在这篇文章中,我们接着上一篇的内容接着分析。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//启动应用的检测
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
//SpringBoot的上下文
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
//失败分析报告
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
//SpringBoot的runlistener
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
//参数解析
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
//配置环境变量
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
//输出Banner信息
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建应用上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
//refresh上下文之前的准备
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
listeners.finished(context, null);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}SpringApplication中的run方法的内容如上所示,上面就是整个SpringBoot应用启动的主要调用方法,run方法中的参数即是我们的应用参数。下面我们来简单的分析一下这个启动过程。
StopWatch主要是监控启动过程,统计启动时间,检测应用是否已经启动或者停止。
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}通过在上一篇文章中的问题,对于getSpringFactoriesInstances这个方法你应该不陌生来吧。这里也是从META-INF/spring.factories中获取类型为org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener的配置值,这个默认的配置值为:org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener。我们进入到EventPublishingRunListener这个类看一下它的构造函数
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
//创建一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
//把之前在SpringApplication中获取到的listener循环放入到SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster中
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}通过上面的分析,我们可以看到EventPublishingRunListener把SpringApplication中的监听器,都放到了SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster中,进行了统一的管理。listeners.starting();启动事件监听,这里以后我们单独开章节详细说明.
//创建应用参数解析器
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);我们看一下DefaultApplicationArguments的构造函数的内容:
public DefaultApplicationArguments(String[] args) {
//首先判断不能为null,这里大家可以想一下可变参数如果不传值的话看看是什么内容
Assert.notNull(args, "Args must not be null");
//调用Source对应用参数进行解析
this.source = new Source(args);
this.args = args;
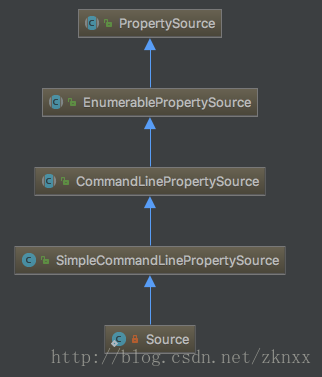
}Source(String[] args) {
//调用父类的构造函数 Source的继承关系如下图所示
super(args);
}
public SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(String... args) {
//对应参数进行解析的工作
super(new SimpleCommandLineArgsParser().parse(args));
}
大家在配置应用参数的时候,是这样这样配置的 - -key=value,为什么要以- -开头呢?在SimpleCommandLineArgsParser的parse方法中你会找到答案。并且Source这个类还继承类PropertySource这个类。
//准备环境变量
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,applicationArguments);
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
//获取环境变量
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//将应用参数放入到环境变量持有对象中
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//监听器监听环境变量对象的变化
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
//如果非web环境,则转换为StandardEnvironment对象
if (!this.webEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()) .convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
}
return environment;
} private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
//如果已经创建过存放环境变量的对象了,则直接返回
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
//如果是web环境则创建StandardServletEnvironment对象
if (this.webEnvironment) {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
//非web环境,创建StandardEnvironment
return new StandardEnvironment();
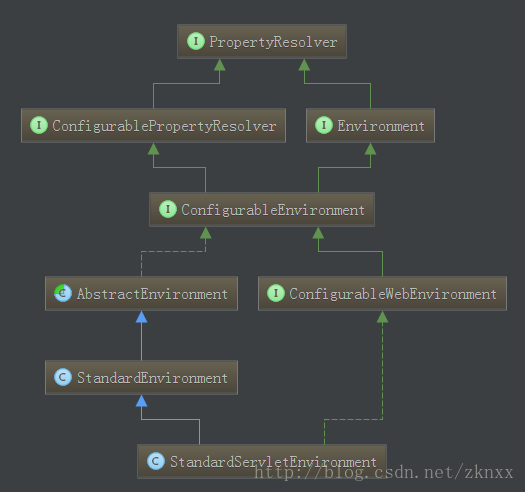
}StandardServletEnvironment的UML图如下所示,StandardServletEnvironment集成了系统变量、环境变量、配置属性信息等内容。这些内容我们以后单开一个篇章来说一下。
//这句话是输出SpringBoot的Banner信息,可以从指定的位置加载信息,可以输出为文字形式,也可以输出为图片形式,如我们常见的SpringBoot的logo就是在这里输出的
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
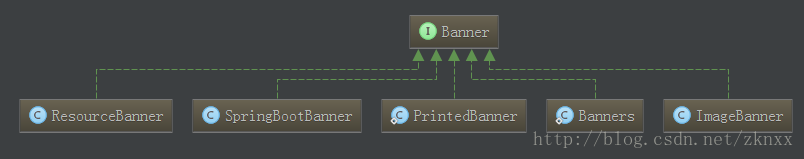
Banner的UML类图如下所示:
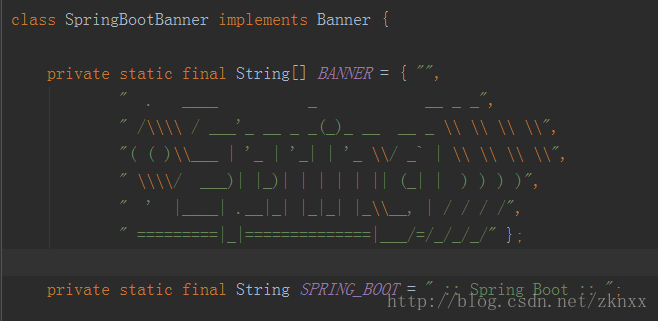
我们最常见的SpringBoot的logo“图像”就在SpringBootBanner这个类中定义的,这个也是SpringBoot默认的Banner类。
//创建SpringBoot的应用上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
//DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
/// DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
contextClass = Class.forName(this.webEnvironment
? DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS : DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiate(contextClass);
}因为我们是web开发环境,所以这里我们的web上下文是AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext这个对象,一定要记住这个类,要仔细的看看它的UML类图。




















 1420
1420











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








