注解篇
现在的开发,越来越多的使用到注解简化开发,比如spring_boot、spring_cloud中的一系列注解,这就让我非常感兴趣的事情
接触spring原始开发并不多,也知道前期spring开发会带来一大堆xml的配置,因为在下还是比较渣的coder
我也在面试过程中经常被问spring的特性什么什么的,像我这样从spring_boot往回走的人不多吧,不理解注解都不好意思说spring,mybatis也是
好处
①学习注解能够读懂别人写的代码,特别是框架相关的代码,在学习或工作中会去看别人的代码,很多知识是和注解相关的引用体现,不好好研究一下就不能很顺畅的看懂其代码套路
②让我们注解编程更加简洁,代码更加清晰,趋向于programmer的进阶,engineer的方向前进,可以将很多逻辑才能实现的方法转化成一个注解来替代,来一套让自己飞起来的服务
③让自己的逼格别具特色,让别人也向你学习
大家都会使用注解,但不一定都会自定义注解来解决问题,开始学习
概念
Java提供了一种原程序中的元素关联任何信息和任何元数据的途径和方法
就像学校里起步学Java时就教面向对面的概念,比较抽象,需要在后面的编程学习或工作中才能慢慢领悟的方式学习---知新而温故
解析注解
★Java中的常见注解
① JDK常见注解: @Override 、@Deprecated 、@Suppvisewarnings等
创建一个接口和一个实现类
public interface Dog {
String kind();
Integer age();
void work();
}
public class SingleDog implements Dog {
@Override
public String kind() {return null;}
@Override
public Integer age() {return null;}
@Override
public void work() {}
}
@Override出现,覆盖父类的方法,可以发现如果将接口的方法注掉,标@Override的实现方法就会出现问题
每只Dog都有品种,年龄,但不是每只Dog都能work,所以决定将此方法作废,使用@Deprecated注解
public interface Dog {
String kind();
Integer age();
@Deprecated
void work();
}
此时实现的方法不会出现什么问题,在调用的时候就会出现提示信息,如下:
public class DemoMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog=new SingleDog();
dog.kind();
dog.age();
dog.work();
}
}
有的编程工具还会出现警告,也有某些编程洁癖的公司是不允许出现警告和此类问题
在方法上加@Suppvisewarnings注解,就可以去除警告和删除线
public class DemoMain {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog=new SingleDog();
dog.kind();
dog.age();
dog.work();
}
}
② 第三方注解
Spring常见注解: @Autowired 、@Service 、@Repository等
Mybatis常见注解: @InsertProvider 、@Select 、 @Options等
下面以@Autowired示例,对比引入前后的展示效果:
》类的实现
public class DogManagerImpl implements DogMapper {
private DogDao dogDao;
public void setDogDao(DogDao dogDao) {
this.dogDao = dogDao;
}
//...
}
配置文件
<bean id="DogManagerImpl" class ="com.cloud.eureka.demo.DogManager">
<property name="dogDao" ref="dogDao" />
</bean>
<bean id="dogDao" class ="com.cloud.eureka.demo.DogManagerImpl">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="mySessionFactory" />
</bean>
》引入@Autowired
public class DogManagerImpl implements DogMapper {
@Autowired
private DogDao dogDao;
//...
}
两种引入对比,我这么懒的人,肯定用@Autowired
★注解的分类
①按运行机制分
- 源码注解: 只在源码中存在,编译成class文件时就不存在
- 编译时注解: 在源码和class文件中都存在,例如@Override 、@Deprecated等,比如Override在编译时告诉编译器,这个子类方法是覆盖父类的方法;如果实现,没有覆盖,那么代码上就会报错
- 运行时注解: 在运行时起作用,可以影响运行逻辑,例如@Autowired
②按来源分
- 来自JDK的注解
- 来自第三方的注解 : 这个使用的最多
- 自定义的注解
③元注解
- 给注解的注解
★自定义注解
》自定义的语法要求 》注解的注解(元注解)
import java.lang.annotation.*;
//@Target、@Retention、@Inherited、@Documented 为元注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
//以public @interface关键字定义注解
public @interface MyAnnotation {
//成员的类型有规范,包括基本类型、String、Class、Annotation、Enumeration
//成员大部分使用基本类型、Enumeration以及String,其他的比较少见
//成员不可以List、Map、对象等类型
//没有成员的注解称为标识注解
//成员以无参数、无异常方式声明
String hello();
//如果注解只有一个成员,则成员的名字必须为value,此处的必须是一个规范
//如果MyAnnotation只有一个成员,那么使用的方式@MyAnnotation("val")
//正常使用方式@MyAnnotation(value="val")
String value();
//可以为成员指定一个默认值default
int age() default 21;
}
@Target 定义一个注解的作用域,其有一个成员ElementType[] value();是一个枚举数组
ElementType常量提供简答的分类,常用于@Target元注释用于指定编写注释的合法位置,给定类型
/** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */
TYPE,
/** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */
FIELD,
/** Method declaration */
METHOD,
/** Formal parameter declaration */
PARAMETER,
/** Constructor declaration */
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** Local variable declaration */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** Annotation type declaration */
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/** Package declaration */
PACKAGE,
/** Type parameter declaration */
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/** Use of a type */
TYPE_USE@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)注解定义运行机制,声明生命周期类型 SOURCE, CLASS, RUNTIME
@Inherrited注解允许子类继承
@Documented生成javadoc时会包含注解信息,标识注解
》使用自定义注解
@MyAnnotation(hello = "tom",value = "val",age = 18)
public String demo(){
return "demo";
}
★解析注解
概念: 通过反射获取类、函数或成员上的运行时注解信息,从而实现动态控制程序运行的逻辑
下面定义一个注解,通过反射解析注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();
}public interface Dog {
String kind();
String name();
void work();
}@MyAnnotation("这是实现类")
public class DogImpl implements Dog {
@Override
@MyAnnotation("这是kind方法")
public String kind() {return null;}
@Override
public String name() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void work() {}
}import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ParseAnnotation {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1.类加载器
Class c = Class.forName("com.cloud.eureka.demo.DogImpl");
//2.找到类上的注解
boolean b = c.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class);
if (b) {
//3.获取注解示例
MyAnnotation annotation = (MyAnnotation) c.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println("3。" + annotation.value());
}
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
//4.找到方法上的注解
Method[] methods = c.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
boolean mb = method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class);
if (mb) {
//5.获取注解示例
MyAnnotation annotation = (MyAnnotation) method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println("5。" + annotation.value());
}
}
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
//6.获取方法的注解
for (Method method : methods) {
Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
if (annotation instanceof MyAnnotation) {
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;
System.out.println("6。" + myAnnotation.value());
}
}
}
}
}控制台输出:
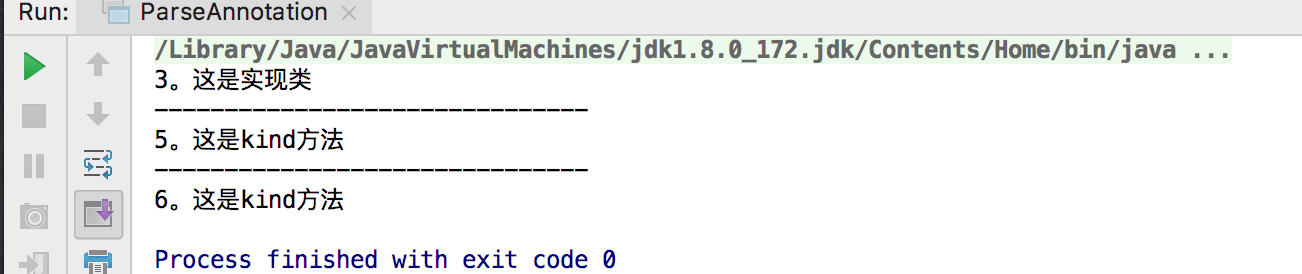
将MyAnnotation注解的元注解@Retention改成@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE),就会反射不到,因为这个作用域只在源码级别存在,编译运行就不存在了; 元注解@Retention改成@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS),运行结构控制台依然是空的,执行的main是运行时的环境,只能是运行时注解@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
提示: @Inherited元注解在接口实现时是无效的,是类与类的继承才会有效果,并且只会继承类上的注解信息,不会继承方法上的注解
------------------------------------------------------------------






















 15万+
15万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








