这个程序输出:最短路径矩阵
例如:W[0][5]=9 代表vo->v5的最短路径为9
W=:
0 1 3 7 4 9
1 0 2 6 3 8
3 2 0 4 1 6
7 6 4 0 3 2
4 3 1 3 0 5
9 8 6 2 5 0
package com.xh.Floyd;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Floyd_01 {
public static int M = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public static int MAXSUM(int a,int b){
return (a!=M&&b!=M)?(a+b):M;
}
public static ArrayList<Integer[][]> flody(Integer[][] dist){
Integer[][] path=new Integer[6][6];//存储的是从i->j经过的最后一个节点
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
path[i][j]=i;
}
}
for(int k=0;k<6;k++){
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
if(dist[i][j]>MAXSUM(dist[i][k], dist[k][j])){
path[i][j]=path[k][j];//存储的是从i->j经过的最后一个节点
dist[i][j]=MAXSUM(dist[i][k], dist[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
ArrayList<Integer[][]> list =new ArrayList<Integer[][]>();
list.add(dist);
list.add(path);
return list;
}
public static Integer[] reverse(Integer[] chain,int count){
int temp;
for(int i=0,j=count-1;i<j;i++,j--){
temp=chain[i];
chain[i]=chain[j];
chain[j]=temp;
}
return chain;
}
public static void display_path(ArrayList<Integer[][]> list){
Integer[][] dist=list.get(0);
Integer[][] path=list.get(1);
Integer[] chain=new Integer[6];
System.out.println("orign->dist"+" dist "+" path");
for (int i = 0; i <6; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
if(i!=j){//只是避免了vi->vi的输出
//输出源到目的地
System.out.print("\n "+(i)+"->"+(j)+" ");
//输出最短路径的长度
if(dist[i][j]==M){
System.out.print(" NA ");
}else{
System.out.print(dist[i][j]+" ");
int count=0;
int k=j;
do {
k=chain[count++]=path[i][k];
} while (i!=k);
chain=reverse(chain,count);
//输出路径
System.out.print(chain[0]+"");
for(k=1;k<count;k++){
System.out.print("->"+(chain[k]));
}
System.out.print("->"+j);
}
}
}
}
}
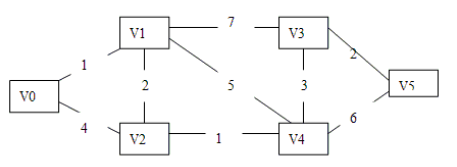
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[][] dist = {
{ 0, 1, 4, M, M, M },
{ 1, 0, 2, 7, 5, M },
{ 4, 2, 0, M, 1, M },
{ M, 7, M, 0, 3, 2 },
{ M, 5, 1, 3, 0, 6 },
{ M, M, M, 2, 6, 0 } };// 建立一个权值矩阵
ArrayList<Integer[][]> list=flody(dist);
display_path(list);
}
} 























 353
353

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








