SQL Server2000中死锁经验总结<?xml:namespace prefix = o ns = "urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:office" />
Terrylee,<?xml:namespace prefix = st1 ns = "urn:schemas-microsoft-com:office:smarttags" />2005年12月24日
将死锁减至最少
虽然不能完全避免死锁,但可以使死锁的数量减至最少。将死锁减至最少可以增加事务的吞吐量并减少系统开销,因为只有很少的事务:
- 回滚,而回滚会取消事务执行的所有工作。
- 由于死锁时回滚而由应用程序重新提交。
下列方法有助于最大限度地降低死锁:
- 按同一顺序访问对象。
- 避免事务中的用户交互。
- 保持事务简短并在一个批处理中。
- 使用低隔离级别。
- 使用绑定连接。
按同一顺序访问对象
如果所有并发事务按同一顺序访问对象,则发生死锁的可能性会降低。例如,如果两个并发事务获得 Supplier 表上的锁,然后获得 Part 表上的锁,则在其中一个事务完成之前,另一个事务被阻塞在 Supplier 表上。第一个事务提交或回滚后,第二个事务继续进行。不发生死锁。将存储过程用于所有的数据修改可以标准化访问对象的顺序。
<?xml:namespace prefix = v ns = "urn:schemas-microsoft-com:vml" />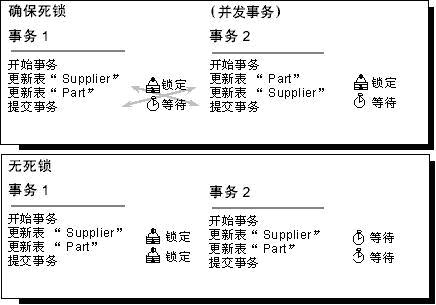
避免事务中的用户交互
避免编写包含用户交互的事务,因为运行没有用户交互的批处理的速度要远远快于用户手动响应查询的速度,例如答复应用程序请求参数的提示。例如,如果事务正在等待用户输入,而用户去吃午餐了或者甚至回家过周末了,则用户将此事务挂起使之不能完成。这样将降低系统的吞吐量,因为事务持有的任何锁只有在事务提交或回滚时才会释放。即使不出现死锁的情况,访问同一资源的其它事务也会被阻塞,等待该事务完成。
保持事务简短并在一个批处理中
在同一数据库中并发执行多个需要长时间运行的事务时通常发生死锁。事务运行时间越长,其持有排它锁或更新锁的时间也就越长,从而堵塞了其它活动并可能导致死锁。
保持事务在一个批处理中,可以最小化事务的网络通信往返量,减少完成事务可能的延迟并释放锁。
使用低隔离级别
确定事务是否能在更低的隔离级别上运行。执行提交读允许事务读取另一个事务已读取(未修改)的数据,而不必等待第一个事务完成。使用较低的隔离级别(例如提交读)而不使用较高的隔离级别(例如可串行读)可以缩短持有共享锁的时间,从而降低了锁定争夺。
使用绑定连接
使用绑定连接使同一应用程序所打开的两个或多个连接可以相互合作。次级连接所获得的任何锁可以象由主连接获得的锁那样持有,反之亦然,因此不会相互阻塞
检测死锁
如果发生死锁了,我们怎么去检测具体发生死锁的是哪条SQL语句或存储过程?
这时我们可以使用以下存储过程来检测,就可以查出引起死锁的进程和SQL语句。SQL Server自带的系统存储过程sp_who和sp_lock也可以用来查找阻塞和死锁, 但没有这里介绍的方法好用。
 use
master
use
master go
go
 create
procedure
sp_who_lock
create
procedure
sp_who_lock as
as
 begin
begin
 declare
@spid
int
,
@bl
int
,
declare
@spid
int
,
@bl
int
, @intTransactionCountOnEntry
int
,
@intTransactionCountOnEntry
int
, @intRowcount
int
,
@intRowcount
int
, @intCountProperties
int
,
@intCountProperties
int
, @intCounter
int
@intCounter
int

 create
table
#tmp_lock_who (
create
table
#tmp_lock_who ( id
int
identity
(
1
,
1
),
id
int
identity
(
1
,
1
), spid
smallint
,
spid
smallint
, bl
smallint
)
bl
smallint
)
 IF
@@ERROR
<>
0
RETURN
@@ERROR
IF
@@ERROR
<>
0
RETURN
@@ERROR

 insert
into
#tmp_lock_who(spid,bl)
select
0
,blocked
insert
into
#tmp_lock_who(spid,bl)
select
0
,blocked from
(
select
*
from
sysprocesses
where
blocked
>
0
) a
from
(
select
*
from
sysprocesses
where
blocked
>
0
) a  where
not
exists
(
select
*
from
(
select
*
from
sysprocesses
where
blocked
>
0
) b
where
not
exists
(
select
*
from
(
select
*
from
sysprocesses
where
blocked
>
0
) b  where
a.blocked
=
spid)
where
a.blocked
=
spid) union
select
spid,blocked
from
sysprocesses
where
blocked
>
0
union
select
spid,blocked
from
sysprocesses
where
blocked
>
0

 IF
@@ERROR
<>
0
RETURN
@@ERROR
IF
@@ERROR
<>
0
RETURN
@@ERROR

 --
找到临时表的记录数
--
找到临时表的记录数
 select
@intCountProperties
=
Count
(
*
),
@intCounter
=
1
select
@intCountProperties
=
Count
(
*
),
@intCounter
=
1
 from
#tmp_lock_who
from
#tmp_lock_who
 IF
@@ERROR
<>
0
RETURN
@@ERROR
IF
@@ERROR
<>
0
RETURN
@@ERROR

 if
@intCountProperties
=
0
if
@intCountProperties
=
0
 select
'
现在没有阻塞和死锁信息
'
as
message
select
'
现在没有阻塞和死锁信息
'
as
message
 --
循环开始
--
循环开始
 while
@intCounter
<=
@intCountProperties
while
@intCounter
<=
@intCountProperties
 begin
begin
 --
取第一条记录
--
取第一条记录
 select
@spid
=
spid,
@bl
=
bl
select
@spid
=
spid,
@bl
=
bl from
#tmp_lock_who
where
Id
=
@intCounter
from
#tmp_lock_who
where
Id
=
@intCounter
 begin
begin
 if
@spid
=
0
if
@spid
=
0
 select
'
引起数据库死锁的是:
'
+
CAST
(
@bl
AS
VARCHAR
(
10
))
+
'
进程号,其执行的SQL语法如下
'
select
'
引起数据库死锁的是:
'
+
CAST
(
@bl
AS
VARCHAR
(
10
))
+
'
进程号,其执行的SQL语法如下
'
 else
else
 select
'
进程号SPID:
'
+
CAST
(
@spid
AS
VARCHAR
(
10
))
+
'
被
'
+
'
进程号SPID:
'
+
CAST
(
@bl
AS
VARCHAR
(
10
))
+
'
阻塞,其当前进程执行的SQL语法如下
'
select
'
进程号SPID:
'
+
CAST
(
@spid
AS
VARCHAR
(
10
))
+
'
被
'
+
'
进程号SPID:
'
+
CAST
(
@bl
AS
VARCHAR
(
10
))
+
'
阻塞,其当前进程执行的SQL语法如下
'
 DBCC
INPUTBUFFER (
@bl
)
DBCC
INPUTBUFFER (
@bl
) end
end

 --
循环指针下移
--
循环指针下移
 set
@intCounter
=
@intCounter
+
1
set
@intCounter
=
@intCounter
+
1
 end
end

 drop
table
#tmp_lock_who
drop
table
#tmp_lock_who
 return
0
return
0
 end
end

杀死锁和进程
如何去手动的杀死进程和锁?最简单的办法,重新启动服务。但是这里要介绍一个存储过程,通过显式的调用,可以杀死进程和锁。
 use
master
use
master go
go

 if
exists
(
select
*
from
dbo.sysobjects
where
id
=
object_id
(N
'
[dbo].[p_killspid]
'
)
and
OBJECTPROPERTY
(id, N
'
IsProcedure
'
)
=
1
)
if
exists
(
select
*
from
dbo.sysobjects
where
id
=
object_id
(N
'
[dbo].[p_killspid]
'
)
and
OBJECTPROPERTY
(id, N
'
IsProcedure
'
)
=
1
) drop
procedure
[
dbo
]
.
[
p_killspid
]
drop
procedure
[
dbo
]
.
[
p_killspid
]
 GO
GO

 create
proc
p_killspid
create
proc
p_killspid @dbname
varchar
(
200
)
--
要关闭进程的数据库名
@dbname
varchar
(
200
)
--
要关闭进程的数据库名
 as
as
 declare
@sql
nvarchar
(
500
)
declare
@sql
nvarchar
(
500
)  declare
@spid
nvarchar
(
20
)
declare
@spid
nvarchar
(
20
)
 declare
#tb
cursor
for
declare
#tb
cursor
for
 select
spid
=
cast
(spid
as
varchar
(
20
))
from
master..sysprocesses
where
dbid
=
db_id
(
@dbname
)
select
spid
=
cast
(spid
as
varchar
(
20
))
from
master..sysprocesses
where
dbid
=
db_id
(
@dbname
) open
#tb
open
#tb fetch
next
from
#tb
into
@spid
fetch
next
from
#tb
into
@spid
 while
@@fetch_status
=
0
while
@@fetch_status
=
0
 begin
begin
 exec
(
'
kill
'
+
@spid
)
exec
(
'
kill
'
+
@spid
) fetch
next
from
#tb
into
@spid
fetch
next
from
#tb
into
@spid
 end
end
 close
#tb
close
#tb deallocate
#tb
deallocate
#tb go
go

 --
用法
--
用法
 exec
p_killspid
'
newdbpy
'
exec
p_killspid
'
newdbpy
'

查看锁信息
如何查看系统中所有锁的详细信息?在企业管理管理器中,我们可以看到一些进程和锁的信息,这里介绍另外一种方法。
 --
查看锁信息
--
查看锁信息
 create
table
#t(req_spid
int
,obj_name sysname)
create
table
#t(req_spid
int
,obj_name sysname)
 declare
@s
nvarchar
(
4000
)
declare
@s
nvarchar
(
4000
) ,
@rid
int
,
@dbname
sysname,
@id
int
,
@objname
sysname
,
@rid
int
,
@dbname
sysname,
@id
int
,
@objname
sysname
 declare
tb
cursor
for
declare
tb
cursor
for
 select
distinct
req_spid,dbname
=
db_name
(rsc_dbid),rsc_objid
select
distinct
req_spid,dbname
=
db_name
(rsc_dbid),rsc_objid from
master..syslockinfo
where
rsc_type
in
(
4
,
5
)
from
master..syslockinfo
where
rsc_type
in
(
4
,
5
) open
tb
open
tb fetch
next
from
tb
into
@rid
,
@dbname
,
@id
fetch
next
from
tb
into
@rid
,
@dbname
,
@id
 while
@@fetch_status
=
0
while
@@fetch_status
=
0
 begin
begin
 set
@s
=
'
select @objname=name from [
'
+
@dbname
+
'
]..sysobjects where id=@id
'
set
@s
=
'
select @objname=name from [
'
+
@dbname
+
'
]..sysobjects where id=@id
'
 exec
sp_executesql
@s
,N
'
@objname sysname out,@id int
'
,
@objname
out,
@id
exec
sp_executesql
@s
,N
'
@objname sysname out,@id int
'
,
@objname
out,
@id
 insert
into
#t
values
(
@rid
,
@objname
)
insert
into
#t
values
(
@rid
,
@objname
) fetch
next
from
tb
into
@rid
,
@dbname
,
@id
fetch
next
from
tb
into
@rid
,
@dbname
,
@id
 end
end
 close
tb
close
tb deallocate
tb
deallocate
tb
 select
进程id
=
a.req_spid
select
进程id
=
a.req_spid ,数据库
=
db_name
(rsc_dbid)
,数据库
=
db_name
(rsc_dbid) ,类型
=
case
rsc_type
when
1
then
'
NULL 资源(未使用)
'
,类型
=
case
rsc_type
when
1
then
'
NULL 资源(未使用)
'
 when
2
then
'
数据库
'
when
2
then
'
数据库
'
 when
3
then
'
文件
'
when
3
then
'
文件
'
 when
4
then
'
索引
'
when
4
then
'
索引
'
 when
5
then
'
表
'
when
5
then
'
表
'
 when
6
then
'
页
'
when
6
then
'
页
'
 when
7
then
'
键
'
when
7
then
'
键
'
 when
8
then
'
扩展盘区
'
when
8
then
'
扩展盘区
'
 when
9
then
'
RID(行 ID)
'
when
9
then
'
RID(行 ID)
'
 when
10
then
'
应用程序
'
when
10
then
'
应用程序
'
 end
end
 ,对象id
=
rsc_objid
,对象id
=
rsc_objid ,对象名
=
b.obj_name
,对象名
=
b.obj_name ,rsc_indid
,rsc_indid from
master..syslockinfo a
left
join
#t b
on
a.req_spid
=
b.req_spid
from
master..syslockinfo a
left
join
#t b
on
a.req_spid
=
b.req_spid
 go
go
 drop
table
#t
drop
table
#t
总结
虽然不能完全避免死锁,但我们可以将死锁减至最少,并通过一定的方法来检测死锁。






















 3979
3979











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








