方案实施
1、 spring和ehcache集成
主要获取ehcache作为操作ehcache的对象。
spring.xml中注入ehcacheManager和ehCache对象,ehcacheManager是需要加载ehcache.xml配置信息,创建ehcache.xml中配置不同策略的cache。
<!-- ehCache 配置管理器 -->
<bean id="ehcacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:ehcache.xml" />
<!--true:单例,一个cacheManager对象共享;false:多个对象独立 -->
<property name="shared" value="true" />
<property name="cacheManagerName" value="ehcacheManager" />
</bean>
<!-- ehCache 操作对象 -->
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager"> <property name="cacheManager" ref="ehcacheManager"/>
</bean>
<!-- 启用缓存注解功能(请将其配置在Spring主配置文件中) -->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager"/>
2、 spring和自带的缓存支持
<!-- Spring自己的基于java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap实现的缓存管理器(该功能是从Spring3.1开始提供的) -->
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager"> <property name="caches"> <set> <bean name="SimplePageCachingFilter" class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean" /> </set> </property> </bean>
3.spring和redis集成
主要获取redisTemplate作为操作redis的对象。
redis.properties配置信息
#host 写入redis服务器地址 redis.ip=127.0.0.1 #Port redis.port=6379 #Passord redis.password=123456 #连接超时30000 redis.timeout=30 #最大分配的对象数 redis.pool.maxActive=100 #最大能够保持idel状态的对象数 redis.pool.maxIdle=30 #当池内没有返回对象时,最大等待时间 redis.pool.maxWait=1000 #当调用borrow Object方法时,是否进行有效性检查 redis.pool.testOnBorrow=true #当调用return Object方法时,是否进行有效性检查 redis.pool.testOnReturn=true
spring注入jedisPool、redisConnFactory、redisTemplate对象
<!-- 加载redis.propertis -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations" value="classpath:redis.properties"/>
</bean>
<!-- Redis 连接池 -->
<bean id="jedisPool" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
<property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.pool.maxActive}" />
<property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.pool.maxIdle}" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.pool.testOnBorrow}" />
<property name="testOnReturn" value="${redis.pool.testOnReturn}" />
<property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.pool.maxWait}" />
</bean>
<!-- Redis 连接工厂 -->
<bean id="redisConnFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory">
<property name="hostName" value="${redis.ip}" />
<property name="port" value="${redis.port}" />
<!-- property name="password" value="${redis.password}" -->
<property name="timeout" value="${redis.timeout}" />
<property name="poolConfig" ref="jedisPool" />
</bean>
<!-- redis 操作对象 -->
<bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate">
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="redisConnFactory" />
</bean>
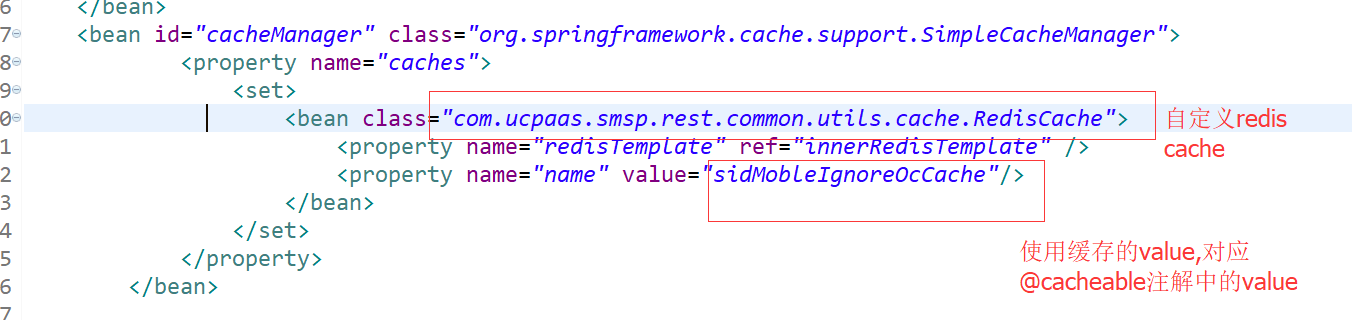
<!-- 自定义缓存 -->
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager">
<property name="caches">
<set>
<bean class="org.cpframework.cache.redis.RedisCache">
<property name="redisTemplate" ref="redisTemplate" />
<property name="name" value="default"/>
</bean>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 启用缓存注解功能(请将其配置在Spring主配置文件中) -->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager"/>
4.spring 缓存注解解释
缓存注解有以下三个:
@Cacheable @CacheEvict @CachePut
1.
@Cacheable(value=”accountCache”),这个注释的意思是,当调用这个方法的时候,会从一个名叫 accountCache 的缓存中查询,如果没有,则执行实际的方法,并将执行的结果存入缓存中,否则返回缓存中的对象。这里的缓存中的 key 就是参数 userName,value 就是 Account 对象。“accountCache”缓存是在 spring*.xml 中定义的名称。
例子1:
@Cacheable(value="accountCache")// 使用了一个缓存名叫 accountCache
public Account getAccountByName(String userName) {
// 方法内部实现不考虑缓存逻辑,直接实现业务
System.out.println("real query account."+userName);
return getFromDB(userName);
}
例子2:
@Cacheable(value="accountCache",condition="#userName.length() <=4")// 缓存名叫 accountCache ,condition:用来条件判断,满足条件的则进行缓存
public Account getAccountByName(String userName) {
// 方法内部实现不考虑缓存逻辑,直接实现业务
return getFromDB(userName);
}
2.
@CacheEvict 注释来标记要清空缓存的方法,当这个方法被调用后,即会清空缓存。注意其中一个 @CacheEvict(value=”accountCache”,key=”#account.getName()”),其中的 Key 是用来指定缓存的 key 的,这里因为我们保存的时候用的是 account 对象的 name 字段,所以这里还需要从参数 account 对象中获取 name 的值来作为 key,前面的 # 号代表这是一个 SpEL 表达式,此表达式可以遍历方法的参数对象
例子3:
@CacheEvict(value="accountCache",key="#account.getName()")// 清空accountCache 缓存
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
updateDB(account);
}
@CacheEvict(value="accountCache",allEntries=true)// 清空accountCache 缓存
public void reload() {
reloadAll()
}
@Cacheable(value="accountCache",condition="#userName.length() <=4")// 缓存名叫 accountCache
public Account getAccountByName(String userName) {
// 方法内部实现不考虑缓存逻辑,直接实现业务
return getFromDB(userName);
}
3.
@CachePut 注释,这个注释可以确保方法被执行,同时方法的返回值也被记录到缓存中,实现缓存与数据库的同步更新。
@CachePut(value="accountCache",key="#account.getName()")// 更新accountCache 缓存
public Account updateAccount(Account account) {
return updateDB(account);
}
附录:
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict 注释介绍
通过上面的例子,我们可以看到 spring cache 主要使用两个注释标签,即 @Cacheable、@CachePut 和 @CacheEvict,我们总结一下其作用和配置方法。
表 1. @Cacheable 作用和配置方法
@Cacheable 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
| @Cacheable 主要的参数 | ||
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者 @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
表 2. @CachePut 作用和配置方法
@CachePut 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用
| @CachePut 主要的参数 | ||
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者 @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
表 3. @CacheEvict 作用和配置方法
@CachEvict 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空
| @CacheEvict 主要的参数 | ||
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”mycache”) 或者 @CachEvict(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才清空缓存 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”, condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
| allEntries | 是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true) |
| beforeInvocation | 是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,beforeInvocation=true) |
补充示例
自定义redis cache
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import org.springframework.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleValueWrapper;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
public class RedisCache implements Cache {
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
private String name;
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> getRedisTemplate() {
return redisTemplate;
}
public void setRedisTemplate(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public Object getNativeCache() {
return this.redisTemplate;
}
@Override
public ValueWrapper get(Object key) {
final String keyf = (String) key;
Object object = null;
object = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Object>() {
public Object doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
byte[] key = keyf.getBytes();
byte[] value = connection.get(key);
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
return toObject(value);
}
});
return (object != null ? new SimpleValueWrapper(object) : null);
}
@Override
public void put(Object key, Object value) {
final String keyf = (String) key;
final Object valuef = value;
final long liveTime = 86400;
redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Long>() {
public Long doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
byte[] keyb = keyf.getBytes();
byte[] valueb = toByteArray(valuef);
connection.set(keyb, valueb);
if (liveTime > 0) {
connection.expire(keyb, liveTime);
}
return 1L;
}
});
}
private byte[] toByteArray(Object obj) {
byte[] bytes = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.flush();
bytes = bos.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (oos != null) {
oos.close();
}
if (bos != null) {
bos.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return bytes;
}
private Object toObject(byte[] bytes) {
Object obj = null;
ByteArrayInputStream bis = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
obj = ois.readObject();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (ois != null) {
ois.close();
}
if (bis != null) {
bis.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return obj;
}
@Override
public void evict(Object key) {
final String keyf = (String) key;
redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Long>() {
public Long doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
return connection.del(keyf.getBytes());
}
});
}
@Override
public void clear() {
redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<String>() {
public String doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
connection.flushDb();
return "ok";
}
});
}
@Override
public <T> T get(Object key, Class<T> type) {
return null;
}
@Override
public ValueWrapper putIfAbsent(Object key, Object value) {
return null;
}
}

注意:
1、应用缓存的方法要使用 public 2、同一个类中调用缓存方法,需要 这样,才会生效






















 2207
2207

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








