安装Apache2:
apt-get install apache2
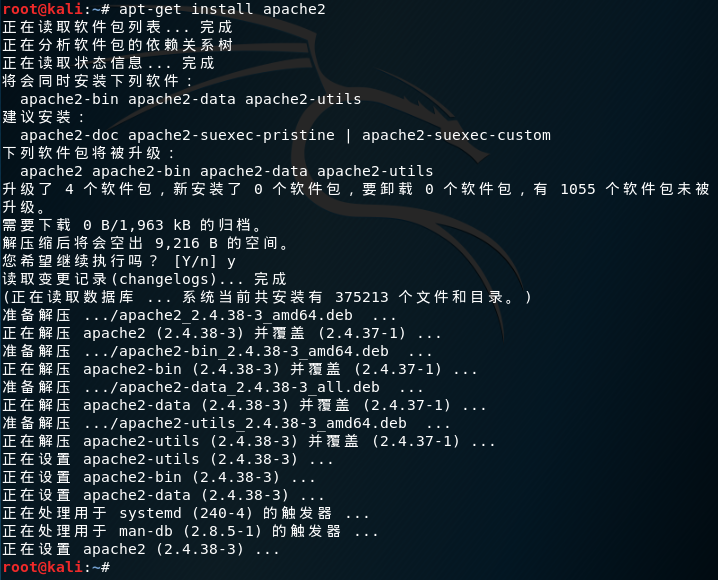
启动Apache2服务:
service apache2 start
在终端运行启动后,打开浏览器URL访问 http://localhost/ 或 127.0.0.1
显示的网页就是Apache2 Web Server 默认页[It works],由此可以断定Apache2 Web服务器正在运行

Apache的默认网页位于:/var/www/html/index.html ;可以通过编辑index.html文件提供想要的任何信息,可以通过更改文件代码改变html页面的显示方式和内容


<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> <title>Apache2 Debian Default Page: It works</title> <style type="text/css" media="screen"> * { margin: 0px 0px 0px 0px; padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px; } body, html { padding: 3px 3px 3px 3px; background-color: #D8DBE2; font-family: Verdana, sans-serif; font-size: 11pt; text-align: center; } div.main_page { position: relative; display: table; width: 800px; margin-bottom: 3px; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto; padding: 0px 0px 0px 0px; border-width: 2px; border-color: #212738; border-style: solid; background-color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center; } div.page_header { height: 99px; width: 100%; background-color: #F5F6F7; } div.page_header span { margin: 15px 0px 0px 50px; font-size: 180%; font-weight: bold; } div.page_header img { margin: 3px 0px 0px 40px; border: 0px 0px 0px; } div.table_of_contents { clear: left; min-width: 200px; margin: 3px 3px 3px 3px; background-color: #FFFFFF; text-align: left; } div.table_of_contents_item { clear: left; width: 100%; margin: 4px 0px 0px 0px; background-color: #FFFFFF; color: #000000; text-align: left; } div.table_of_contents_item a { margin: 6px 0px 0px 6px; } div.content_section { margin: 3px 3px 3px 3px; background-color: #FFFFFF; text-align: left; } div.content_section_text { padding: 4px 8px 4px 8px; color: #000000; font-size: 100%; } div.content_section_text pre { margin: 8px 0px 8px 0px; padding: 8px 8px 8px 8px; border-width: 1px; border-style: dotted; border-color: #000000; background-color: #F5F6F7; font-style: italic; } div.content_section_text p { margin-bottom: 6px; } div.content_section_text ul, div.content_section_text li { padding: 4px 8px 4px 16px; } div.section_header { padding: 3px 6px 3px 6px; background-color: #8E9CB2; color: #FFFFFF; font-weight: bold; font-size: 112%; text-align: center; } div.section_header_red { background-color: #CD214F; } div.section_header_grey { background-color: #9F9386; } .floating_element { position: relative; float: left; } div.table_of_contents_item a, div.content_section_text a { text-decoration: none; font-weight: bold; } div.table_of_contents_item a:link, div.table_of_contents_item a:visited, div.table_of_contents_item a:active { color: #000000; } div.table_of_contents_item a:hover { background-color: #000000; color: #FFFFFF; } div.content_section_text a:link, div.content_section_text a:visited, div.content_section_text a:active { background-color: #DCDFE6; color: #000000; } div.content_section_text a:hover { background-color: #000000; color: #DCDFE6; } div.validator { } </style> </head> <body> <div class="main_page"> <div class="page_header floating_element"> <img src="/icons/openlogo-75.png" alt="Debian Logo" class="floating_element"/> <span class="floating_element"> Apache2 Debian Default Page </span> </div> <!-- <div class="table_of_contents floating_element"> <div class="section_header section_header_grey"> TABLE OF CONTENTS </div> <div class="table_of_contents_item floating_element"> <a href="#about">About</a> </div> <div class="table_of_contents_item floating_element"> <a href="#changes">Changes</a> </div> <div class="table_of_contents_item floating_element"> <a href="#scope">Scope</a> </div> <div class="table_of_contents_item floating_element"> <a href="#files">Config files</a> </div> </div> --> <div class="content_section floating_element"> <div class="section_header section_header_red"> <div id="about"></div> It works! </div> <div class="content_section_text"> <p> This is the default welcome page used to test the correct operation of the Apache2 server after installation on Debian systems. If you can read this page, it means that the Apache HTTP server installed at this site is working properly. You should <b>replace this file</b> (located at <tt>/var/www/html/index.html</tt>) before continuing to operate your HTTP server. </p> <p> If you are a normal user of this web site and don't know what this page is about, this probably means that the site is currently unavailable due to maintenance. If the problem persists, please contact the site's administrator. </p> </div> <div class="section_header"> <div id="changes"></div> Configuration Overview </div> <div class="content_section_text"> <p> Debian's Apache2 default configuration is different from the upstream default configuration, and split into several files optimized for interaction with Debian tools. The configuration system is <b>fully documented in /usr/share/doc/apache2/README.Debian.gz</b>. Refer to this for the full documentation. Documentation for the web server itself can be found by accessing the <a href="/manual">manual</a> if the <tt>apache2-doc</tt> package was installed on this server. </p> <p> The configuration layout for an Apache2 web server installation on Debian systems is as follows: </p> <pre> /etc/apache2/ |-- apache2.conf | `-- ports.conf |-- mods-enabled | |-- *.load | `-- *.conf |-- conf-enabled | `-- *.conf |-- sites-enabled | `-- *.conf </pre> <ul> <li> <tt>apache2.conf</tt> is the main configuration file. It puts the pieces together by including all remaining configuration files when starting up the web server. </li> <li> <tt>ports.conf</tt> is always included from the main configuration file. It is used to determine the listening ports for incoming connections, and this file can be customized anytime. </li> <li> Configuration files in the <tt>mods-enabled/</tt>, <tt>conf-enabled/</tt> and <tt>sites-enabled/</tt> directories contain particular configuration snippets which manage modules, global configuration fragments, or virtual host configurations, respectively. </li> <li> They are activated by symlinking available configuration files from their respective *-available/ counterparts. These should be managed by using our helpers <tt> a2enmod, a2dismod, </tt> <tt> a2ensite, a2dissite, </tt> and <tt> a2enconf, a2disconf </tt>. See their respective man pages for detailed information. </li> <li> The binary is called apache2. Due to the use of environment variables, in the default configuration, apache2 needs to be started/stopped with <tt>/etc/init.d/apache2</tt> or <tt>apache2ctl</tt>. <b>Calling <tt>/usr/bin/apache2</tt> directly will not work</b> with the default configuration. </li> </ul> </div> <div class="section_header"> <div id="docroot"></div> Document Roots </div> <div class="content_section_text"> <p> By default, Debian does not allow access through the web browser to <em>any</em> file apart of those located in <tt>/var/www</tt>, <a href="http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/mod_userdir.html" rel="nofollow">public_html</a> directories (when enabled) and <tt>/usr/share</tt> (for web applications). If your site is using a web document root located elsewhere (such as in <tt>/srv</tt>) you may need to whitelist your document root directory in <tt>/etc/apache2/apache2.conf</tt>. </p> <p> The default Debian document root is <tt>/var/www/html</tt>. You can make your own virtual hosts under /var/www. This is different to previous releases which provides better security out of the box. </p> </div> <div class="section_header"> <div id="bugs"></div> Reporting Problems </div> <div class="content_section_text"> <p> Please use the <tt>reportbug</tt> tool to report bugs in the Apache2 package with Debian. However, check <a href="http://bugs.debian.org/cgi-bin/pkgreport.cgi?ordering=normal;archive=0;src=apache2;repeatmerged=0" rel="nofollow">existing bug reports</a> before reporting a new bug. </p> <p> Please report bugs specific to modules (such as PHP and others) to respective packages, not to the web server itself. </p> </div> </div> </div> <div class="validator"> </div> </body> </html>
若是想让浏览器浏览我们想要的HTML内容,可以在该目录下添加新的HTML文件【添加新的HTML网页】:
<! index2.html >
<html> <body> <h1> 第一个Apache-Web中的HTML页面 </h1> <p> Hello ! Apache ! </p> <p> Is you to </p> </body> </html>
然后打开浏览器,访问 http://localhost/ 或 127.0.0.1 并没有看见自己的网站,依旧是apache默认的网页,这是因为index.html是默认第一加载的页面,此时的真实完整的URL是: http://localhost/index.html ;若想访问自己添加的页面,则需要改变URL:http://localhost/index2.html
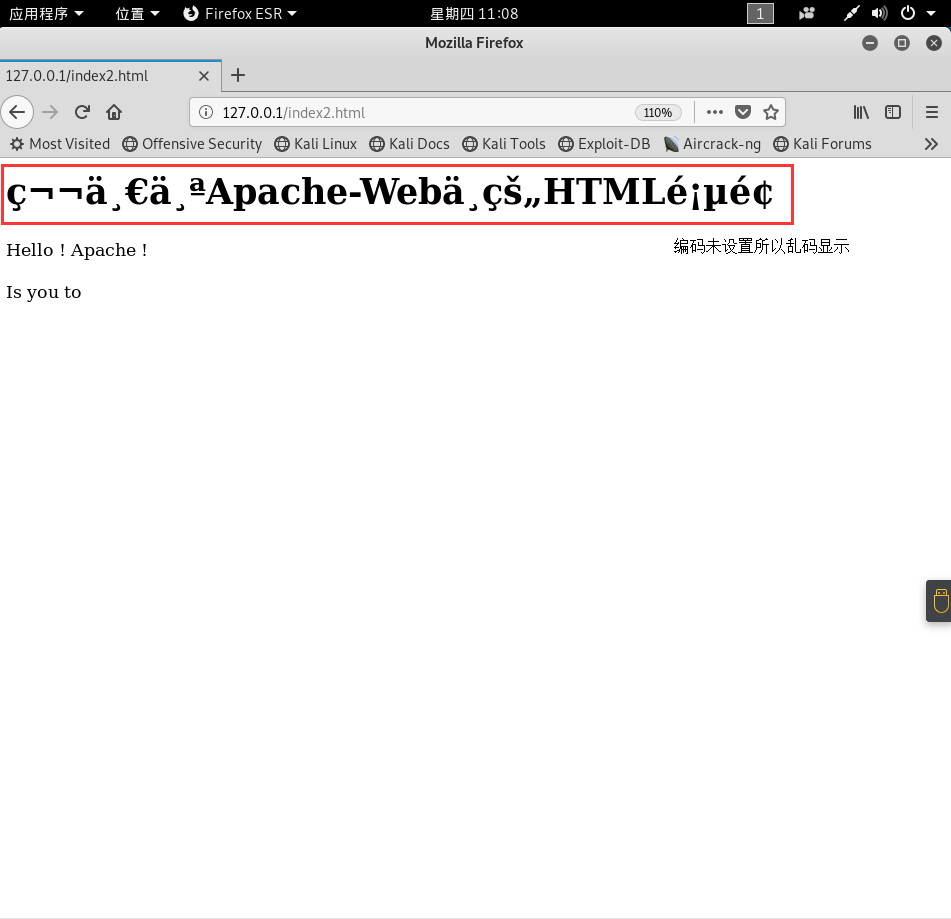
`
——————
至此,Apache的简单安装运行介绍完毕!
如果需要关闭服务:service apache2 stop
如果需要重启服务:serivce apache2 restart




















 2459
2459











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








