把常用数据库持久化对象,作为缓存保存在内存中,减少与数据库交互次数,可以提高性能。
一级缓存:session级别的缓存,属于事务范围。hibernate框架内置。
二级缓存:sessionFactory级别的缓存,属于进程范围的缓存。需引入外部缓存插件并配置。
二级缓存提供商:
1》EHCache
2》OSCache
3》Swarm Cache
4》JBOSS Cache
EHCache、OSCache主要用于单机数据库软件,SwarmCache和JBossCache主要用于集群环境。
二级缓存四个部分组成:
1》类级别缓存区
2》集合级别的缓存区
3》更新时间戳
4》查询缓存(三级缓存)
二级缓存并发策略,与事务隔离级别相对应:
1》非严格读写(nonstrict-read-write) -------- read uncommitted
2》读写型(read-write) ----------------------- read committed
3》事务型(transactional) -------------------- repeatable read
4》只读型(read-only) ------------------------ serializable
数据库中极少被改动的数据,比较适用于放入二级缓存。
本文使用EHCache进行Hibernate框架二级缓存。
1.配置使用EHCache:
1)添加jar包:
解压hibernate后从lib/optional/ehcache得到
hibernate-ehcache-4.2.7.SP1.jar
slf4j-api-1.6.1.jar
2)配置hibernate.cfg.xml:
(1)开启二级缓存:
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- 开启二级缓存 -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
(2)配置hibernate.cfg.xml 缓存的供应商:
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- 开启二级缓存 -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<!-- hibernate3配置:指明缓存供应商 -->
<!--
<property name="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider
</property>
-->
<!-- hibernate4配置:指明缓存供应商 -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">
org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory
</property>
(3)指定对哪些数据应用二级缓存:
有两种配置方式POJO.hbm.xml配置,和hibernate.cfg.xml配置。
例:在hibernate.cfg.xml配置,<class-cache>类级别缓存;<collection-cache>集合级别缓存
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- 开启二级缓存 -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<!-- 指明缓存供应商 -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">
org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory
</property>
<!-- property、mapping等配置在中间 -->
<!-- 类级别配置:指明使用二级缓存的类:
usage=二级缓存并非策略
class=对应的POJO -->
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="cn.cvu.hibernate.domain.PojoUser"/>
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="cn.cvu.hibernate.domain.PojoOrder"/>
<!-- 集合级别配置:指明使用二级缓存的集合:
usage=二级缓存并非策略
collection=对应POJO中的集合变量 -->
<collection-cache usage="read-write" collection="cn.cvu.hibernate.domain.PojoUser.orders"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
3)建立ehcache.xml:
在src下创建,主要用来配置EHCache插件的属性。可以将hibernate解压的/project/etc/ehcache.xml复制到src下进行修改。
4)测试:
(1)开启状态:
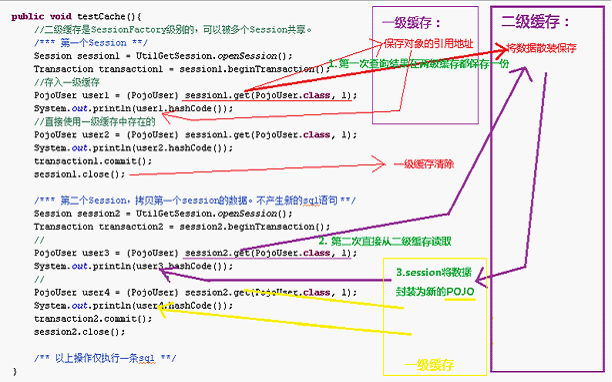
public void testCache(){
//二级缓存是SessionFactory级别的,可以被多个Session共享。
/*** 第一个Session **/
Session session1 = UtilGetSession.openSession();
Transaction transaction1 = session1.beginTransaction();
//存入一级缓存和二级缓存
PojoUser user1 = (PojoUser) session1.get(PojoUser.class, 1);
System.out.println(user1.hashCode());
//直接使用一级缓存中存在的数据
PojoUser user2 = (PojoUser) session1.get(PojoUser.class, 1);
System.out.println(user2.hashCode());
transaction1.commit();
session1.close();
/*** 第二个Session,不产生新的sql语句 **/
Session session2 = UtilGetSession.openSession();
Transaction transaction2 = session2.beginTransaction();
//使用二级缓存中的数据在新的一级缓存封装数据
PojoUser user3 = (PojoUser) session2.get(PojoUser.class, 1);
System.out.println(user3.hashCode());
//使用新一级缓存中的数据
PojoUser user4 = (PojoUser) session2.get(PojoUser.class, 1);
System.out.println(user4.hashCode());
transaction2.commit();
session2.close();
/** 以上操作仅执行一条sql **/
} 
(2)关闭状态:

2.二级缓存存储原理:
1)类级别缓存区:
(1)散装数据的存储:每次使用二级缓存,将获得一个新的对象:
(2)Query接口可以将数据放置到类级别的二级缓存中,但是不能使用query接口的list方法从缓存中获取数据,能存不能取:
@Test
public void testCache(){
Session session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//Query接口可以将数据放置到类级别的二级缓存中,但是不能使用list方法从缓存中获取数据
Query query1 = session.createQuery("from PojoUser");
//Query可以向二级缓存存入数据
List<PojoUser> list1 = query1.list(); //生成第一条sql
System.out.println(list1);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//直接从二级缓存获取,无sql生成
PojoUser user = (PojoUser) session.get(PojoUser.class, 2);
System.out.println("直接读取二级缓存:" + user);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Query query2 = session.createQuery("from PojoUser");
//Query不能从二级缓存读取数据
List<PojoUser> list2 = query2.list(); //因为不能读,生成第2条sql
System.out.println(list2);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
} 
2)集合级别缓冲区:
(1)测试集合缓存:
public void testCacheList() {
Session session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
PojoUser user1 = (PojoUser) session.get(PojoUser.class, 1);
System.out.println("第1次查询集合:" + user1.getOrders().size()); // 存入二级缓存
transaction.commit();
session.close();
session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
PojoUser user2 = (PojoUser) session.get(PojoUser.class, 1);
System.out.println("第2次查询集合:" + user2.getOrders().size()); // 从二级缓存取数据
for (PojoOrder order : user2.getOrders()) { // 从二级缓存取数据
System.out.println("订单:" + order.getName());
}
transaction.commit();
session.close();
} 
(2)注释 <collection-cache/> 测试:
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">
org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
<!-- property、mapping等配置在中间 -->
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="cn.cvu.hibernate.domain.PojoUser"/>
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="cn.cvu.hibernate.domain.PojoOrder"/>
<!-- 注释掉集合配置 -->
<!-- <collection-cache usage="read-write"
collection="cn.cvu.hibernate.domain.PojoUser.orders"/> -->
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration> 
(3)注释<class-cache class="PojoOrder"/>测试:
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">
org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
<!-- property、mapping等配置在中间 -->
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="cn.cvu.hibernate.domain.PojoUser"/>
<!-- 注释集合所保存的数据类
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="cn.cvu.hibernate.domain.PojoOrder"/> -->
<collection-cache usage="read-write"
collection="cn.cvu.hibernate.domain.PojoUser.orders"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration> 
(4)集合级别缓存存放的是保存在类级别缓冲区中的数据对象的OID:

3)一级缓存同步:
当一级缓存中的数据发生更新,会自动同步到二级缓存。
public void testCacheList() {
Session session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
PojoUser user1 = (PojoUser) session.get(PojoUser.class, 1);
System.out.println("第1次:" + user1.getName()); // 存入一级缓存和二级缓存
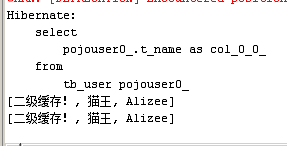
user1.setName("二级缓存!");//从一级缓存更新到二级缓存,也更新到数据库
transaction.commit();
session.close();
session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
PojoUser user2 = (PojoUser) session.get(PojoUser.class, 1);
System.out.println("第2次:" + user2.getName()); // 从二级缓存取数据
transaction.commit();
session.close();
} 
3.将二级缓存数据保存到硬盘:
配置ehcache.xml文件:
1)保存路径:

2)默认缓存配置:
默认配置对全局有效。如需要可单独配置对应POJO的<cache>,<cache name="cn.itcast.domain.POJO" name="对应POJO" 其它属性...> 。

3)测试:
在hibernate.cfg.xml中缓存全部POJO,查询大量数据(超过defaultCache的maxElementsInMemory,并且overflowToDisk为true),在diskStore配置的目录查看是否有缓存文件。
4.更新时间戳区域:
相关:org.hibernate.cache.spi.UpdateTimestampsCache
作用:保证二级缓存数据有效性。
情景:事务1查询了数据,保存到二级缓存,当事务1再次使用本线程的二级缓存前,有事务2更新了数据库,导致事务1的二级缓存数据是无效的。更新时间戳在二级缓存开辟一个区域,保存每次读写的时间,当执行查询时先对比时间戳区内的版本,如果大于类缓存区中的版本,就重新查询数据库。
public void testTimer(){
Session session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//存入一级缓存和二级缓存
PojoUser user1 = (PojoUser) session.get(PojoUser.class, 2); //创建时间戳t1
System.out.println(user1);
//直接修改数据库,模拟多用户访问
session.createQuery("update PojoUser set name='猫王' where id = 2").executeUpdate(); //创建时间戳t2
transaction.commit();
session.close();
session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//读取二级缓存,首先检查时间戳,如果有异,重新查询数据库
PojoUser user2 = (PojoUser) session.get(PojoUser.class, 2); //判断t2大于t1
System.out.println(user2);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
} 
注意:hibernate能感知的操作才会创建时间戳。
5.Query的iterate方法:
list方法只能写,不能读二级缓存。
Query的iterate方法返回List集合的迭代器对象Iterator。使用Query的iterate方法遍历时,集合中保存的是只有OID的代理对象,当访问对象的其它属性时,才进行初始化。初始化时,优先查找二级缓存;如果缓存中不存在,则生成SQL语句查询数据库。
当使用二级缓存时,iterate比list 效率要好。
public void testTimer(){
Session session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//3条记录存入二级缓存
session.createQuery("from PojoOrder where id <= 3").list();
transaction.commit();
session.close();
session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//读取二级缓存,获得3条,剩余2条执行sql
Iterator iterate = session.createQuery("from PojoOrder where id <= 5").iterate();
while (iterate.hasNext()) {
PojoOrder order = (PojoOrder) iterate.next();
System.out.println(order.getName());
}
transaction.commit();
session.close();
} 
6.查询缓存:
之前类级别缓存、集合级别缓存,都是将数据存入类级别缓冲区,通过id查询对象。key是对象的id,value是缓存对象;这里的查询缓存key是HQL语句或SQL语句,value是查询结果数据。查询缓存依赖二级缓存。
1)启用查询缓存:
在hibernate.cfg.xml中添加:
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- 启用查询缓存 -->
<property name= "hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
2)写入和读取都setCacheable为true :
public void testTimer(){
Session session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//表中的一列,数据对象的部分属性 无法缓存,之后的操作无法使用。设置cacheAble为true即可
List list1 = session.createQuery("select name from PojoUser").setCacheable(true).list();
System.out.println(list1);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
session = UtilGetSession.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//要想从缓存读取,设置cacheAble为true即可
List list2 = session.createQuery("select name from PojoUser").setCacheable(true).list();
System.out.println(list2);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
} 
- end






















 1084
1084

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








