1. asyncio概述
Python 3.4 的标准库中添加了 asyncio 模块,它在 单线程 中使用 事件循环(event loop) 来驱动 协程(coroutines) 从而实现 并发(concurrency)。此模块的主要组件和概念包括:
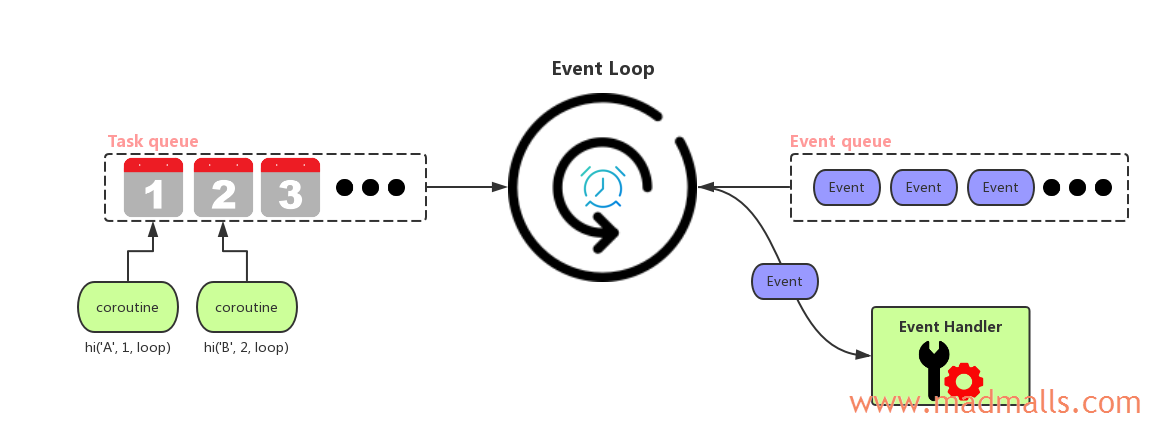
Event Loop: 每个线程中只能有一个 事件循环,每次只能运行一个 任务(Task)。事件循环会不断地重复 "监听事件发生 -- 处理该事件" 这一过程。当 Task A 在等待 Future 对象运行完成时,会把控制权 交还 给 事件循环(通过 yield 关键字),这样 事件循环 就可以运行 Task B。一段时间后,Task A 所等待的 Future 对象完成了,事件循环 会唤醒 Task A 继续运行,从而实现 并发
Coroutines: 协程可以在执行期间 暂停(suspend),这样就可以在等待外部的处理(例如,等待网络 I/O 数据)完成之后,从之前暂停的地方 恢复执行(resume)
Futures: Future 对象是一个"占位符",用来保存尚未完成的操作的结果(或异常)。在 asyncio 模块中,所有需要异步完成的操作都对应一个 Future 对象,当操作完成时,将数据设置为 Future 对象的结果。Python 3.4 时实现了 __iter__ 方法,可以在 协程 中使用 yield from future 等待 Future 对象的 返回值; Python 3.5+ 实现了 __await__ 方法,可以在 协程 中使用 await future 或 yield from future(有一行代码: __iter__ = __await__)等待 Future 对象的 返回值
Tasks: Task 类是 Future 的子类,用来包装 我们写的 协程,当 事件循环 启动后,Task 会自动调用 result = coro.send(None) 驱动 协程 的运行,相当于 http://www.madmalls.com/blog/post/coroutine-in-python/#16-yield-from 中的 调用方,而 Future 相当于 end-point(sink),Future 的 __await__ 方法中的 yield self 会直接将 Future 对象本身传递给 Task 中的 result,并把控制权 交还 给 事件循环。同时,Task 会向 事件循环 注册事件: 当 Future 对象完成时,请执行我的 __wakeup() 方法 唤醒 我。所以,当 Future 对象结束时,Task 被唤醒,再次执行 coro.send(None),最终获取到 Future 对象的结果(可能被协程链中的其它协程处理过),并设置为 Task 的结果,详情见章节 5 的总结
由于 asyncio 模块使用 单线程,任何阻塞操作都会阻塞整个 事件循环,所以任何 阻塞型操作 都要换成 非阻塞型的异步操作。标准库中的 socket 模块,所有的方法比如 socket.accept() 和 socket.recv() 等都是是 阻塞型操作,所以要换成 非阻塞型的异步操作 比如 loop.sock_accept() 和 loop.sock_recv() 等。同时,asyncio 模块的 事件循环 基于 Python 3.4 中新增的 selectors 模块,使用操作系统底层提供的 I/O multiplexing 来同时监听多个 socket 上的 可读/可写 事件,从而实现了 异步网络 I/O
2. Event Loop
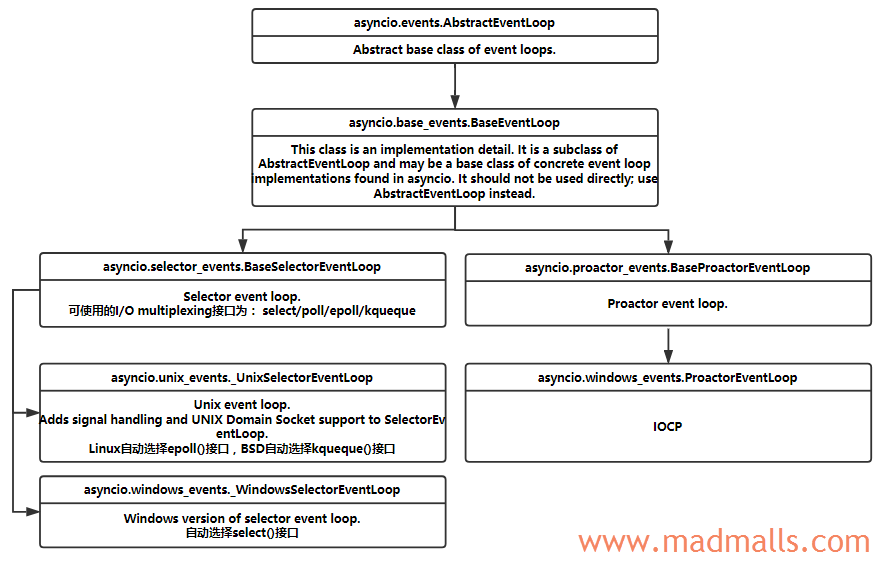
asyncio 实现了两种 事件循环 对象:
asyncio.SelectorEventLoop: (默认使用)基于 Python 3.4 中添加的 selectors 模块,它会根据 OS 自动选择最优的 I/O multiplexing 接口,比如在 Linux 中会使用 epoll,在 BSD 中使用 Kqueue
asyncio.ProactorEventLoop: 只能用于 Windows 系统,使用 IOCP(I/O Completion Ports),参考 MSDN documentation on I/O Completion Ports
2.1 获取事件循环
使用 asyncio.get_event_loop() 获取当前的 事件循环:
# For Linux
In [1]: import asyncio
In [2]: loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
In [3]: loop
Out[3]: <_unixselectoreventloop running="False" closed="False" debug="False">
# For Windows
In [1]: import asyncio
In [2]: loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
In [3]: loop
Out[3]: <_windowsselectoreventloop running="False" closed="False" debug="False">
2.2 设置事件循环
使用 asyncio.set_event_loop(loop) 设置 事件循环,Windows 中默认使用 asyncio.windows_events._WindowsSelectorEventLoop,只支持 sockets,不支持 Pipes 和 subprocesses,我们可以更换为 asyncio.windows_events.ProactorEventLoop,更详细的区别参考: https://docs.python.org/3/library/asyncio-eventloops.html#windows
In [1]: import sys
In [2]: import asyncio
In [3]: asyncio.get_event_loop()
Out[3]: <_windowsselectoreventloop running="False" closed="False" debug="False">
In [4]: if sys.platform == 'win32':
...: loop = asyncio.ProactorEventLoop()
...: asyncio.set_event_loop(loop)
...:
In [5]: asyncio.get_event_loop()
Out[5]:
设置 asyncio.SelectorEventLoop 使用的 I/O multiplexing 接口:
在 Mac OS 10.6、10.7 和 10.8 中,默认的事件循环是 asyncio.SelectorEventLoop,它会自动选择 selectors.KqueueSelector,使用操作系统底层提供的 Kquque 接口实现 I/O multiplexing,但是它不支持字符设备,可以更换为 selectors.SelectSelector():
import asyncio
import selectors
selector = selectors.SelectSelector()
loop = asyncio.SelectorEventLoop(selector)
asyncio.set_event_loop(loop)
2.3 管理事件循环策略
asyncio.get_event_loop_policy(): 获取当前事件循环策略。Get the current event loop policy.
asyncio.set_event_loop_policy(policy): 更换事件循环策略。Set the current event loop policy. If policy is None, the default policy is restored.
可以替换 asyncio 中默认的事件循环策略,比如使用 uvloop,它用 Cython 编写,基于 libuv。uvloop 可以让 asyncio 更快,测试表明比 tornado、curio、gevent 等快 两倍,几乎接近于 Go 程序的速度
(1) 安装 uvloop
# pip install uvloop
(2) 使用 uvloop.EventLoopPolicy()
In [1]: import asyncio
In [2]: import uvloop
In [3]: asyncio.set_event_loop_policy(uvloop.EventLoopPolicy())
In [4]: asyncio.get_event_loop()
Out[4]:
2.4 运行事件循环
事件循环需要启动才会不断循环监视事件并处理事件,常用方法:
AbstractEventLoop.run_until_complete(future): 运行事件循环,直到传入的 asyncio.Future 对象完成(如果传入协程,首先会自动将协程包装成 Task 对象,后面会细讲),返回 Future 对象的结果或抛出异常
AbstractEventLoop.run_forever(): 一直运行事件循环,直到调用 AbstractEventLoop.stop() 后才会停止
AbstractEventLoop.stop(): 停止正在运行的事件循环
AbstractEventLoop.close(): 关闭事件循环,The loop must not be running. Pending callbacks will be lost. This clears the queues and shuts down the executor, but does not wait for the executor to finish. 一旦关闭了事件循环后,就不能再调用 run_until_complete 等方法
2.5 基于内部时钟调度 callback
asyncio 的默认事件循环中有一个内部时钟,不同于 time.time(),可以用 AbstractEventLoop.time() 获取当前的内部时间
(1) call_soon - 立即调用
运行 AbstractEventLoop.call_soon(callback, *args, context=None) 方法后,会立即将 callback 回调函数注册到事件循环上,如果其它地方也执行了 call_soon() 函数,将按照类似 FIFO 队列的方式依次执行对应的 callback,当 callback 执行完成后,控制权交还给事件循环
call_soon() 返回 asyncio.events.Handle 对象,可以调用该对象的 cancel() 方法取消执行 callback
import time
import asyncio
def hello_world(loop):
print('When calling hello_world in event loop is: {}'.format(loop.time()))
print('Hello World')
loop.stop()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
print('The current time of time.time() is {}'.format(time.time()))
print('The current time in event loop is: {}'.format(loop.time()))
# Arrange for a callback to be called as soon as possible.
h = loop.call_soon(hello_world, loop)
print(type(h))
print(h)
# Blocking call interrupted by loop.stop()
loop.run_forever()
loop.close()
# Output:
The current time of time.time() is 1533901306.6052473
The current time in event loop is: 3821.5
) at d:/python-code/test_asyncio.py:4>
When calling hello_world in event loop is: 3821.5
Hello World
call_soon() 不是线程安全的,call_soon_threadsafe() 方法跟 call_soon 功能类似,只不过它是线程安全的
(2) call_later - 延迟调用
运行 AbstractEventLoop.call_later(delay, callback, *args, context=None) 方法后,将在 delay 秒后执行 callback
call_later() 返回 asyncio.events.TimeHandle 对象,可以调用该对象的 cancel() 方法取消执行 callback
import time
import asyncio
def hello_world(loop):
print('When calling hello_world in event loop is: {}'.format(loop.time()))
print('Hello World')
loop.stop()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
print('The current time of time.time() is {}'.format(time.time()))
print('The current time in event loop is: {}'.format(loop.time()))
# Arrange for the callback to be called after the given delay seconds (either an int or float).
h = loop.call_later(1, hello_world, loop)
print(type(h))
print(h)
# Blocking call interrupted by loop.stop()
loop.run_forever()
loop.close()
# Output:
The current time of time.time() is 1533902066.982436
The current time in event loop is: 4581.875
) at d:/python-code/test_asyncio.py:4>
When calling hello_world in event loop is: 4582.875
Hello World
(3) call_at - 具体时刻调用
运行 AbstractEventLoop.call_at(when, callback, *args, context=None) 方法后,将在 when(可以是用 int 或 float 表示的 asyncio 内部时钟的 timestamp)指定的时刻执行 callback
call_at() 返回 asyncio.events.TimeHandle 对象,可以调用该对象的 cancel() 方法取消执行 callback
import time
import asyncio
def say_number(n, loop):
print('Callback say_number output {} at {}'.format(n, loop.time()))
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
print('The current time of time.time() is {}'.format(time.time()))
阅读全文





















 2994
2994











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








