GEF中定义的模型一般包括两个部分。
1. 业务模型。类似POJO,模型要代表一定的业务含义,需要能体现所表示业务的含义。特别是那些需要图形表示的属性,如本案例中的长宽、船名等。从实践的角度来看,通常我把从需求分析得到的领域对象作为Model一个自定义属性。
2. 保存图形的状态信息。如图形的颜色、辅助线、位置、Listerner等。
创建“org.jport.gef.berth.model”package。
可视化船舶调度系统,需要展示的数据模型就是船舶信息,如到离泊时间,装卸进度,位置等信息,从领域建模的角度来看,这就是一个领域对象。从程序角度来看,就是一个POJO。
既然是POJO,那么可以进行EJB3注解实现持久化,也可以是一个DTO,这样就为GEF的显示与数据分离奠定了基础,使GEF成为一个轻量级的客户端。
ShipInfo.java
|
package org.jport.gef.berth.domain;
import java.util.Date;
public
class
ShipInfo{
//船名
public String shipName;
//船载货物的名称
public String CargoName;
//货物数量
public String CargoAmount;
//预计靠泊日期、时间
public Date forcastDate;
//预计停泊泊位
public String berthNum;
//getter and setter method
……
}
|
容器的创建。为了更加清晰的显示GEF的模型信息,通常创建一个父类来处理GEF通用的属性,如listener, 父子关系等。
1. BaseModel.java
|
package org.jport.gef.berth.model;
import java.beans.PropertyChangeListener;
import java.beans.PropertyChangeSupport;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.geometry.Rectangle;
public
class BaseModel{
private String name;
//定义模型的位置和大小
private Rectangle layout;
private List<BaseModel> children;
private BaseModel parent;
private PropertyChangeSupport listeners;
//定义与模型操作相关的产量
public
static
final String
PROPERTY_LAYOUT = "ModelLayout";
public
static
final String
PROPERTY_ADD = "ModelAddChild";
public
static
final String
PROPERTY_REMOVE = "ModelRemoveChild";
public
static
final String
PROPERTY_RENAME = "ModelRename";
public BaseModel(){
this.name = "modelName";
this.layout =
new Rectangle();
this.children =
new ArrayList<BaseModel>();
this.parent =
null;
this.listeners =
new PropertyChangeSupport(
this);
}
public
void setName(String name) {
String oldName =
this.name;
this.name = name;
getListeners().firePropertyChange(
PROPERTY_RENAME, oldName,
this.name);
}
public String getName() {
return
this.name;
}
public
void setLayout(Rectangle newLayout) {
Rectangle oldLayout =
this.layout;
this.layout = newLayout;
getListeners().firePropertyChange(
PROPERTY_LAYOUT, oldLayout, newLayout);
}
public Rectangle getLayout() {
return
this.layout;
}
public
boolean addChild(BaseModel child) {
boolean b =
this.children.add(child);
if (b) {
child.setParent(
this);
getListeners().firePropertyChange(
PROPERTY_ADD,
null, child);
}
return b;
}
public
boolean removeChild(BaseModel child) {
boolean b =
this.children.remove(child);
if (b)
getListeners().firePropertyChange(
PROPERTY_REMOVE, child,
null);
return b;
}
public List<BaseModel> getChildrenArray() {
return
this.children;
}
public
void setParent(BaseModel parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public BaseModel getParent() {
return
this.parent;
}
public
void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) {
listeners.addPropertyChangeListener(listener);
}
public PropertyChangeSupport getListeners() {
return listeners;
}
public
void removePropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) {
listeners.removePropertyChangeListener(listener);
}
public
boolean contains(BaseModel child) {
return children.contains(child);
}
}
|
BaseModel具有GEF模型的基本属性,是通用的。可以通过扩展这个类,以减少模型复杂性。
抽出父类后,ShipModel就简洁多了。
|
package org.jport.gef.berth.model;
import org.jport.gef.berth.domain.ShipInfo;
public
class ShipModel
extends BaseModel{
public ShipInfo shipInfo;
public ShipInfo getShipInfo() {
return shipInfo;
}
public
void setShipInfo(ShipInfo shipInfo) {
this.shipInfo = shipInfo;
}
}
|
在GEF框架下,每个模型都对应一个figure,在下一节中创建ShipModel对应的Firgure。创建:DiagramModel.java。DiagramModel将作为所有ShipModel的父类容器。创建父类并不是GEF必须的,但这样做会带来方便。
|
package org.jport.gef.berth.model;
import org.jport.gef.berth.domain.ShipInfo;
public
class DiagramModel
extends BaseModel{
}
|
Figure是视图部分,即MVC的View部分。Gef的视图部分采用的是Draw2d,本文在前面简单的介绍过Draw2d。
创建ShipFigure.java,
|
package org.jport.gef.berth.figure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.ColorConstants;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Graphics;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Label;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.PositionConstants;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.RectangleFigure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.XYLayout;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.geometry.Rectangle;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Color;
import org.jport.gef.berth.util.ColorCache;
public
class ShipFigure
extends RectangleFigure {
// 位置第一列 标签
private Label shipNameCH =
new Label("船名:");
private Label shipNameCHValue =
new Label();
@Override
protected
void fillShape(Graphics graphics) {
super.fillShape(graphics);
drawBorders(graphics, bounds);
}
public ShipFigure() {
setLayoutManager(
new XYLayout());
setLocation(shipNameCH);
getLayoutManager().setConstraint(shipNameCH,
new Rectangle(5, 5, 80, 15));
add(shipNameCH);
setLocation(shipNameCHValue);
getLayoutManager().setConstraint(shipNameCHValue,
new Rectangle(85, 5, 100, 15));
add(shipNameCHValue);
}
private
void setLocation(Label label) {
//
TODO Auto-generated method stub
label.setTextAlignment(PositionConstants.
LEFT);
label.setLabelAlignment(PositionConstants.
LEFT);
label.setIconAlignment(PositionConstants.
LEFT);
label.setForegroundColor(ColorConstants.
blue);
}
private
static
void drawBorders(Graphics gc, Rectangle bounds) {
// 这里控制背景颜色
Color foreColor, backColor, borderColor;
foreColor = ColorCache.
tooltipBg[0];
backColor = ColorCache.
tooltipBg[1];
borderColor = ColorCache.
tooltipBg[2];
gc.setForegroundColor(foreColor);
gc.setBackgroundColor(backColor);
gc.fillGradient(bounds.x, bounds.y, bounds.width, bounds.height,
true);
// draw border
gc.setForegroundColor(borderColor);
gc.drawRectangle(bounds.x, bounds.y, bounds.width - 1,
bounds.height - 1);
}
}
|
这个类实现的图形是这样:
创建:DiagramFigure.java,这个类只是作为将来模型的背景。
|
package org.jport.gef.berth.figure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.ColorConstants;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Graphics;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Label;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.PositionConstants;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.RectangleFigure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.XYLayout;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.geometry.Rectangle;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Color;
import org.jport.gef.berth.util.ColorCache;
public
class DiagramFigure
extends RectangleFigure {
@Override
protected
void fillShape(Graphics graphics) {
super.fillShape(graphics);
drawBorders(graphics, bounds);
}
public DiagramFigure() {
setLayoutManager(
new XYLayout());
}
private
static
void drawBorders(Graphics gc, Rectangle bounds) {
// 这里控制背景颜色
Color foreColor, backColor, borderColor;
foreColor = ColorCache.
tooltipBg[0];
backColor = ColorCache.
tooltipBg[1];
borderColor = ColorCache.
tooltipBg[2];
gc.setForegroundColor(foreColor);
gc.setBackgroundColor(backColor);
gc.fillGradient(bounds.x, bounds.y, bounds.width, bounds.height,
true);
// draw border
gc.setForegroundColor(borderColor);
gc.drawRectangle(bounds.x, bounds.y, bounds.width - 1,
bounds.height - 1);
}
}
|
在前面我们创建了Model和Figure,但Model与Figure相互间还不认识对方。在MVC框架下,控制器是模型和视图之间的桥梁。
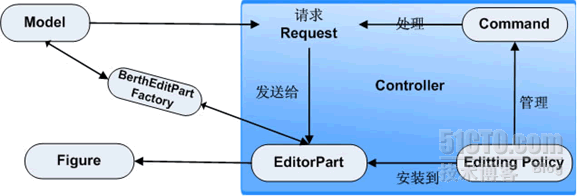
控制器的实现较为复杂,下图是控制器的结构图:
从图中可以看出Controller主要包括EidtorPart、Eidtting Policy、Commad三部分。GEF的处理流程大致如下:
Model在创建时,GEF通过BerthEditorPartFactory创建与Model对应的EditorPart。
|
public EditPart createEditPart(EditPart context, Object model) {
AbstractGraphicalEditPart part =
null;
if (model
instanceof DiagramModel) {
part =
new DiagramPart();
}
else
if (model
instanceof ShipModel) {
part =
new ShipPart();
}
part.setModel(model);
return part;
}
|
当模型发生改变时,GEF把模型改变装换为request并发送给EditorPart,EditorPart根据不同的Role类型,分发给安装的Editting Policy处理:
|
public
class ShipPart
extends AbstractEditPart{
@Override
protected
void createEditPolicies() {
installEditPolicy(EditPolicy.
LAYOUT_ROLE,
new BerthEditLayoutPolicy());
}
……
}
|
EditPolicy获得处理请求的事件后,就会根据request的类型,把请求分发给Command处理。
|
@Override
protected Command createChangeConstraintCommand(EditPart child, Object constraint) {
AbstractLayoutCommand command =
null;
if (child
instanceof ShipPart) {
command =
new ShipChangeLayoutCommand();
}
else
if(child
instanceof DiagramPart)
{
command =
new
DiagramChangeLayoutCommand();
}
command.setModel(child.getModel());
command.setConstraint((Rectangle)constraint);
return command;
}
|
在EditPolicy中对Command进行赋值后,Command就会执行:
|
public
class ShipChangeLayoutCommand
extends AbstractLayoutCommand {
……
public
void execute() {
this.model.setLayout(layout);
}
……
}
|
那么当Command执行后,怎么影响视图的改变呢?
Model发生改变后,就会发出FirePropertyChange事件,
|
public
void setLayout(Rectangle newLayout) {
Rectangle oldLayout =
this.layout;
this.layout = newLayout;
getListeners().firePropertyChange(
PROPERTY_LAYOUT, oldLayout, newLayout);
}
|
因为model对应的EditPart会在被激活时向model注册监听,
|
public
abstract
class AbstractEditPart
extends AbstractGraphicalEditPart
implements PropertyChangeListener {
public
void activate() {
super.activate();
((BaseModel) getModel()).addPropertyChangeListener(
this);
}
……
}
|
editorPart听到改变事件后,即可处理视图的改变:
|
public
class ShipPart
extends AbstractEditPart{
protected
void refreshVisuals(){
ShipFigure figure = (ShipFigure)getFigure();
ShipModel model = (ShipModel)getModel();
figure.setShipName(model.getShipInfo().getShipName());
figure.setLayout(model.getLayout());
}
public
void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent evt) {
if (evt.getPropertyName().equals(BaseModel.
PROPERTY_LAYOUT)) refreshVisuals();
……
}
|
在前面的几节中,创建了GEF应用所需的模型、视图、控制器,下一个问题:如何显示?创建“BerthGraphicalEditor.java”
|
package org.jport.gef.berth.ui;
……
public
class BerthGraphicalEditor
extends GraphicalEditor {
public
static
final String
ID = "org.jport.gef.berth.ui.BerthGraphicalEditor";
private DiagramModel model;
public BerthGraphicalEditor() {
setEditDomain(
new DefaultEditDomain(
this));
}
public
void doSave(IProgressMonitor monitor) {
}
public
void doSaveAs() {
}
public
boolean isDirty() {
return
false;
}
public
boolean isSaveAsAllowed() {
return
false;
}
public DiagramModel
createBusiness(){
DiagramModel diagramModel =
new DiagramModel();
ShipModel shipModel=
new ShipModel();
shipModel.setName("TestShipName");
shipModel.setLayout(
new Rectangle(30, 50, BerthConstants.
SHIP_LENGTH, BerthConstants.
SHIP_WIDTH));
diagramModel.addChild(shipModel);
return diagramModel;
}
protected
void initializeGraphicalViewer() {
GraphicalViewer viewer = getGraphicalViewer();
model =
createBusiness();
viewer.setContents(model);
}
protected
void configureGraphicalViewer() {
double[] zoomLevels;
super.configureGraphicalViewer();
GraphicalViewer viewer = getGraphicalViewer();
viewer.setEditPartFactory(
new AppEditPartFactory());
}
}
|
每个Editor都会对应一个EditorInput,用来初始化Editor。
在plugin.xml中,配置editor。
|
<extension
point="org.eclipse.ui.editors">
<editor
class="org.jport.gef.berth.ui.BerthGraphicalEditor"
contributorClass="org.jport.gef.warehouse.ui.
OverviewGraphicalEditorActionBarContributor"
default="true"
icon="
icons/sample.gif"
id="org.jport.gef.berth.ui.BerthGraphicalEditor"
name="泊位调度">
</editor>
</ extension >
|
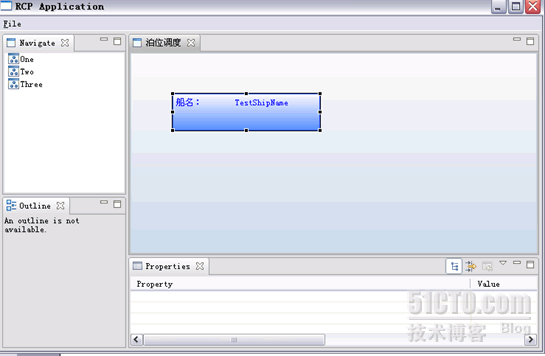
此时,在运行项目,可以得到下面的界面:
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/growup/551845






















 1135
1135











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








