 28 } 29 }
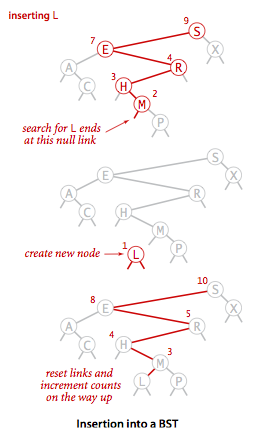
插入操作
如果理解了上面的查找操作,插入操作其实也很好理解,我们首先要找到我们新插入结点的位置,其思想和查找操作一样。找到插入的位置后我们就将新结点插入二叉树。只是这里还要加一个步骤:更新结点的size,因为我们刚刚新插入了结点,该结点的父节点,父节点的父节点的size都要加一。
二叉树插入流程图
插入操作的实现同样有多种实现方法,但是递归的实现应该是最为清晰的。下面的代码的思想和get基本类似,只是多了x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;这一步骤用来更新结点的size大小。
1 /** 2 * Inserts the specified key-value pair into the symbol table, overwriting the old 3 * value with the new value if the symbol table already contains the specified key. 4 * Deletes the specified key (and its associated value) from this symbol table 5 * if the specified value is null. 6 * 7 * @param key the key 8 * @param val the value 9 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if key is null 10 */ 11 public void put(Key key, Value val) { 12 if(key == null) { 13 throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to put() is null"); 14 } 15 if(val == null) { 16 delete(key); 17 return; 18 } 19 root = put(root, key, val); 20 // assert check(); // Check integrity of BST data structure. 21 } 22 private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) { 23 if(x == null) { 24 return new Node(key, val, 1); 25 } else { 26 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 27 if(cmp < 0) { 28 x.left = put(x.left, key, val) 29 } else if(cmp > 0) { 30 x.right = put(x.right, key, val); 31 } else { 32 x.val = val; 33 } 34 // reset links and increment counts on the way up 35 x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; 36 return x; 37 } 38 }
select与rank的实现
select的实现
上面我们的get()操作是通过指定的key去在二叉查找树中查询其关联的结点,二叉查找树的另外一个优点就是它可以一定程度上保证数据的有序性,所以我们可以较高效的去查询第n小的数据。
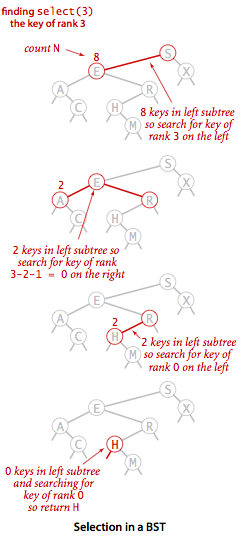
首先我们来思考一个问题:怎么知道一个二叉查找树中小于指定结点的子结点的个数?这一点根据二叉查找树的性质-左子树中的结点都要小于根结点很容易实现,我们只需要统计左子树的大小就行了。结合下面这幅图,以查找二叉树第4小的结点我们来看一下select操作的具体流程。
依次遍历二叉树,我们来到了下图中的E结点,E结点的左子树有2个结点,它是二叉树中第3小的结点,所以我们可以判断出要查找的结点肯定在E结点的右子树中。由于我们要查找第4小的结点,而E又是二叉树中第3小的结点,所以我们要查找的这个结点接下来肯定要满足一个特征:E的右子树中只有0个比它更小的结点,即右子树中最小的结点H。
二叉树select流程图
select的实现如下,实际就是根据左子树的结点数目来判断当前结点在二叉树中的大小。
1 /** 2 * Return the kth smallest key in the symbol table. 3 * 4 * @param k the order statistic 5 * @return the kth smallest key in the symbol table 6 * @throws IllegalArgumentException unless k is between 0 and n-1 7 */ 8 public Key select(int k) { 9 if (k < 0 || k >= size()) { 10 throw new IllegalArgumentException("called select() with invalid argument: " + k); 11 } else { 12 Node x = select(root, k); 13 return x.key; 14 } 15 } 16 // Return the key of rank k. 17 public Node select(Node x, int k) { 18 if(x == null) { 19 return null; 20 } else { 21 int t = size(x.left); 22 if(t > k) { 23 return select(x.left, k); 24 } else if(t < k) { 25 return select(x.right, k); 26 } else { 27 return x; 28 } 29 } 30 }
rank就是查找指定的键key在二叉树中的排名,实现代码如下,思想和上面一致我就不重复解释了。
1 /** 2 * Return the number of keys in the symbol table strictly less than key. 3 * 4 * @param key the key 5 * @return the number of keys in the symbol table strictly less than key 6 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if key is null 7 */ 8 public int rank(Key key) { 9 if (key == null) { 10 throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to rank() is null"); 11 } else { 12 return rank(key, root); 13 } 14 } 15 public int rank(Key key, Node x) { 16 if(x == null) { 17 return 0; 18 } else { 19 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 20 if(cmp < 0) { 21 return rank(key, x.left); 22 } else if(cmp > 0) { 23 return 1 + size(x.left) + rank(key, x.right); 24 } else { 25 return size(x.left); 26 } 27 } 28 }
删除操作
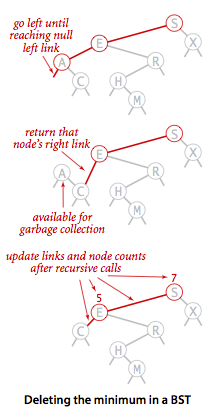
删除操作是二叉查找树中最难实现的方法,在实现它之前,我们先来看一下如何删除二叉查找树中最小的结点。
为了实现deleteMin(),我们首先要找到这个最小的节点,很明显这个结点就是树中最左边的结点A,我们重点关注的是怎么删除这个结点A。在我们下面这幅图中结点E的左子树中的两个结点A和C都是小于结点E的,我们只需要将结点E的左链接由A变为C即可,然后A就会自动被GC回收。最后一步就是更新节点的size了。
二叉树deletetMin流程图
具体的实现代码如下:
1 /** 2 * Removes the smallest key and associated value from the symbol table. 3 * 4 * @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty 5 */ 6 public void deleteMin() { 7 if (isEmpty()) { 8 throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow"); 9 } else { 10 root = deleteMin(root); 11 // assert check(); // Check integrity of BST data structure. 12 } 13 } 14 private Node deleteMin(Node x) { 15 if(x.left == null) { 16 return x.right; 17 } else { 18 x.left = deleteMin(x.left); 19 x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; 20 return x; 21 } 22 }
删除最大的结点也是一个道理,我就不重复解释了:
1 /** 2 * Removes the largest key and associated value from the symbol table. 3 * 4 * @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty 5 */ 6 public void deleteMax() { 7 if (isEmpty()) { 8 throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow"); 9 } else { 10 root = deleteMax(root); 11 // assert check(); // Check integrity of BST data structure. 12 } 13 } 14 private Node deleteMax(Node x) { 15 if (x.right == null) { 16 return x.left; 17 } else { 18 x.right = deleteMax(x.right); 19 x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; 20 return x; 21 } 22 }
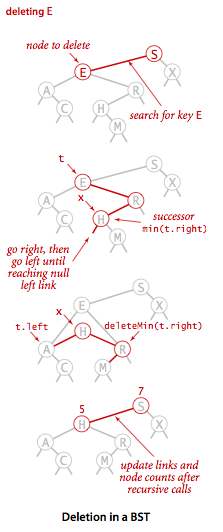
接下来我们结合下图来一步步完整地看一下整个删除操作的过程,首先还是和上面一样我们要找到需要删除的结点E,然后我们要在E的右子树中找到最小结点,这里是H,接下来我们就用H替代E就行了。为什么可以直接用H替代E呢?因为H结点大于E的左子树的所有结点,小于E的右子树中的其它所有结点,所以这一次替换并不会破坏二叉树的特性。
二叉树delete流程图
实现代码如下,这里解释一下执行到了// find key后的代码,这个时候会出现三种情况:
- 结点的右链接为空,这个时候我们直接返回左链接来替代删除结点。
- 结点的左链接为空,这个时候返回右链接来替代删除结点。
- 左右链接都不为空的话,就是我们上图中的那种情形了。
1 /** 2 * Removes the specified key and its associated value from this symbol table 3 * (if the key is in this symbol table). 4 * 5 * @param key the key 6 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if key is null 7 */ 8 public void delete(Key key) { 9 if (key == null) { 10 throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to delete() is null"); 11 } else { 12 root = delete(root, key); 13 // assert check(); // Check integrity of BST data structure. 14 } 15 } 16 private Node delete(Key key) { 17 if(x == null) { 18 return null; 19 } else { 20 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 21 if(cmp < 0) { 22 x.left = delete(x.left, key); 23 } else if(cmp > 0) { 24 x.right = delete(x.right, key); 25 } else { 26 // find key 27 if(x.right == null) { 28 return x.left; 29 } else if(x.left == null) { 30 return x.right; 31 } else { 32 Node t = x; 33 x = min(t.right); 34 x.right = deleteMin(t.right); 35 x.left = t.left; 36 } 37 } 38 // update links and node count after recursive calls 39 x.size = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; 40 return x; 41 } 42 }
floor和ceiling的实现
floor的实现
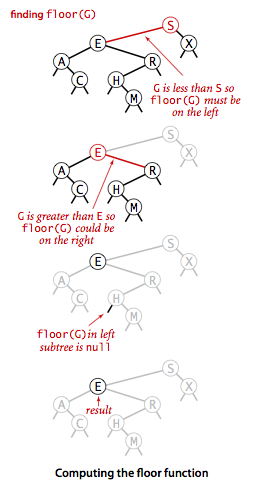
floor()要实现的就是向下取整,我们来分析一下它的执行流程:
- 如果指定的键key小于根节点的键,那么小于等于key的最大结点肯定就在左子树中了。
- 如果指定的键key大于根结点的键,情况就要复杂一些,这个时候要分两种情况:1>当右子树中存在小于等于key的结点时,小于等于key的最大结点则在右子树中;2>反之根节点自身就是小于等于key的最大结点了。
二叉树floor流程图
具体实现代码如下:
1 /** 2 * Returns the largest key in the symbol table less than or equal to key. 3 * 4 * @param key the key 5 * @return the largest key in the symbol table less than or equal to key 6 * @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no such key 7 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if key is null 8 */ 9 public Key floor(Key key) { 10 if (key == null) { 11 throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to floor() is null"); 12 } 13 if (isEmpty()) { 14 throw new NoSuchElementException("called floor() with empty symbol table"); 15 } 16 Node x = floor(root, key); 17 if (x == null) { 18 return null; 19 } else { 20 return x.key; 21 } 22 } 23 private Node floor(Node x, Key key) { 24 if (x == null) { 25 return null; 26 } else { 27 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 28 if(cmp == 0) { 29 return x; 30 } else if(cmp < 0) { 31 return floor(x.left, key); 32 } else { 33 Node t = floor(x.right, key); 34 if(t != null) { 35 return t; 36 } else { 37 return x; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 }
ceiling的实现
ceiling()则与floor()相反,它做的是向下取整,即找到大于等于key的最小结点。但是两者的实现思路是一致的,只要将上面的左变为右,小于变为大于就行了:
1 /** 2 * Returns the smallest key in the symbol table greater than or equal to {@code key}. 3 * 4 * @param key the key 5 * @return the smallest key in the symbol table greater than or equal to {@code key} 6 * @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no such key 7 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null} 8 */ 9 public Key ceiling(Key key) { 10 if(key == null) { 11 throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to ceiling() is null"); 12 } 13 if(isEmpty()) { 14 throw new NoSuchElementException("called ceiling() with empty symbol table"); 15 } 16 Node x = ceiling(root, key); 17 if(x == null) { 18 return null; 19 } else { 20 return x.key; 21 } 22 } 23 private Node ceiling(Node x, Key key) { 24 if(x == null) { 25 return null; 26 } else { 27 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 28 if(cmp == 0) { 29 return x; 30 } else if(cmp < 0) { 31 Node t = ceiling(x.left, key); 32 if (t != null) { 33 return t; 34 } else { 35 return x; 36 } 37 } else { 38 return ceiling(x.right, key); 39 } 40 } 41 }





















 581
581











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








