使用场景
在一些业务场景中,当Serverlet容器初始化完成、重启、关闭等等一系列动作之后,需要处理一些操作,比如一些数据的加载、初始化缓存、特定任务的注册等等。这个时候我们就可以使用Spring提供的ApplicationListener来进行操作。
原理
ApplicationListener是一个接口,里面只有一个onApplicationEvent方法,方法的参数为ApplicationEvent,ApplicationEvent是个抽象类,顾名思义就是Spring应用的一些Event,ApplicationEvent又有一个抽象子类ApplicationContextEvent,这里用到的就是ApplicationContextEvent的实现类。查看ApplicationContextEvent文档的实现类,有ContextClosedEvent, ContextRefreshedEvent, ContextStartedEvent, ContextStoppedEvent,这四个都是spring context包中的核心实现:
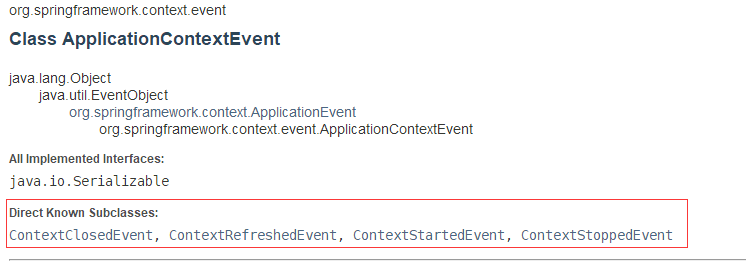
ApplicationEvent
|-ApplicationContextEvent
|-ContextClosedEvent:应用关闭事件
|-ContextRefreshedEvent:应用刷新事件
|-ContextStartedEvent:应用开启事件
|-ContextStoppedEvent:应用停止事件
另外:spring boot扩展了两个实现:
EmbeddedServletContainerInitializedEvent:内嵌Servlet容器初始化事件
ApplicationReadyEvent:spring Application启动完成事件
用法
本文以在Spring boot下的使用为例来进行说明。首先,需要实现ApplicationListener接口并实现onApplicationEvent方法。把需要处理的操作放在onApplicationEvent中进行处理:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedServletContainerInitializedEvent;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStartedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStoppedEvent;
/**
* Created by dongsilin on 2017/12/18.
*/
@Slf4j
public class AppApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
log.info("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
if (event instanceof ContextStartedEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ContextStartedEvent");
}
if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ContextRefreshedEvent");
}
if (event instanceof ContextClosedEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ContextClosedEvent");
}
if (event instanceof ContextStoppedEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ContextStoppedEvent");
}
if (event instanceof EmbeddedServletContainerInitializedEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "EmbeddedServletContainerInitializedEvent");
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent){
log.info("================:{}", "ApplicationReadyEvent");
}
log.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>:{}\n", event.getClass().getName());
}
}@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public AppApplicationListener appApplicationListener(){
return new AppApplicationListener();
}
}启动运行结果:
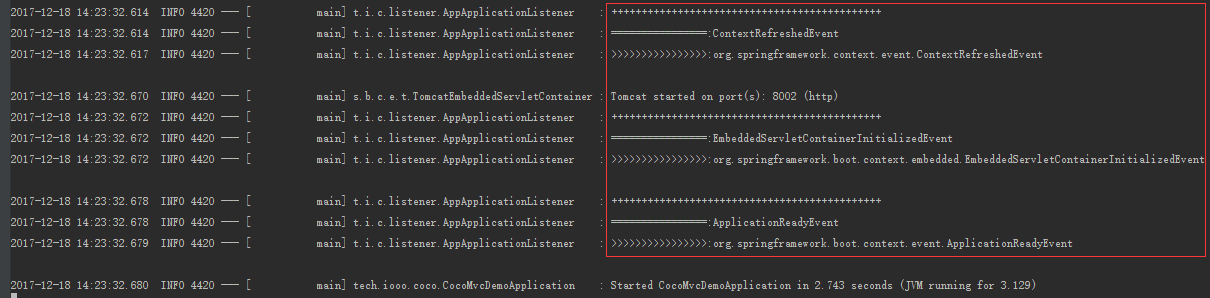
关闭运行结果:

二次调用问题
此处使用Spring boot来进行操作,没有出现二次调用的问题。在使用传统的applicationContext.xml和project-servlet.xml配置中会出现二次调用的问题。主要原因是初始化root容器之后,会初始化project-servlet.xml对应的子容器。我们需要的是只执行一遍即可。那么上面打印父容器的代码用来进行判断排除子容器即可。在业务处理之前添加如下判断:
if(contextRefreshedEvent.getApplicationContext().getParent() != null){
return;
}这样其他容器的初始化就会直接返回,而父容器(Parent为null的容器)启动时将会执行相应的业务操作。
关联知识
在spring中InitializingBean接口也提供了类似的功能,只不过它进行操作的时机是在所有bean都被实例化之后才进行调用。根据不同的业务场景和需求,可选择不同的方案来实现。






















 970
970

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








