【2014/10/12 21:40】文章待续~
1.函数自身捕获处理异常的情况
以下的样例介绍了try~catch语句中出现异常时语句的运行顺序:
package month10;
import java.lang.*;
public class TryCatch{
/*
* 函数产生一个ArithmeticException异常
*/
public static void First(){
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例");
try{
//double m=5.0/0; 在java中,浮点数double和float能够除0。返回无穷大
int m=5/0;
System.out.println(m+"第一个函数不会继续执行了");
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("第一个函数捕获了异常");
}
finally{
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
/*
* 函数产生一个OutIndexOfException异常
*/
public static void Second(){
System.out.println("第二个异常处理的样例");
int[] arr=new int[3];
try{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
arr[i]=i;
}
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("第二个函数捕获了异常");
}
finally{
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("程序执行開始");
First();
Second();
System.out.println("程序执行结束");
}
}
运行的结果例如以下:
2. 函数自身不处理异常,抛出异常,直接外层函数处理
try抛出了异常。try语句块中抛出异常之后的语句不会再被运行。
package month10;
import java.lang.*;
public class TryCatch{
/*
* 函数产生一个ArithmeticException异常
*/
public void First(){
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例");
try{
//double m=5.0/0; 在java中,浮点数double和float能够除0,返回无穷大
int m=5/0;
System.out.println(m+"第一个函数不会继续执行了");
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){
//throw用在程序中明白表示这里抛出一个异常。 后面跟一个异常对象(实例).
throw new ArithmeticException("ArithmeticException");
//后面不跟语句
}
finally{
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
/*
* 函数产生一个OutIndexOfException异常
*/
public void Second(){
System.out.println("第二个异常处理的样例");
int[] arr=new int[3];
try{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
arr[i]=i;
}
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
throw new ArithmeticException("ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException");
}
finally{
//上面的样例这里写的输出语句有错误
System.out.println("第二个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
/*
* 封装了First、Second
*/
public void Thrid(){
System.out.println("函数三将First/Second開始执行");
try{
First();
Second();
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("接受异常"+e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("函数三之后的语句");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("程序执行開始");
TryCatch temp=new TryCatch();
temp.Thrid();
System.out.println("程序执行结束");
}
}
函数的运行效果例如以下:
3.函数抛出异常,向上抛,外层函数处理
验证函数执行产生异常,外层函数既没有对异常进行捕获处理、亦没有声明抛出异常、异常信息是否会一直向上抛,直到被处理。
package month10;
import java.lang.*;
public class TryCatch{
/*
* 函数产生一个ArithmeticException异常
*/
public void First(){
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例");
try{
//double m=5.0/0; 在java中,浮点数double和float能够除0,返回无穷大
int m=5/0;
System.out.println(m+"第一个函数不会继续执行了");
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){
//throw用在程序中明白表示这里抛出一个异常。 后面跟一个异常对象(实例).
throw new ArithmeticException("ArithmeticException");
//后面不跟语句
}
finally{
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
/*
* 函数产生一个OutIndexOfException异常
*/
public void Second(){
System.out.println("第二个异常处理的样例");
int[] arr=new int[3];
try{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
arr[i]=i;
}
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
throw new ArithmeticException("ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException");
}
finally{
//上面的样例这里写的输出语句有错误
System.out.println("第二个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
/*
* 封装了First、Second,
* 函数对First、Second抛出的异常不进行处理
*/
public void Thrid(){
System.out.println("函数三将First/Second開始执行");
First();
Second();
System.out.println("函数三之后的语句");
}
/*
* 调用函数Thrid
*/
public void Four(){
try{
Thrid();
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("函数3没有进行异常抛出,可是函数1的异常会一直向上抛,直到被捕获");
}
System.out.println("函数4之后的语句");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("程序执行開始");
TryCatch temp=new TryCatch();
temp.Four();
System.out.println("程序执行结束");
}
}
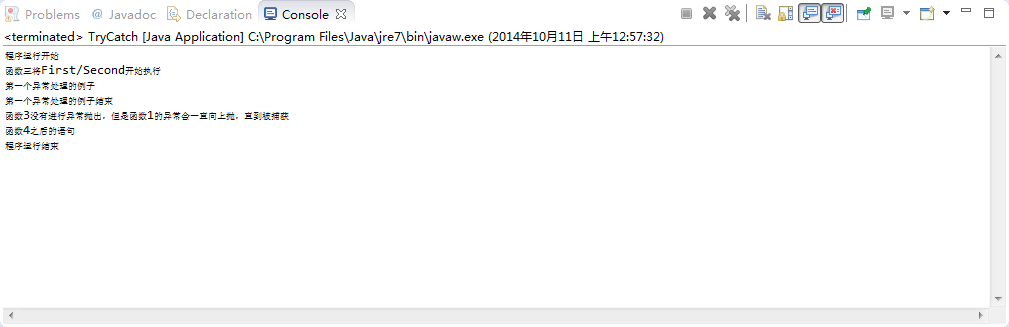
执行结果例如以下:
4.验证Checked Exception 是否也符合
上面的样例都验证的是执行时异常。不能全然说明问题。如今,验证Checked Exception。
:函数产生异常,若由函数调用者来捕获处理异常,继续之后的程序代码运行;若产生异常未捕获,异常会沿着调用栈下移,一直找到与之匹配的处理方法,若被处理。从处理的地方開始运行之后的代码;若到达调用栈底仍未找到,程序终止。
加入了CExce()函数,用于生产FileNotFoundException异常。
大家差分吧。
package month10;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.*;
public class TryCatch{
/*
* 函数产生一个ArithmeticException异常
*/
public void First(){
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例");
try{
//double m=5.0/0; 在java中,浮点数double和float能够除0。返回无穷大
int m=5/0;
System.out.println(m+"第一个函数不会继续执行了");
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){
//throw用在程序中明白表示这里抛出一个异常。 后面跟一个异常对象(实例).
throw new ArithmeticException("ArithmeticException");
//后面不跟语句
}
finally{
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
/*
* 函数产生一个OutIndexOfException异常
*/
public void Second(){
System.out.println("第二个异常处理的样例");
int[] arr=new int[3];
try{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
arr[i]=i;
}
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
throw new ArithmeticException("ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException");
}
finally{
//上面的样例这里写的输出语句有错误
System.out.println("第二个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
/*
* 封装了First、Second,
* 函数对First、Second抛出的异常不进行处理
* 加入了CExce()函数
*/
public void Thrid(){
System.out.println("函数三将CExce/First/Second開始执行");
CExce();
First();
Second();
System.out.println("函数三之后的语句");
}
/*
* 调用函数Thrid
*/
public void Four(){
try{
Thrid();
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("函数3没有进行异常抛出。此时Checked Exception异常函数Cexce的异常自己捕获处理了异常。此时捕获First的异常");
}
System.out.println("函数4之后的语句");
}
/*
*
*/
public void CExce(){
FileInputStream fis=null;
FileOutputStream fos=null;
try{
//目录下没有这个文件,会产生FileNoFoundException。fis=new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\acer\\Pictures\\boke\\neojos.jpg"); fos=new FileOutputStream("rt.png"); byte[] b=new byte[1024]; int count=0; while((count=fis.read(b))!=-1){ //int read(byte[] b) fos.write(b,0,count); //write(byte[]b,int off,int len) } } catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("IO异常咯"); } finally{ if(fis!=null){ try{ fis.close(); } catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("error1"); } } if(fos!=null){ try{ fos.close(); } catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("error2"); } } //System.out.println("IO over!"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("程序执行開始"); TryCatch temp=new TryCatch(); temp.Four(); System.out.println("程序执行结束"); } }
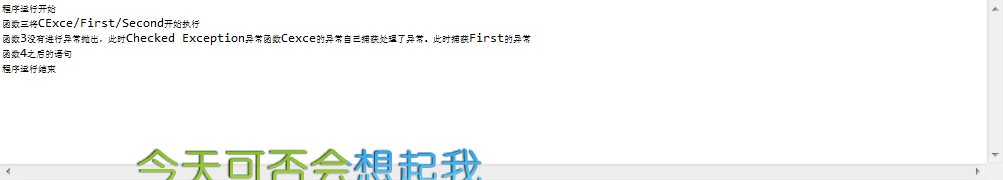
函数执行截图例如以下:
5.函数体声明抛出异常Throws
函数体声明异常,也就是在方法名后面加上throws ExceptionName,..., 方法本身仅仅是抛出异常,由函数调用者来捕获异常。若产生异常,异常会沿着调用栈下移。一直找到与之匹配的处理方法,若到达调用栈底仍未找到。程序终止。
编写代码,你会发现。
对于Throw unchecked Exception的函数,必须在函数体方法声明时追加throws xxException,否则通只是编译器。
在上面的样例中分别在CExce()和Third函数中追加。
import java.lang.*;
public class TryCatch{
/*
* 函数产生一个ArithmeticException异常
*/
public void First(){
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例");
try{
//double m=5.0/0; 在java中。浮点数double和float能够除0。返回无穷大
int m=5/0;
System.out.println(m+"第一个函数不会继续执行了");
}
catch(ArithmeticException e){
//throw用在程序中明白表示这里抛出一个异常。 后面跟一个异常对象(实例).
throw new ArithmeticException("ArithmeticException");
//后面不跟语句
}
finally{
System.out.println("第一个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
/*
* 函数产生一个OutIndexOfException异常
*/
public void Second(){
System.out.println("第二个异常处理的样例");
int[] arr=new int[3];
try{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
arr[i]=i;
}
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
throw new ArithmeticException("ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException");
}
finally{
//上面的样例这里写的输出语句有错误
System.out.println("第二个异常处理的样例结束");
}
}
/*
* 封装了First、Second,
* 函数对First、Second抛出的异常不进行处理
* 加入了CExce()函数
*/
public void Thrid() throws IOException{
System.out.println("函数三将CExce/First/Second開始执行");
CExce();
First();
Second();
System.out.println("函数三之后的语句");
}
/*
* 调用函数Thrid
*/
public void Four(){
try{
Thrid();
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("函数3没有进行异常抛出,此时Checked Exception异常函数Cexce的异常自己捕获处理了异常。此时捕获First的异常"); } System.out.println("函数4之后的语句"); } /* * */ public void CExce() throws FileNotFoundException{ FileInputStream fis=null; FileOutputStream fos=null; try{ //目录下没有这个文件,会产生FileNoFoundException。
fis=new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\acer\\Pictures\\boke\\neojos.jpg"); fos=new FileOutputStream("rt.png"); byte[] b=new byte[1024]; int count=0; while((count=fis.read(b))!=-1){ //int read(byte[] b) fos.write(b,0,count); //write(byte[]b,int off,int len) } } catch(IOException e){ throw new FileNotFoundException("文件未找到异常"); } finally{ if(fis!=null){ try{ fis.close(); } catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("error1"); } } if(fos!=null){ try{ fos.close(); } catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("error2"); } } //System.out.println("IO over!"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("程序执行開始"); TryCatch temp=new TryCatch(); temp.Four(); System.out.println("程序执行结束"); } }
函数运行结果例如以下:
这里图片的内容仅仅是用于提示运行的流程,输出文字没有意义
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








