最近因为项目需要准备看dubbo源码,下载代码之后发现工程有几十个之多,第一次看dubbo源码会有无从下手的感觉。根据学习框架的一般步骤,先看文档,在做demo,进行入门。
跑了demo之后,发现功能很多,实现比较复杂,因为很多信息都在配置文件中体现,感觉可以从配置入口。只要留心就会发现dubbo工程中又很多api工程,会发现dubbo抽象出来很多核心接口模块,每个接口模块下面都会有一个或者多个实现方式。首先来看config工程源码:dubbo-config-api和dubbo-config-spring。
客户端配置:
<dubbo:consumer cluster="failover" loadbalance="mysfpay" retries="1" timeout="60000"/>
<dubbo:application name="demo-consumer" />
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://10.118.242.90:2181"
client="curator" group="china" />
<dubbo:annotation package="com.alibaba" />
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService"/>服务端配置:
<dubbo:application name="demo-provider" />
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://10.118.242.90:2181"
client="curator" group="china" />
<!-- 多协议配置 -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<dubbo:annotation package="com.alibaba" />
<!-- 測試接口 -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.DemoService"
ref="demoService" timeout="6000" cache="lru"/>从上面配置可以发现(在生产者主要是配置要发布出去service,而消费者主要是配置订阅要使用的reference)在配置文件中的每一个标签都可以在dubbo-config-api中找到实体类相对应。
如果注意看这些配置类是存在一些层级关系的,将一些具有通用性的属性定义在抽象类中,将每个标签所特有的属性定义在子类中。
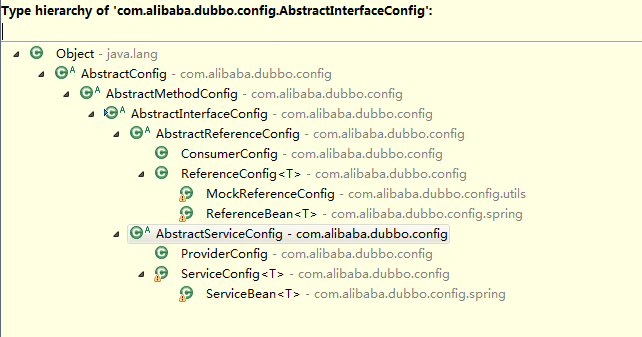
从上图中可以看到标签:dubbo:reference、dubbo:consumer以及dubbo:service、dubbo:provider继承自抽象类AbstractInterfaceConfig,而抽象类中配置有cluster(集群方式)、proxy(代理类型)等属性所以在上面的reference、consumer、service、provider标签中也可以配置cluster和proxy等属性。dubbo-config-api工程中还有两个注解类的定义@interface Reference、@interface Service所以在dubbo中发布服务和订阅服务也可以通过配置来完成。到此我们已经基本看完了dubbo-config-api工程中源码,可以发现在接口工程中主要实现的比较基础通用的代码,如配置属性定义,接口定义。
public abstract class AbstractInterfaceConfig extends AbstractMethodConfig {
// 服务接口的本地实现类名
protected String local;
// 服务接口的本地实现类名
protected String stub;
// 服务监控
protected MonitorConfig monitor;
// 代理类型
protected String proxy;
// 集群方式
protected String cluster;
// 过滤器
protected String filter;
// 监听器
protected String listener;
// 负责人
protected String owner;
// 连接数限制,0表示共享连接,否则为该服务独享连接数
protected Integer connections;
// 连接数限制
protected String layer;
// 应用信息
protected ApplicationConfig application;
// 模块信息
protected ModuleConfig module;
// 注册中心
protected List<RegistryConfig> registries;
// callback实例个数限制
private Integer callbacks;
// 连接事件
protected String onconnect;
// 断开事件
protected String ondisconnect;
// 服务暴露或引用的scope,如果为local,则表示只在当前JVM内查找.
private String scope;
//其他代码暂略...
}public abstract class AbstractServiceConfig extends AbstractInterfaceConfig {
// 服务版本
protected String version;
// 服务分组
protected String group;
// 服务是否已经deprecated
protected Boolean deprecated;
// 延迟暴露
protected Integer delay;
// 是否暴露
protected Boolean export;
// 权重
protected Integer weight;
// 应用文档
protected String document;
// 在注册中心上注册成动态的还是静态的服务
protected Boolean dynamic;
// 是否使用令牌
protected String token;
// 访问日志
protected String accesslog;
// 允许执行请求数
private Integer executes;
protected List<ProtocolConfig> protocols;
// 是否注册
private Boolean register;
}
public class ServiceConfig<T> extends AbstractServiceConfig {
private static final Protocol protocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
private static final ProxyFactory proxyFactory = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ProxyFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
private static final Map<String, Integer> RANDOM_PORT_MAP = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
// 接口类型
private String interfaceName;
private Class<?> interfaceClass;
// 接口实现类引用
private T ref;
// 服务名称
private String path;
// 方法配置
private List<MethodConfig> methods;
private ProviderConfig provider;
private final List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<URL>();
private final List<Exporter<?>> exporters = new ArrayList<Exporter<?>>();
private transient volatile boolean exported;
private transient volatile boolean unexported;
private volatile String generic;
}以上是service配置的继承关系类,这里只列出了属性,reference配置的相关类自己可以下载源码查看。
接下来我们继续来看dubbo-config-spring工程,我们都知道dubbo的配置扩展于spring的配置,在配置文件中我们不仅可以配置spring标签也可以配置dubbo标签,通过类DubboNamespaceHandler、DubboBeanDefinitionParser以及dubbo.xsd、spring.handlers、spring.schemas我们可以看出dubbo对配置文件的解析其实使用的是“spring自定义标签的功能”。在dubbo.xsd文件中进行标签属性的定义,描述自定义组件内容,然后通过DubboBeanDefinitionParser实现了BeanDefinitionParser接口解析XSD文件中定义的属性,最后通过DubboNamespaceHandler扩展自NamespaceHandlerSupport的handler将自定义组件注册到spring容器中。简单来说dubbo-config-spring工程的主要功能就是将dubbo自定标签进行解析并注册到spring容器中。
dubbo.xsd文件中service标签描述内容如下
<xsd:complexType name="serviceType">
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="abstractServiceType">
<xsd:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:element ref="method" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" />
<xsd:element ref="parameter" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" />
<xsd:element ref="beans:property" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" />
</xsd:choice>
<xsd:attribute name="interface" type="xsd:token" use="required">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ Defines the interface to advertise for this service in the service registry. ]]></xsd:documentation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<tool:annotation>
<tool:expected-type type="java.lang.Class"/>
</tool:annotation>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="ref" type="xsd:string" use="optional">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ The service implementation instance bean id. ]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="class" type="xsd:string" use="optional">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ The service implementation class name. ]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="path" type="xsd:string" use="optional">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ The service path. ]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="provider" type="xsd:string" use="optional">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ Deprecated. Replace to protocol. ]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="generic" type="xsd:string" use="optional">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ Generic service. ]]></xsd:documentation>
</xsd:annotation>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:anyAttribute namespace="##other" processContents="lax" />
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>我们来看其中关键步骤的代码,DubboNamespaceHandler类中定义的init方法,DubboBeanDefinitionParser解析器解析组件属性到对应的bean中。
public void init() {
//放入一个map中
//两个参数日一个是节点名称,第二个参数该节点解析的类
registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(AnnotationBean.class, true));
}对自定义标签的具体解析实现代码在DubboBeanDefinitionParser类中的parse方法中。该方法主要作用就是将配置文件中配置的组件,解析描述成一个spring容器中管理的bean对象(RootBeanDefinition),然后将该组件放入spring容器中进行管理。
private static BeanDefinition parse(Element element,
ParserContext parserContext, Class<?> beanClass, boolean required) {
//BeanDefinition是spring中定义的接口描述了一个bean的实例,包括属性值,构造方法参数值和继承自它的类的更多信息,
//RootBeanDefinition实现了BeanDefinition接口,表示该bean是从配置源(配置文件等)加载生成的,
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(beanClass);//设置bean类型
beanDefinition.setLazyInit(false);//设置该bean加载方式
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
if ((id == null || id.length() == 0) && required) {
String generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("name");
if (generatedBeanName == null || generatedBeanName.length() == 0) {
if (ProtocolConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
generatedBeanName = "dubbo";
} else {
generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("interface");
}
}
if (generatedBeanName == null || generatedBeanName.length() == 0) {
generatedBeanName = beanClass.getName();
}
id = generatedBeanName;
int counter = 2;
while (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
id = generatedBeanName + (counter++);
}
}
if (id != null && id.length() > 0) {
if (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate spring bean id "
+ id);
}
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(id,
beanDefinition);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("id", id);
}
//解析为Protocol组件时处理
if (ProtocolConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
for (String name : parserContext.getRegistry()
.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition definition = parserContext.getRegistry()
.getBeanDefinition(name);
PropertyValue property = definition.getPropertyValues()
.getPropertyValue("protocol");
if (property != null) {
Object value = property.getValue();
if (value instanceof ProtocolConfig
&& id.equals(((ProtocolConfig) value).getName())) {
definition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(
"protocol", new RuntimeBeanReference(id));
}
}
}
} else if (ServiceBean.class.equals(beanClass)) {//解析为service时处理
String className = element.getAttribute("class");
if (className != null && className.length() > 0) {
RootBeanDefinition classDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
classDefinition.setBeanClass(ReflectUtils.forName(className));
classDefinition.setLazyInit(false);
parseProperties(element.getChildNodes(), classDefinition);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("ref",
new BeanDefinitionHolder(classDefinition, id + "Impl"));
}
} else if (ProviderConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {//解析为provider时处理
parseNested(element, parserContext, ServiceBean.class, true,
"service", "provider", id, beanDefinition);
} else if (ConsumerConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {//解析为consumer时处理
parseNested(element, parserContext, ReferenceBean.class, false,
"reference", "consumer", id, beanDefinition);
}
Set<String> props = new HashSet<String>();
ManagedMap parameters = null;
//处理该类中的方法、属性给定义的属性赋值
for (Method setter : beanClass.getMethods()) {
...
}
NamedNodeMap attributes = element.getAttributes();
int len = attributes.getLength();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Node node = attributes.item(i);
String name = node.getLocalName();
if (!props.contains(name)) {
if (parameters == null) {
parameters = new ManagedMap();
}
String value = node.getNodeValue();
parameters.put(name, new TypedStringValue(value, String.class));
}
}
if (parameters != null) {
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("parameters",
parameters);
}
return beanDefinition;
}从上面代码我们可以看出dubbo将配置的service、reference放入spring容器中进行管理。






















 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








