字符设备驱动分层结构图
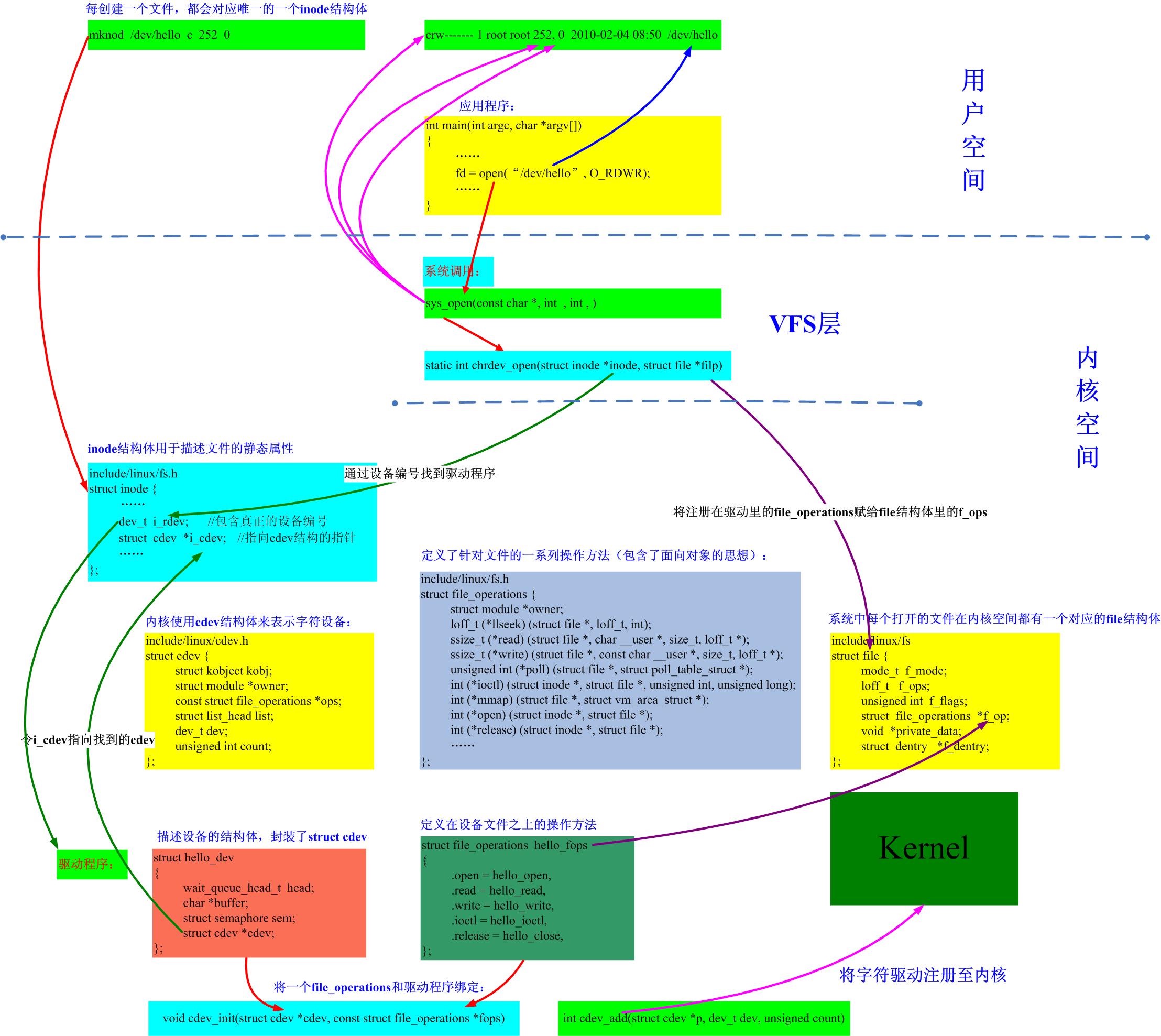
下图展示的是字符设备在打开(open)时的调用细节流程图,主要关注点是file_operations结构体的绑定操作。
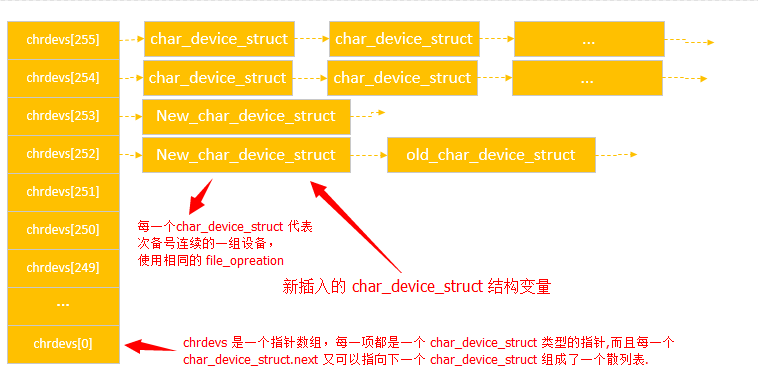
字符设备在内核空间的组织结构图
在 2.4 的内核我们使用 register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hello_fops) 来进行字符设备设备节点的分配,这种方式每一个主设备号只能存放一种设备,它们使用相同的 file_operation 结构体,也就是说内核最多支持 256 个字符设备驱动程序。
在 2.6 的内核之后,新增了一个 register_chrdev_region 函数,它支持将同一个主设备号下的次设备号进行分段,每一段供给一个字符设备驱动程序使用,使得资源利用率大大提升,同时,2.6 的内核保留了原有的 register_chrdev 方法。在 2.6 的内核中这两种方法都会调用到 __register_chrdev_region 函数。
static struct char_device_struct {
struct char_device_struct *next;
unsigned int major;
unsigned int baseminor;
int minorct;
char name[64];
struct cdev *cdev; /* will die */
} *chrdevs[CHRDEV_MAJOR_HASH_SIZE]; 内核中的每一个字符设备驱动程序都由一个 char_device_struct 结构体来描述,包含主设备号、起始次设备号、次设备号个数等信息。
内核使用 chrdevs 这个指针数组来管理所有的字符设备驱动程序,数组范围 0-255 ,看上去好像还是只支持 256 个字符设备驱动程序,其实并不然,每一个 char_device_struct 结构都含有一个 next 指针,它可以指向与其主设备号相同的其它字符设备驱动程序,它们之间主设备号相同,各自的次设备号范围相互不重叠。
字符设备驱动模板
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
/* 1. 确定主设备号 */
static int major;
static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("hello_open\n");
return 0;
}
/*读函数*/
static ssize_t hello_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ppos)
{
char data[] = "hello world."
/*读数据到用户空间:内核空间->用户空间交换数据*/
if (copy_to_user(buf, (void*)data, sizeof(data)))
{
ret = - EFAULT;
}
return ret;
}
/* 2. 构造file_operations */
static struct file_operations hello_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_open,
.read = hello_read,
};
#define HELLO_CNT 2
static struct cdev hello_cdev;
static struct class *cls;
static int hello_init(void)
{
dev_t devid;
/* 3. 告诉内核 */
#if 0 // 老方法
/* (major, 0), (major, 1), ..., (major, 255)都对应hello_fops */
major = register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hello_fops);
#else // 新方法
if (major) {
devid = MKDEV(major, 0);
/* (major,0~1) 对应 hello_fops, (major, 2~255)都不对应hello_fops */
register_chrdev_region(devid, HELLO_CNT, "hello");
} else {
/* (major,0~1) 对应 hello_fops, (major, 2~255)都不对应hello_fops */
alloc_chrdev_region(&devid, 0, HELLO_CNT, "hello");
major = MAJOR(devid);
}
cdev_init(&hello_cdev, &hello_fops);
cdev_add(&hello_cdev, devid, HELLO_CNT);
#endif
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello");
device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello0"); /* /dev/hello0 */
device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 1), NULL, "hello1"); /* /dev/hello1 */
return 0;
}
static void hello_exit(void)
{
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 0));
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 1));
class_destroy(cls);
cdev_del(&hello_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major, 0), HELLO_CNT);
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); 下面是Makefile
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m:=hello.o
else
KERNELDIR?=/lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD:=$(shell pwd)
default:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
endif
下面可以写一个应用程序测试一下:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fp = NULL;
char buf[4096];
/*打开设备文件*/
fp = fopen("/dev/hello0","r+");
if (fp == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
/*读设备*/
fread(buf, sizeof(buf), 1, fp);
/*检测结果*/
printf("buf: %s\n",buf);
return 0;
}






















 3007
3007

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








