Axis2可以通过模块(Module)进行扩展。Axis2模块至少需要有两个类,这两个类分别实现了Module和Handler接口。开发和使用一个Axis2模块的步骤如下:
1. 编写实现Module接口的类。Axis2模块在进行初始化、销毁等动作时会调用该类中相应的方法)。
2. 编写实现Handler接口的类。该类是Axis2模块的业务处理类。
3. 编写module.xml文件。该文件放在META-INF目录中,用于配置Axis2模块。
4. 在axis2.xml文件中配置Axis2模块。
5. 在services.xml文件中配置Axis2模块。每一个Axis2模块都需要使用<module>元素引用才能使用。
6. 发布Axis2模块。需要使用jar命令将Axis2模块压缩成.mar包(文件扩展名必须是.mar),然后将.mar文件放在
<Tomcat安装目录>\webapps\axis2\WEB-INF\modules目录中。
先来编写一个WebService类,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
package service;
public class MyService{
public String getGreeting(String name){
return "您好 " + name;
}
}
|
下面我们来编写一个记录请求和响应SOAP消息的Axis2模块。当客户端调用WebService方法时,该Axis2模块会将请求和响应SOAP消息输出到Tomcat控制台上。
第1步:编写LoggingModule类
LoggingModule类实现了Module接口,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
package module;
import org.apache.axis2.AxisFault;
import org.apache.axis2.context.ConfigurationContext;
import org.apache.axis2.description.AxisDescription;
import org.apache.axis2.description.AxisModule;
import org.apache.axis2.modules.Module;
import org.apache.neethi.Assertion;
import org.apache.neethi.Policy;
public class LoggingModule implements Module {
// initialize the module
public void init(ConfigurationContext configContext, AxisModule module)
throws AxisFault {
System.out.println("init");
}
public void engageNotify(AxisDescription ad) throws AxisFault {
}
// shutdown the module
public void shutdown(ConfigurationContext cc)
throws AxisFault {
System.out.println("shutdown");
}
public String[] getPolicyNamespaces() {
return null;
}
public void applyPolicy(Policy policy, AxisDescription ad)
throws AxisFault {
}
public boolean canSupportAssertion(Assertion assertion) {
return true;
}
}
|
在本例中LoggingModule类并没实现实际的功能,但该类必须存在。当Tomcat启动时会装载该Axis2模块,同时会调用LoggingModule类的init方法,并在Tomcat控制台中输出“init”。
第2步:编写LogHandler类
LogHandler类实现了Handler接口,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
package module;
import org.apache.axis2.AxisFault;
import org.apache.axis2.context.MessageContext;
import org.apache.axis2.engine.Handler;
import org.apache.axis2.handlers.AbstractHandler;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
public class LogHandler extends AbstractHandler implements Handler {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(LogHandler.class);
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public InvocationResponse invoke(MessageContext msgContext)
throws AxisFault {
// 向Tomcat控制台输出请求和响应SOAP消息
log.info(msgContext.getEnvelope().toString());
return InvocationResponse.CONTINUE;
}
public void revoke(MessageContext msgContext) {
log.info(msgContext.getEnvelope().toString());
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
|
LogHandler类的核心方法是invoke,当使用该Axis2模块的WebService的方法被调用时,LogHandler类的invoke方法被调用。
第3步:编写module.xml文件
在META-INF目录中建立一个module.xml文件,内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
<module name="logging" class="module.LoggingModule">
<InFlow>
<handler name="InFlowLogHandler" class="module.LogHandler">
<order phase="loggingPhase"/>
</handler>
</InFlow>
<OutFlow>
<handler name="OutFlowLogHandler" class="module.LogHandler">
<order phase="loggingPhase"/>
</handler>
</OutFlow>
<OutFaultFlow>
<handler name="FaultOutFlowLogHandler" class="module.LogHandler">
<order phase="loggingPhase"/>
</handler>
</OutFaultFlow>
<InFaultFlow>
<handler name="FaultInFlowLogHandler" class="module.LogHandler">
<order phase="loggingPhase"/>
</handler>
</InFaultFlow>
</module>
|
第4步:在axis2.xml文件中配置Axis2模块
打开axis2.xml文件,分别在如下四个<phaseOrder>元素中加入<phasename="loggingPhase"/>:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
<phaseOrder type="InFlow">
<phase name="soapmonitorPhase"/>
<phase name="loggingPhase"/>
</phaseOrder>
<phaseOrder type="OutFlow">
<!--相关代码略-->
<phase name="Security"/>
<phase name="loggingPhase"/>
</phaseOrder>
<phaseOrder type="InFaultFlow">
<!--相关代码略-->
<phase name="soapmonitorPhase"/>
<phase name="loggingPhase"/>
</phaseOrder>
<phaseOrder type="OutFaultFlow">
<!--相关代码略-->
<phase name="Security"/>
<phase name="loggingPhase"/>
</phaseOrder>
|
第5步:在services.xml文件中引用logging模块
services.xml文件的内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<service name="myService">
<description>
使用logging模块
</description>
<!-- 引用logging模块 -->
<module ref="logging"/>
<parameter name="ServiceClass">
service.MyService
</parameter>
<messageReceivers>
<messageReceiver mep="http://www.w3.org/2004/08/wsdl/in-out"
class="org.apache.axis2.rpc.receivers.RPCMessageReceiver" />
</messageReceivers>
</service>
|
第6步:发布logging模块
到现在为止,我们应用可以建立两个发行包:logging.mar和service.aar。其中logging.mar文件是Axis2模块的发行包,该包的目录结构如下:
logging.mar
module\LoggingModule.class
module\LogHandler.class
META-INF\module.xml
service.aar文件是本例编写的WebService发行包,该包的目录结构如下:
service.aar
service\MyService.class
META-INF\services.xml
将logging.mar文件放在<Tomcat安装目录>\webapps\axis2\WEB-INF\modules目录中,将service.aar文件放在<Tomcat安装目录>\webapps\axis2\WEB-INF\services目录中。要注意的是,如果modules目录中包含了modules.list文件,Axis2会只装载在该文件中引用的Axis2模块,因此,必须在该文件中引用logging模块,该文件的内容如下:
addressing-1.4.1.mar
soapmonitor-1.4.1.mar
ping-1.4.1.mar
mex-1.4.1.mar
axis2-scripting-1.4.1.mar
logging.mar
如果modules目录中不包含modules.list文件,则Axis2会装载modules文件中的所有Axis2模块。
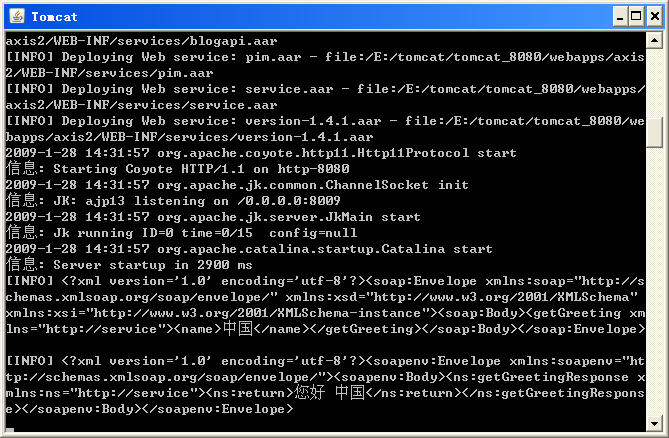
现在启动Tomcat,使用如下的C#代码调用MyService的getGreeting方法则会在Tomcat控制台中输出相应的请求和响应SOAP消息。
|
1
2
3
4
|
// async是引用MyService的服务名
async.myService my = new WSC.asyn.myService();
MessageBox.Show(my.getGreeting("中国"));
MessageBox.Show("完成调用");
|
在执行上面的代码后,在Tomcat控制台中输出的信息如下图所示。






















 5386
5386

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








