在Java中并不存在引用传递(即地址传递),对于变量(可以是基本数据类型,也可以是引用数据类型)而言,可以理解为就是一个地址。传递,存在着拷贝操作。举个列子:
1、在方法参数上,传递的是基本数据类型。
定义了一个用于交换两个整型数的方法:
public static void swap(int a, int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
System.out.println("In swap: a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
}在main方法里初始化两个整型变量,并调用swap方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
System.out.println("Before swap: a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
swap(a, b);
System.out.println("After swap: a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
}
注:假设实参a为0x0001,实参b为0x0002。它们所指向的值分别为1和2。
输出结果为:
After swap: a = 1, b = 2
注:调用swap方法时,由于是值传递,所以可以假设形参a为0x0003,形参b为0x0004。这时实参a和b将自己所指向的值拷贝了一份。根据调用的方法参数列表与声明的方法参数列表一一对应的顺序,这时0x0003所指向的值是1,0x0004所指向的值是2。对应值传递这个概念,这时拷贝的是值1和2。
对于swap方法的作用是指将0x0003和0x0004所指向的值进行了交换。即0x0003所指向的值变成了2,而0x0004所指向的值变成了1。所以对于实参a和b来说并不受影响。 
如果真的存在引用传递的话,这时候形参的值是地址,即拷贝的是0x0001和0x0002。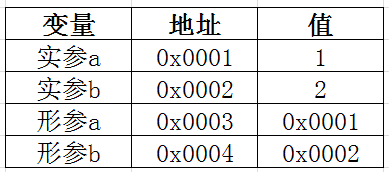
交换作用就会反映到实参a和b上。
2、在方法参数上,传递的是引用数据类型。
这里以Person类为例:
class Person {
private String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "My name is " + this.name + ".";
}
}public static void swap(Person c, Person d) {
Person temp = null;
temp = c;
c = d;
d = temp;
System.out.println("In swap: " + c + ", " + d);
}
在main方法里初始化两个Person类型的引用,并调用swap方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person c = new Person("c");
Person d = new Person("d");
System.out.println("对于引用数据类型");
System.out.println("Before swap: " + c + ", " + d);
swap(c, d);
System.out.println("After swap: " + c + ", " + d);
}
注:假设实参c为0x0001,实参d为0x0002。它们有各自引用的对象0x000c和0x000d。它们是对象在堆区里的存放地址。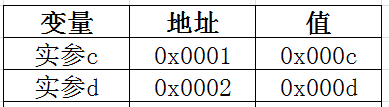
输出结果为:
对于引用数据类型
Before swap: My name is c., My name is d.
In swap: My name is d., My name is c.
After swap: My name is c., My name is d.
注:调用swap方法时,由于是值传递,所以可以假设形参c为0x0003,形参d为0x0004。根据调用的方法参数列表与声明的方法参数列表一一对应的顺序,这时形参c(0x0003)所引用的就是实参c(0x0001)所引用的对象, 形参d(0x0004)所引用的就是实参d(0x0002)所引用的对象 。 对应值传递这个概念,这时拷贝的是0x000c和0x000d。 
此时swap方法的作用是指将0x0003和0x0004对对象的引用进行了交换。
如果真的存在引用传递的话,这时候拷贝的是0x0001和0x0002。
交换作用就会反映到实参c和d上。
注:变量是存放在栈区的,而对象是存放在堆区的。
引用数据类型值传递的图解:
1、swap调用前:
2、调用swap的时候: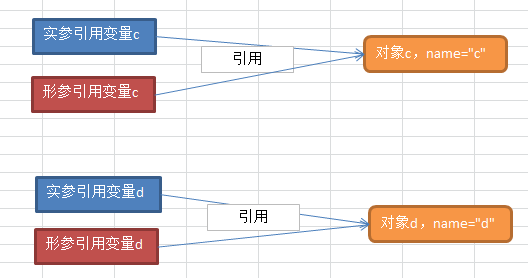
3、swap方法执行完后:
4、swap调用后:
完整的实例程序代码如下:
package com.test;
public class Test {
public static void swap(int a, int b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
System.out.println("In swap: a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
}
public static void swap(Person c, Person d) {
Person temp = null;
temp = c;
c = d;
d = temp;
System.out.println("In swap: " + c + ", " + d);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
Person c = new Person("c");
Person d = new Person("d");
System.out.println("对于基本数据类型");
System.out.println("Before swap: a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
swap(a, b);
System.out.println("After swap: a = " + a + ", b = " + b);
System.out.println("对于引用数据类型");
System.out.println("Before swap: " + c + ", " + d);
swap(c, d);
System.out.println("After swap: " + c + ", " + d);
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "My name is " + this.name + ".";
}
}总结:
1、Java中只存在值传递,并不存在引用传递。
2、若形参引用修改了所引用的对象的状态,则也会反映到实参引用上。























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








