Spring中的标签包括默认标签和自定义标签两种。默认标签的解析是在parseDefaultElement函数中进行的,分别对4种不同标签(import、alias、bean和beans)做了不同的处理。
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//import标签的处理
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
//alias标签的处理
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
//bean标签的处理
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
//beans标签的处理
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}1.bean标签的解析及注册
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//parseBeanDefinitionElement进行元素解析
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
//解析自定义节点
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance. 注册bdHolder
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.发出响应事件,通知相关的监听
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}大致的逻辑总结如下:
- 首先委托BeanDefinitionDelegate类的parseBeanDefinitionElement方法进行元素解析,返回BeanDefinitionHolder的实例bdHolder。
- 返回的bdHolder不为空的情况下若存在默认标签的子节点下再有自定义属性,还需要再次对自定义标签进行解析
- 解析完成后,需要对解析后的bdHolder进行注册。注册操作委托给了BeanDefinitionReaderUtils的registerBeanDefinition方法。
- 最后发出响应事件,通知相关的监听器,这个bean已经加载完了。
时序图
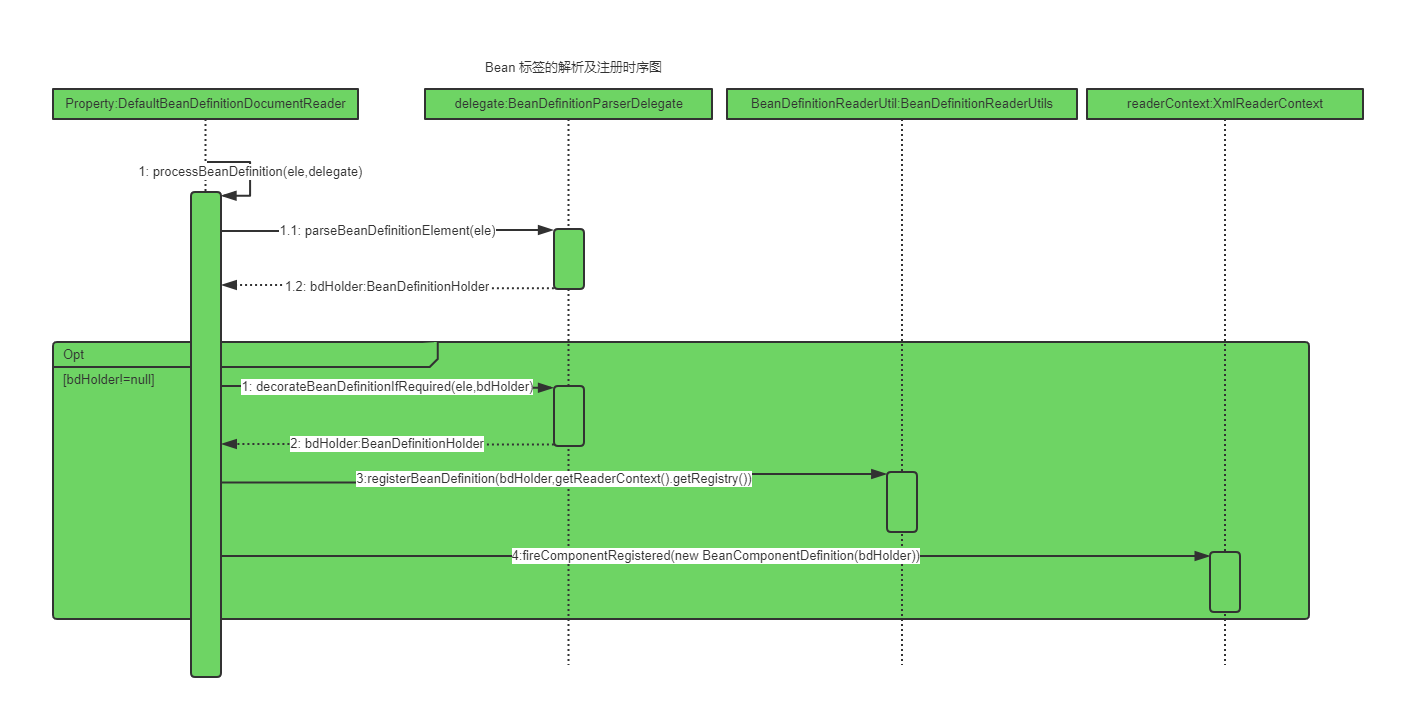
1.解析BeanDefinition
@Nullable
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//解析id属性
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
//解析name属性
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
//分割name属性
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
//如果不存在beanName那么根据Spring中提供的命名规则为当前bean生成对应的beanName
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}在当前层完成的主要工作包括如下内容
- 提取元素的id以及name属性
- 进一步解析其他所有属性并统一封装GenericBeanDefinition类型的实例中
- 如果检测到bean没有指定beanName,name使用默认规则为此Bean生成beanName。
- 将获取到的其他信息封装到BeanDefinitionHolder的实例中
进一步查看步骤(2)其他属性的解析过程
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
//解析class属性
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
//解析parent属性
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
try {
//创建用于承载属性的AbastractBeanDefinition类型的GenericBeanDefinition
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
//硬编码解析默认bean的各种属性
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
//提取description
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
//解析元数据
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
//解析lookup-method属性
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析构造函数参数
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析property子元素
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
//解析qualifier子元素
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}1.创建用于属性承载的BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition是一个接口,在Spring中存在三种实现:RootBeanDefinition、ChildBeanDefinition已经GenericBeanDefinition。父<bean>和子<bean>分别用RootBeanDefinition、ChildBeanDefinition表示,没有父<bean>就使用RootBeanDefinition表示。GenericBeanDefinition是2.5版本后引入的一站式服务类。
protected AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(@Nullable String className, @Nullable String parentName)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
return BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.createBeanDefinition(
parentName, className, this.readerContext.getBeanClassLoader());
}
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(
@Nullable String parentName, @Nullable String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition();
bd.setParentName(parentName);
if (className != null) {
if (classLoader != null) {
//如果classLoader不为空,则使用已传入的classLoader同一虚拟机加载类对象,否则只是记录className
bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader));
}
else {
bd.setBeanClassName(className);
}
}
return bd;
}
2.解析各种属性
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(Element ele, String beanName,
@Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean, AbstractBeanDefinition bd) {
//singleton属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(SINGLETON_ATTRIBUTE)) {
error("Old 1.x 'singleton' attribute in use - upgrade to 'scope' declaration", ele);
}
//scope属性
else if (ele.hasAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setScope(ele.getAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE));
}
else if (containingBean != null) {
// Take default from containing bean in case of an inner bean definition.
//在嵌入beanDifinition情况下且没有单独指定scope属性则使用父类默认的属性
bd.setScope(containingBean.getScope());
}
//abstract属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setAbstract(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE)));
}
//lazy-init属性
String lazyInit = ele.getAttribute(LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isDefaultValue(lazyInit)) {
lazyInit = this.defaults.getLazyInit();
}
//如果没有设置或者设置成其他字符都会被设置为false
bd.setLazyInit(TRUE_VALUE.equals(lazyInit));
//autowire属性
String autowire = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setAutowireMode(getAutowireMode(autowire));
//depends-on属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String dependsOn = ele.getAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setDependsOn(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(dependsOn, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS));
}
//autowire_candidate属性
String autowireCandidate = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isDefaultValue(autowireCandidate)) {
String candidatePattern = this.defaults.getAutowireCandidates();
if (candidatePattern != null) {
String[] patterns = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(candidatePattern);
bd.setAutowireCandidate(PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(patterns, beanName));
}
}
else {
bd.setAutowireCandidate(TRUE_VALUE.equals(autowireCandidate));
}
//primary属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setPrimary(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE)));
}
//init-method属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String initMethodName = ele.getAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setInitMethodName(initMethodName);
}
else if (this.defaults.getInitMethod() != null) {
bd.setInitMethodName(this.defaults.getInitMethod());
bd.setEnforceInitMethod(false);
}
//destory-method属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String destroyMethodName = ele.getAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName);
}
else if (this.defaults.getDestroyMethod() != null) {
bd.setDestroyMethodName(this.defaults.getDestroyMethod());
bd.setEnforceDestroyMethod(false);
}
//factory-method属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setFactoryMethodName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE));
}
//factory-bean属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setFactoryBeanName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE));
}
return bd;
}
3.解析子元素meta
元素meta的使用
<bean id="myTestBean" class="bean.MyTestBean">
<meta key="testStr" value="aaaaaa" />
</bean>当需要使用里面的信息的时候可以通过BeanDefinition的getAttribute(key)方法进行获取
public void parseMetaElements(Element ele, BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor attributeAccessor) {
//获取当前节点的所有子元素
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
//提取meta
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) {
Element metaElement = (Element) node;
String key = metaElement.getAttribute(KEY_ATTRIBUTE);
String value = metaElement.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
BeanMetadataAttribute attribute = new BeanMetadataAttribute(key, value);
attribute.setSource(extractSource(metaElement));
attributeAccessor.addMetadataAttribute(attribute);
}
}
}
4.解析子元素lookup-method
public void parseLookupOverrideSubElements(Element beanEle, MethodOverrides overrides) {
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
//仅当在Spring默认bean的子元素下且为<lookup-method时有效
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, LOOKUP_METHOD_ELEMENT)) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
//获取要修饰的方法
String methodName = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
//获取配置返回的bean
String beanRef = ele.getAttribute(BEAN_ELEMENT);
LookupOverride override = new LookupOverride(methodName, beanRef);
override.setSource(extractSource(ele));
overrides.addOverride(override);
}
}
}
5.解析子元素replaced-method
public void parseReplacedMethodSubElements(Element beanEle, MethodOverrides overrides) {
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
//仅当在Spring默认bean的子元素下且为<replaced-method时有效
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, REPLACED_METHOD_ELEMENT)) {
Element replacedMethodEle = (Element) node;
//提取要替换的旧的方法
String name = replacedMethodEle.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
//提取对应的新的替换方法
String callback = replacedMethodEle.getAttribute(REPLACER_ATTRIBUTE);
ReplaceOverride replaceOverride = new ReplaceOverride(name, callback);
// Look for arg-type match elements.
List<Element> argTypeEles = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(replacedMethodEle, ARG_TYPE_ELEMENT);
for (Element argTypeEle : argTypeEles) {
//记录参数
String match = argTypeEle.getAttribute(ARG_TYPE_MATCH_ATTRIBUTE);
match = (StringUtils.hasText(match) ? match : DomUtils.getTextValue(argTypeEle));
if (StringUtils.hasText(match)) {
replaceOverride.addTypeIdentifier(match);
}
}
replaceOverride.setSource(extractSource(replacedMethodEle));
overrides.addOverride(replaceOverride);
}
}
}
6.解析子元素constructor-arg
public void parseConstructorArgElements(Element beanEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, CONSTRUCTOR_ARG_ELEMENT)) {
parseConstructorArgElement((Element) node, bd);
}
}
}
public void parseConstructorArgElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) {
//提取index属性
String indexAttr = ele.getAttribute(INDEX_ATTRIBUTE);
//提取type属性
String typeAttr = ele.getAttribute(TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
//提取name属性
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(indexAttr)) {
try {
int index = Integer.parseInt(indexAttr);
if (index < 0) {
error("'index' cannot be lower than 0", ele);
}
else {
try {
this.parseState.push(new ConstructorArgumentEntry(index));
//解析ele对应的属性元素
Object value = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, null);
ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder valueHolder = new ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder(value);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(typeAttr)) {
valueHolder.setType(typeAttr);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
valueHolder.setName(nameAttr);
}
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
//不允许重复指定相同参数
if (bd.getConstructorArgumentValues().hasIndexedArgumentValue(index)) {
error("Ambiguous constructor-arg entries for index " + index, ele);
}
else {
bd.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(index, valueHolder);
}
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
}
catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
error("Attribute 'index' of tag 'constructor-arg' must be an integer", ele);
}
}
else {
//没有index属性则忽略去属性,自动寻找
try {
this.parseState.push(new ConstructorArgumentEntry());
Object value = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, null);
ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder valueHolder = new ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder(value);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(typeAttr)) {
valueHolder.setType(typeAttr);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
valueHolder.setName(nameAttr);
}
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
bd.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(valueHolder);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
}
- 解析constructor-arg的子元素
- ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder类型来封装解析出来的元素
- 将type、index、name一并封装在ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder类型中并添加至当前BeanDefinition的constructorArgumentValues的indexedArgumentValues,如果index没有指定genericArgumentValues
public Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String propertyName) {
String elementName = (propertyName != null ?
"<property> element for property '" + propertyName + "'" :
"<constructor-arg> element");
// Should only have one child element: ref, value, list, etc.
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();
Element subElement = null;
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
//对应description和meta不处理
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT) &&
!nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) {
// Child element is what we're looking for.
if (subElement != null) {
error(elementName + " must not contain more than one sub-element", ele);
}
else {
subElement = (Element) node;
}
}
}
//解析constructor-arg上的ref属性
boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
//解析constructor-arg上的value属性
boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
if ((hasRefAttribute && hasValueAttribute) ||
((hasRefAttribute || hasValueAttribute) && subElement != null)) {
/**
* 在constructor-arg上不存在
* 1.同时既有ref属性又有value属性
* 2.存在ref属性或者value属性且又有子元素
*/
error(elementName +
" is only allowed to contain either 'ref' attribute OR 'value' attribute OR sub-element", ele);
}
if (hasRefAttribute) {
//ref属性的处理,使用RuntimeBeanReference封装对应的ref名称
String refName = ele.getAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error(elementName + " contains empty 'ref' attribute", ele);
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
else if (hasValueAttribute) {
//value属性的处理,使用TypedStringValue封装
TypedStringValue valueHolder = new TypedStringValue(ele.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE));
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return valueHolder;
}
else if (subElement != null) {
//解析子元素
return parsePropertySubElement(subElement, bd);
}
else {
// Neither child element nor "ref" or "value" attribute found.
error(elementName + " must specify a ref or value", ele);
return null;
}
}
- 略过description或者meta
- 提取constructor-arg上的ref和value属性,以便于根据规则验证正确性,其规则未在constructor-arg上不存在一下情况。
- ref属性的处理。使用RuntimeBeanReference封装对应的ref名称。
- value属性的处理。使用TypedStringValue封装
- 子元素的处理。
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition bd) {
return parsePropertySubElement(ele, bd, null);
}
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String defaultValueType) {
if (!isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
return parseNestedCustomElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder nestedBd = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, bd);
if (nestedBd != null) {
nestedBd = decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, nestedBd, bd);
}
return nestedBd;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, REF_ELEMENT)) {
// A generic reference to any name of any bean.
String refName = ele.getAttribute(BEAN_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean toParent = false;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
// A reference to the id of another bean in a parent context.
//解析parent
refName = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
toParent = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
error("'bean' or 'parent' is required for <ref> element", ele);
return null;
}
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error("<ref> element contains empty target attribute", ele);
return null;
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName, toParent);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
//对idref解析
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, IDREF_ELEMENT)) {
return parseIdRefElement(ele);
}
//对value子元素的解析
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, VALUE_ELEMENT)) {
return parseValueElement(ele, defaultValueType);
}
//对null子元素的解析
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, NULL_ELEMENT)) {
// It's a distinguished null value. Let's wrap it in a TypedStringValue
// object in order to preserve the source location.
TypedStringValue nullHolder = new TypedStringValue(null);
nullHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return nullHolder;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, ARRAY_ELEMENT)) {
//解析array子元素
return parseArrayElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, LIST_ELEMENT)) {
//解析list子元素
return parseListElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, SET_ELEMENT)) {
//解析set子元素
return parseSetElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, MAP_ELEMENT)) {
//解析map子元素
return parseMapElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, PROPS_ELEMENT)) {
//解析props子元素
return parsePropsElement(ele);
}
else {
error("Unknown property sub-element: [" + ele.getNodeName() + "]", ele);
return null;
}
}
7.解析子元素property
public void parsePropertyElements(Element beanEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, PROPERTY_ELEMENT)) {
parsePropertyElement((Element) node, bd);
}
}
}
public void parsePropertyElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) {
//获取配置元素中name的值
String propertyName = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(propertyName)) {
error("Tag 'property' must have a 'name' attribute", ele);
return;
}
this.parseState.push(new PropertyEntry(propertyName));
try {
//不允许多次对同一属性配置
if (bd.getPropertyValues().contains(propertyName)) {
error("Multiple 'property' definitions for property '" + propertyName + "'", ele);
return;
}
Object val = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, propertyName);
PropertyValue pv = new PropertyValue(propertyName, val);
parseMetaElements(ele, pv);
pv.setSource(extractSource(ele));
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(pv);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
8.解析子元素qualifier
public void parseQualifierElements(Element beanEle, AbstractBeanDefinition bd) {
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, QUALIFIER_ELEMENT)) {
parseQualifierElement((Element) node, bd);
}
}
}
public void parseQualifierElement(Element ele, AbstractBeanDefinition bd) {
String typeName = ele.getAttribute(TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(typeName)) {
error("Tag 'qualifier' must have a 'type' attribute", ele);
return;
}
this.parseState.push(new QualifierEntry(typeName));
try {
AutowireCandidateQualifier qualifier = new AutowireCandidateQualifier(typeName);
qualifier.setSource(extractSource(ele));
String value = ele.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(value)) {
qualifier.setAttribute(AutowireCandidateQualifier.VALUE_KEY, value);
}
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, QUALIFIER_ATTRIBUTE_ELEMENT)) {
Element attributeEle = (Element) node;
String attributeName = attributeEle.getAttribute(KEY_ATTRIBUTE);
String attributeValue = attributeEle.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(attributeName) && StringUtils.hasLength(attributeValue)) {
BeanMetadataAttribute attribute = new BeanMetadataAttribute(attributeName, attributeValue);
attribute.setSource(extractSource(attributeEle));
qualifier.addMetadataAttribute(attribute);
}
else {
error("Qualifier 'attribute' tag must have a 'name' and 'value'", attributeEle);
return;
}
}
}
bd.addQualifier(qualifier);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
2.AbstractBeanDefinition属性
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinition extends BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor
implements BeanDefinition, Cloneable {
/**
* Constant for the default scope name: {@code ""}, equivalent to singleton
* status unless overridden from a parent bean definition (if applicable).
*/
public static final String SCOPE_DEFAULT = "";
/**
* Constant that indicates no autowiring at all.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_NO = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_NO;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring bean properties by name.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring bean properties by type.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring a constructor.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR;
/**
* Constant that indicates determining an appropriate autowire strategy
* through introspection of the bean class.
* @see #setAutowireMode
* @deprecated as of Spring 3.0: If you are using mixed autowiring strategies,
* use annotation-based autowiring for clearer demarcation of autowiring needs.
*/
@Deprecated
public static final int AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT;
/**
* Constant that indicates no dependency check at all.
* @see #setDependencyCheck
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE = 0;
/**
* Constant that indicates dependency checking for object references.
* @see #setDependencyCheck
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_OBJECTS = 1;
/**
* Constant that indicates dependency checking for "simple" properties.
* @see #setDependencyCheck
* @see org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils#isSimpleProperty
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_SIMPLE = 2;
/**
* Constant that indicates dependency checking for all properties
* (object references as well as "simple" properties).
* @see #setDependencyCheck
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ALL = 3;
/**
* Constant that indicates the container should attempt to infer the
* {@link #setDestroyMethodName destroy method name} for a bean as opposed to
* explicit specification of a method name. The value {@value} is specifically
* designed to include characters otherwise illegal in a method name, ensuring
* no possibility of collisions with legitimately named methods having the same
* name.
* <p>Currently, the method names detected during destroy method inference
* are "close" and "shutdown", if present on the specific bean class.
*/
public static final String INFER_METHOD = "(inferred)";
@Nullable
private volatile Object beanClass;
@Nullable
private String scope = SCOPE_DEFAULT;
private boolean abstractFlag = false;
private boolean lazyInit = false;
private int autowireMode = AUTOWIRE_NO;
private int dependencyCheck = DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE;
@Nullable
private String[] dependsOn;
private boolean autowireCandidate = true;
private boolean primary = false;
private final Map<String, AutowireCandidateQualifier> qualifiers = new LinkedHashMap<>();
@Nullable
private Supplier<?> instanceSupplier;
private boolean nonPublicAccessAllowed = true;
private boolean lenientConstructorResolution = true;
@Nullable
private String factoryBeanName;
@Nullable
private String factoryMethodName;
@Nullable
private ConstructorArgumentValues constructorArgumentValues;
@Nullable
private MutablePropertyValues propertyValues;
@Nullable
private MethodOverrides methodOverrides;
@Nullable
private String initMethodName;
@Nullable
private String destroyMethodName;
private boolean enforceInitMethod = true;
private boolean enforceDestroyMethod = true;
private boolean synthetic = false;
private int role = BeanDefinition.ROLE_APPLICATION;
@Nullable
private String description;
@Nullable
private Resource resource;
3.解析默认标签中的自定义标签元素
public BeanDefinitionHolder decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(
Element ele, BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) {
BeanDefinitionHolder finalDefinition = definitionHolder;
// Decorate based on custom attributes first.
NamedNodeMap attributes = ele.getAttributes();
//遍历所有的属性,看看是否有适用于修饰的属性
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = attributes.item(i);
finalDefinition = decorateIfRequired(node, finalDefinition, containingBd);
}
// Decorate based on custom nested elements.
NodeList children = ele.getChildNodes();
//遍历所有的子节点,看看是否适用于修饰的子元素
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = children.item(i);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
finalDefinition = decorateIfRequired(node, finalDefinition, containingBd);
}
}
return finalDefinition;
}
public BeanDefinitionHolder decorateIfRequired(
Node node, BeanDefinitionHolder originalDef, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) {
//获取自定义标签的命名空间
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(node);
//对于非默认标签进行修饰
if (namespaceUri != null && !isDefaultNamespace(namespaceUri)) {
//根据命名空间找到对应的处理器
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler != null) {
//进行修饰
BeanDefinitionHolder decorated =
handler.decorate(node, originalDef, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
if (decorated != null) {
return decorated;
}
}
else if (namespaceUri.startsWith("http://www.springframework.org/")) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", node);
}
else {
// A custom namespace, not to be handled by Spring - maybe "xml:...".
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No Spring NamespaceHandler found for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]");
}
}
}
return originalDef;
}
4.注册解析的BeanDefinition
1.通过beanName注册BeanDefinition
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
/**
* 注册前的最后一次校验,这里的校验不同于之前的XML文件校验
* 主要是对于AbstractBeanDefinition属性中的methodOverrides校验
* 校验methodOverrides是否与工厂方法并存或者methodOverrides对应的方法根本不存在
*/
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
//如果对应的beanName已经注册且在配置中配置了bean不允许被覆盖,则抛出异常
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
//重置所有beanName对应的缓存
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}
- 对AbstractBeanDefinition的校验。
- 对beanName已经注册的情况的处理。如果设置了不允许bean的覆盖,则需要抛出异常,否则直接覆盖
- 加入map缓存
- 清除解析之前留下的对应beanName缓存
2.通过别名注册BeanDefinition
@Override
public void registerAlias(String name, String alias) {
Assert.hasText(name, "'name' must not be empty");
Assert.hasText(alias, "'alias' must not be empty");
synchronized (this.aliasMap) {
//如果beanName与alias相同的话不吉利alias,并删除对应的alias
if (alias.equals(name)) {
this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Alias definition '" + alias + "' ignored since it points to same name");
}
}
else {
String registeredName = this.aliasMap.get(alias);
if (registeredName != null) {
if (registeredName.equals(name)) {
// An existing alias - no need to re-register
return;
}
//如果alias不允许被覆盖则抛出异常
if (!allowAliasOverriding()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot define alias '" + alias + "' for name '" +
name + "': It is already registered for name '" + registeredName + "'.");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding alias '" + alias + "' definition for registered name '" +
registeredName + "' with new target name '" + name + "'");
}
}
//档A->B存在时,若再次出现A->C->B时候则会抛出异常
checkForAliasCircle(name, alias);
this.aliasMap.put(alias, name);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Alias definition '" + alias + "' registered for name '" + name + "'");
}
}
}
}
- alias与beanName相同情况处理。若alias与beanName并名称相同则不需要处理并删除掉原有alias。
- alias覆盖处理。若aliasName已经使用并已经指向了另一beanName则需要用户的设置进行处理。
- alias循环检查。当A->B存在时,若再次出现A->C->B时候则会抛出异常。
- 注册alias。
5.通知监听器解析及注册完成
默认Spring中并没有对此事件做任何逻辑处理。
2.alias标签的解析
protected void processAliasRegistration(Element ele) {
//获取beanName
String name = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
//获取alias
String alias = ele.getAttribute(ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean valid = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
getReaderContext().error("Name must not be empty", ele);
valid = false;
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(alias)) {
getReaderContext().error("Alias must not be empty", ele);
valid = false;
}
if (valid) {
try {
//注册alias
getReaderContext().getRegistry().registerAlias(name, alias);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register alias '" + alias +
"' for bean with name '" + name + "'", ele, ex);
}
//别名注册后通知监听器做相应处理
getReaderContext().fireAliasRegistered(name, alias, extractSource(ele));
}
}
3.import标签的解析
protected void importBeanDefinitionResource(Element ele) {
//获取resource属性
String location = ele.getAttribute(RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE);
//如果不存在resource属性不作任何处理
if (!StringUtils.hasText(location)) {
getReaderContext().error("Resource location must not be empty", ele);
return;
}
// Resolve system properties: e.g. "${user.dir}"
location = getReaderContext().getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location);
Set<Resource> actualResources = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
// Discover whether the location is an absolute or relative URI
boolean absoluteLocation = false;
try {
absoluteLocation = ResourcePatternUtils.isUrl(location) || ResourceUtils.toURI(location).isAbsolute();
}
catch (URISyntaxException ex) {
// cannot convert to an URI, considering the location relative
// unless it is the well-known Spring prefix "classpath*:"
}
// Absolute or relative?
//如果是绝对URI则直接根据地质加载对应的配置文件
if (absoluteLocation) {
try {
int importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(location, actualResources);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]");
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error(
"Failed to import bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]", ele, ex);
}
}
else {
// No URL -> considering resource location as relative to the current file.
try {
int importCount;
//Resuorce存在多个子实现类,而每个resource的createRelative实现方式不一样,所以这里先使用子类的方法尝试解析
Resource relativeResource = getReaderContext().getResource().createRelative(location);
if (relativeResource.exists()) {
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(relativeResource);
actualResources.add(relativeResource);
}
else {
//如果解析不成功,则使用默认的解析器ResourcePatternResolver进行解析
String baseLocation = getReaderContext().getResource().getURL().toString();
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(
StringUtils.applyRelativePath(baseLocation, location), actualResources);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]");
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to resolve current resource location", ele, ex);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error(
"Failed to import bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]", ele, ex);
}
}
//解析后进行监听器激活处理
Resource[] actResArray = actualResources.toArray(new Resource[0]);
getReaderContext().fireImportProcessed(location, actResArray, extractSource(ele));
}






















 597
597











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








