效果:
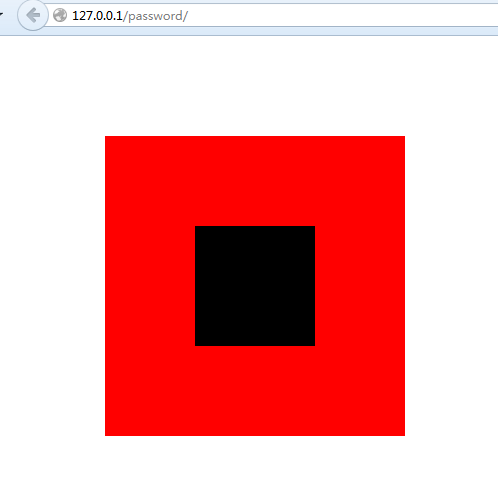
实现代码1:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style type="text/css"> body{margin: 0; padding: 0;} #div1{ margin-top: 100px; margin-left: 150px; width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: red; position: relative; } #div2{ width: 120px; height: 120px; background-color: black; position: absolute; /*(300-120)/2/300*/ top: 30%; left: 30%; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="classname"> <div id="div2" class="classname"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
实现代码2:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style type="text/css"> body{margin: 0; padding: 0;} #div1{ margin-top: 100px; margin-left: 150px; width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: red; } #div2{ width: 120px; height: 120px; background-color: black; /*(300-120)/2/300=30%*/ position: relative; top: 30%; left: 30%; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1" class="classname"> <div id="div2" class="classname"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
实现代码3:




 本文详细介绍了如何使用CSS的定位属性(如position、top、left)来创建响应式和动态布局,通过实例展示了如何调整元素的位置以适应不同屏幕尺寸,确保网页设计的灵活性和用户体验。
本文详细介绍了如何使用CSS的定位属性(如position、top、left)来创建响应式和动态布局,通过实例展示了如何调整元素的位置以适应不同屏幕尺寸,确保网页设计的灵活性和用户体验。
















 1999
1999

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








