简介:spring security 实现的权限控制,可以分别保护后台方法的管理,url连接访问的控制,以及页面元素的权限控制等,
security的保护,配置有简单到复杂基本有三部:
1) 采用硬编码的方式:具体做法就是在security.xml文件中,将用户以及所拥有的权限写死,一般是为了查看环境搭建的检查状态.
2) 数据库查询用户以及权限的方式,这种方式就是在用户的表中直接存入了权限的信息,比如 role_admin,role_user这样的权限信息,取出来的时候,再将其拆分.
3) 角色权限动态配置,这种方式值得是将权限角色单独存入数据库中,与用户进行相关联,然后进行相应的设置.
下面就这三种方式进行相应的程序解析
初始化环境搭建
新建web项目,导入其中的包,环境搭建就算是完了,下面一部我们开始security权限控制中方法的第一种.
硬编码配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.0"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/security/*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/security/dispatcher-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- 权限 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>下面我们就开始配置mvc的配置文件,名称为dispatcher-servlet.xml的springmvc的配置文件内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd">
<!--
使Spring支持自动检测组件,如注解的Controller
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <!-- 开启AOP -->
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"
p:prefix="/jsp/"
p:suffix=".jsp"
/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter">
<property name="messageConverters">
<list >
<ref bean="mappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter" />
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="mappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter" class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter" />
<!-- 数据库连接配置 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/power"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="516725"></property>
<property name="minPoolSize" value="10"></property>
<property name="MaxPoolSize" value="50"></property>
<property name="MaxIdleTime" value="60"></property><!-- 最少空闲连接 -->
<property name="acquireIncrement" value="5"></property><!-- 当连接池中的连接耗尽的时候 c3p0一次同时获取的连接数。 -->
<property name="TestConnectionOnCheckout" value="true" ></property>
</bean>
<bean id="JdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref local="dataSource"/>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 事务申明 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" >
<ref local="dataSource"/>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- Aop切入点 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="within(com.ucs.security.dao.*)" id="serviceOperaton"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txadvice" pointcut-ref="serviceOperaton"/>
</aop:config>
<tx:advice id="txadvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
</beans>下一步我们开始配置spring-securoty.xml的权限控制配置,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.1.xsd">
<!-- 对所有页面进行拦截,需要ROLE_USER权限 -->
<http auto-config='true'>
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER" />
</http>
<!-- 权限配置 jimi拥有两种权限 bob拥有一种权限 -->
<authentication-manager>
<authentication-provider>
<user-service>
<user name="jimi" password="123" authorities="ROLE_USER, ROLE_ADMIN" />
<user name="bob" password="456" authorities="ROLE_USER" />
</user-service>
</authentication-provider>
</authentication-manager>
</beans:beans>到此为止,权限的配置基本就结束了,下面就启动服务,securoty会为我们自动生成一个登陆页面,在地址栏中输入:http://localhost:8080/项目名称/spring_security_login,会出现一个登陆界面,尝试一下吧.看看登陆以后能不能按照你的权限配置进行控制.
下一步,我们开始讲解第二种,数据库的用户登陆并实现获取权限进行操作.
数据库权限控制
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`Id` int(11) NOT NULL auto_increment,
`logname` varchar(255) default NULL,
`password` varchar(255) default NULL,
`role_ids` varchar(255) default NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`Id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;我们修改spring-security.xml文件,让其不在写死这些权限和用户的控制:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.1.xsd">
<!-- 启用方法控制访问权限 用于直接拦截接口上的方法,拥有权限才能访问此方法-->
<global-method-security jsr250-annotations="enabled"/>
<!-- 自己写登录页面,并且登陆页面不拦截 -->
<http pattern="/jsp/login.jsp" security="none" />
<!-- 配置拦截页面 --> <!-- 启用页面级权限控制 使用表达式 -->
<http auto-config='true' access-denied-page="/jsp/403.jsp" use-expressions="true">
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')" />
<!-- 设置用户默认登录页面 -->
<form-login login-page="/jsp/login.jsp"/>
</http>
<authentication-manager>
<!-- 权限控制 引用 id是myUserDetailsService的server -->
<authentication-provider user-service-ref="myUserDetailsService"/>
</authentication-manager>
</beans:beans>下面编辑了自己的登陆页面,我们做一个解释:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>登录界面</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>登录界面</h3>
<form action="/项目根目录/j_spring_security_check" method="post">
<table>
<tr><td>User:</td><td><input type='text' name='j_username' value=''></td></tr>
<tr><td>Password:</td><td><input type='password' name='j_password'/></td></tr>
<tr><td colspan='2'><input name="submit" type="submit" value="Login"/></td></tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="sec" uri="http://www.springframework.org/security/tags" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; utf-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h5><a href="../j_spring_security_logout">logout</a></h5>
<!-- 拥有ROLE_ADMIN权限的才看的到 -->
<sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')">
<form action="#">
账号:<input type="text" /><br/>
密码:<input type="password"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>
</form>
</sec:authorize>
<p/>
<sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')">
显示拥有ROLE_USER权限的页面<br/>
<form action="#">
账号:<input type="text" /><br/>
密码:<input type="password"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>
</form>
</sec:authorize>
<p/>
<h5>测试方法控制访问权限</h5>
<a href="addreport_admin.do">添加报表管理员</a><br/>
<a href="deletereport_admin.do">删除报表管理员</a>
</body>
</html>下面展示的是访问controller层
package com.ucs.security.server;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import com.ucs.security.face.SecurityTestInterface;
@Controller
public class SecurityTest {
@Resource
private SecurityTestInterface dao;
@RequestMapping(value="/jsp/getinput")//查看最近收入
@ResponseBody
public boolean getinput(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletRequest res){
boolean b=dao.getinput();
return b;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/jsp/geoutput")//查看最近支出
@ResponseBody
public boolean geoutput(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletRequest res){
boolean b=dao.geoutput();
return b;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/jsp/addreport_admin")//添加报表管理员
@ResponseBody
public boolean addreport_admin(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletRequest res){
boolean b=dao.addreport_admin();
return b;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/jsp/deletereport_admin")//删除报表管理员
@ResponseBody
public boolean deletereport_admin(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletRequest res){
boolean b=dao.deletereport_admin();
return b;
}
@RequestMapping(value="/jsp/user")//普通用户登录
public ModelAndView user_login(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletRequest res){
dao.user_login();
return new ModelAndView("user");
}
}我们再次写入了一个内部方法调用的接口,这个我们可以使用权限进行方法的保护,在配置文件中<global-method-security jsr250-annotations="enabled"/>就是在接口上设置权限,当拥有权限时才能调用方法,没有权限是不能调用方法的,保证了安全性
package com.ucs.security.face;
import javax.annotation.security.RolesAllowed;
import com.ucs.security.pojo.Users;
public interface SecurityTestInterface {
boolean getinput();
boolean geoutput();
@RolesAllowed("ROLE_ADMIN")//拥有ROLE_ADMIN权限的用户才可进入此方法
boolean addreport_admin();
@RolesAllowed("ROLE_ADMIN")
boolean deletereport_admin();
Users findbyUsername(String name);
@RolesAllowed("ROLE_USER")
void user_login();
}package com.ucs.security.dao;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowCallbackHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.ucs.security.face.SecurityTestInterface;
import com.ucs.security.pojo.Users;
@Repository("SecurityTestDao")
public class SecurityTestDao implements SecurityTestInterface{
Logger log=Logger.getLogger(SecurityTestDao.class);
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTamplate;
public boolean getinput() {
log.info("getinput");
return true;
}
public boolean geoutput() {
log.info("geoutput");
return true;
}
public boolean addreport_admin() {
log.info("addreport_admin");
return true;
}
public boolean deletereport_admin() {
log.info("deletereport_admin");
return true;
}
public Users findbyUsername(String name) {
final Users users = new Users();
jdbcTamplate.query("SELECT * FROM USER WHERE logname = ?",
new Object[] {name},
new RowCallbackHandler() {
@Override
public void processRow(java.sql.ResultSet rs)
throws SQLException {
users.setName(rs.getString("logname"));
users.setPassword(rs.getString("password"));
users.setRole(rs.getString("role_ids"));
}
});
log.info(users.getName()+" "+users.getPassword()+" "+users.getRole());
return users;
}
@Override
public void user_login() {
log.info("拥有ROLE_USER权限的方法访问:user_login");
}
}下面就是重要的一个类:MyUserDetailsService这个类需要去实现UserDetailsService这个接口:
package com.ucs.security.context;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.GrantedAuthorityImpl;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.ucs.security.face.SecurityTestInterface;
import com.ucs.security.pojo.Users;
/**
* 在spring-security.xml中如果配置了
* <authentication-manager>
<authentication-provider user-service-ref="myUserDetailsService" />
</authentication-manager>
* 将会使用这个类进行权限的验证。
*
* **/
@Service("myUserDetailsService")
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService{
@Resource
private SecurityTestInterface dao;
//登录验证
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String name)
throws UsernameNotFoundException {
System.out.println("show login name:"+name+" ");
Users users =dao.findbyUsername(name);
Set<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuths=obtionGrantedAuthorities(users);
boolean enables = true;
boolean accountNonExpired = true;
boolean credentialsNonExpired = true;
boolean accountNonLocked = true;
//封装成spring security的user
User userdetail = new User(users.getName(), users.getPassword(), enables, accountNonExpired, credentialsNonExpired, accountNonLocked, grantedAuths);
return userdetail;
}
//查找用户权限
public Set<GrantedAuthority> obtionGrantedAuthorities(Users users){
String roles[] = users.getRole().split(",");
Set<GrantedAuthority> authSet=new HashSet<GrantedAuthority>();
for (int i = 0; i < roles.length; i++) {
authSet.add(new GrantedAuthorityImpl(roles[i]));
}
return authSet;
}
}然后将从数据库查到的密码和权限设置到security自己的User类中,security会自己去匹配前端发来的密码和用户权限去对比,然后判断用户是否可以登录进来。登录失败还是停留在登录界面。
在user.jsp中测试了用户权限来验证是否可以拦截没有权限用户去访问资源:
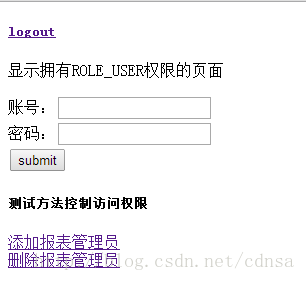
点击添加报表管理员或者删除报表管理员时候会跳到403.jsp因为没有权限去访问资源,在接口上我们设置了访问的权限:
- @RolesAllowed("ROLE_ADMIN")//拥有ROLE_ADMIN权限的用户才可进入此方法
- boolean addreport_admin();
- @RolesAllowed("ROLE_ADMIN")
- boolean deletereport_admin();
因为登录进来的用户时ROLE_USER权限的。就被拦截下来。logout是登出,返回到登录界面,并且用户在security中的缓存清掉了。一样会对资源进行拦截。
下面我们就开始研究第三种方式,需要用将角色可访问资源链接保存到数据库,可以随时更改,也就是我们所谓的url的控制,什么鸡毛,就是数据库存放了角色权限,可以实时更改,而不再xml文件中写死.
下面链接,我给大家提供了一个源码的下载链接 , 这是本届讲解的内容的源码,运行无误,狼心货 http://download.csdn.net/detail/u014201191/8929187
角色权限管理
# Host: localhost (Version: 5.0.22-community-nt)
# Date: 2014-03-28 14:58:01
# Generator: MySQL-Front 5.3 (Build 4.81)
/*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */;
#
# Structure for table "power"
#
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `power`;
CREATE TABLE `power` (
`Id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`power_name` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`resource_ids` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`Id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
#
# Data for table "power"
#
INSERT INTO `power` VALUES (1,'查看报表','1,2,'),(2,'管理系统','3,4,');
#
# Structure for table "resource"
#
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `resource`;
CREATE TABLE `resource` (
`Id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`resource_name` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`resource_url` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`Id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
#
# Data for table "resource"
#
INSERT INTO `resource` VALUES (1,'查看最近收入','/jsp/getinput.do'),(2,'查看最近支出','/jsp/geoutput.do'),(3,'添加报表管理员','/jsp/addreport_admin.do'),(4,'删除报表管理员','/jsp/deletereport_admin.do');
#
# Structure for table "role"
#
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role`;
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`Id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`role_name` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`role_type` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`power_ids` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`Id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
#
# Data for table "role"
#
INSERT INTO `role` VALUES (1,'系统管理员','ROLE_ADMIN','1,2,'),(2,'报表管理员','ROLE_USER','1,');
#
# Structure for table "user"
#
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`Id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`logname` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`role_ids` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`Id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
SELECT * FROM USER;
#
# Data for table "user"
#
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (1,'admin','123456','ROLE_USER,ROLE_ADMIN'),(3,'zhang','123','ROLE_USER');
COMMIT;下面我们就开始写入spring-security.xml的配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.1.xsd">
<!-- 启用方法控制访问权限 用于直接拦截接口上的方法,拥有权限才能访问此方法-->
<global-method-security jsr250-annotations="enabled"/>
<!-- 自己写登录页面,并且登陆页面不拦截 -->
<http pattern="/jsp/login.jsp" security="none" />
<!-- 配置拦截页面 --> <!-- 启用页面级权限控制 使用表达式 -->
<http auto-config='true' access-denied-page="/jsp/403.jsp" use-expressions="true">
<!-- requires-channel="any" 设置访问类型http或者https -->
<intercept-url pattern="/admin/**" access="hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')" requires-channel="any"/>
<!-- intercept-url pattern="/admin/**" 拦截地址的设置有加载先后的顺序,
admin/**在前面请求admin/admin.jsp会先去拿用户验证是否有ROLE_ADMIN权限,有则通过,没有就拦截。如果shi
pattern="/**" 设置在前面,当前登录的用户有ROLE_USER权限,那么就可以登录到admin/admin.jsp
所以两个配置有先后的。
-->
<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')" requires-channel="any"/>
<!-- 设置用户默认登录页面 -->
<form-login login-page="/jsp/login.jsp"/>
<!-- 基于url的权限控制,加载权限资源管理拦截器,如果进行这样的设置,那么
<intercept-url pattern="/admin/**" 就可以不进行配置了,会在数据库的资源权限中得到对应。
对于没有找到资源的权限为null的值就不需要登录才可以查看,相当于public的。可以公共访问
-->
<custom-filter ref="securityFilter" before="FILTER_SECURITY_INTERCEPTOR"/>
</http>
<!-- 当基于方法权限控制的时候只需要此配置,在接口上加上权限即可控制方法的调用
<authentication-manager>
<authentication-provider user-service-ref="myUserDetailsService"/>
</authentication-manager>
-->
<!-- 资源权限控制 -->
<beans:bean id="securityFilter" class="com.ucs.security.context.MySecurityFilter">
<!-- 用户拥有的权限 -->
<beans:property name="authenticationManager" ref="myAuthenticationManager" />
<!-- 用户是否拥有所请求资源的权限 -->
<beans:property name="accessDecisionManager" ref="myAccessDecisionManager" />
<!-- 资源与权限对应关系 -->
<beans:property name="securityMetadataSource" ref="mySecurityMetadataSource" />
</beans:bean>
<authentication-manager alias="myAuthenticationManager">
<!-- 权限控制 引用 id是myUserDetailsService的server -->
<authentication-provider user-service-ref="myUserDetailsService"/>
</authentication-manager>
</beans:beans>同时,我们增加在xml文件中配置的java类:
package com.ucs.security.context;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDecisionManager;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.InsufficientAuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("myAccessDecisionManager")
public class MyAccessDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager{
Logger log=Logger.getLogger(MyAccessDecisionManager.class);
@Override
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException,
InsufficientAuthenticationException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//如果对应资源没有找到角色 则放行
if(configAttributes == null){
return ;
}
log.info("object is a URL:"+object.toString()); //object is a URL.
Iterator<ConfigAttribute> ite=configAttributes.iterator();
while(ite.hasNext()){
ConfigAttribute ca=ite.next();
String needRole=ca.getAttribute();
for(GrantedAuthority ga:authentication.getAuthorities()){
if(needRole.equals(ga.getAuthority())){ //ga is user's role.
return;
}
}
}
throw new AccessDeniedException("no right");
}
@Override
public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return true;
}
}MySecurityFilter这个类是拦截中一个主要的类,拦截的时候会先通过这里:
package com.ucs.security.context;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.security.access.intercept.AbstractSecurityInterceptor;
import org.springframework.security.access.intercept.InterceptorStatusToken;
import org.springframework.security.web.FilterInvocation;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
public class MySecurityFilter extends AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements Filter {
Logger log=Logger.getLogger(MySecurityFilter.class);
private FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource securityMetadataSource;
public SecurityMetadataSource obtainSecurityMetadataSource() {
return this.securityMetadataSource;
}
public FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource getSecurityMetadataSource() {
return securityMetadataSource;
}
public void setSecurityMetadataSource(
FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource securityMetadataSource) {
this.securityMetadataSource = securityMetadataSource;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi=new FilterInvocation(req,res,chain);
log.info("--------MySecurityFilter--------");
invok(fi);
}
private void invok(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
// object为FilterInvocation对象
//1.获取请求资源的权限
//执行Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = SecurityMetadataSource.getAttributes(object);
//2.是否拥有权限
//获取安全主体,可以强制转换为UserDetails的实例
//1) UserDetails
// Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
//this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
//用户拥有的权限
//2) GrantedAuthority
//Collection<GrantedAuthority> authenticated.getAuthorities()
log.info("用户发送请求! ");
InterceptorStatusToken token = null;
token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
} finally {
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
}
}
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public Class<? extends Object> getSecureObjectClass() {
//下面的MyAccessDecisionManager的supports方面必须放回true,否则会提醒类型错误
return FilterInvocation.class;
}
}package com.ucs.security.context;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute;
import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityConfig;
import org.springframework.security.web.FilterInvocation;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.ucs.security.face.SecurityTestInterface;
import com.ucs.security.pojo.URLResource;
@Service("mySecurityMetadataSource")
public class MySecurityMetadataSource implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource{
//由spring调用
Logger log=Logger.getLogger(MySecurityMetadataSource.class);
@Resource
private SecurityTestInterface dao;
private static Map<String, Collection<ConfigAttribute>> resourceMap = null;
/*public MySecurityMetadataSource() {
loadResourceDefine();
}*/
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return true;
}
//加载所有资源与权限的关系
private void loadResourceDefine() {
if(resourceMap == null) {
resourceMap = new HashMap<String, Collection<ConfigAttribute>>();
/*List<String> resources ;
resources = Lists.newArrayList("/jsp/user.do","/jsp/getoutput.do");*/
List<URLResource> findResources = dao.findResource();
for(URLResource url_resource:findResources){
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes = new ArrayList<ConfigAttribute>();
ConfigAttribute configAttribute = new SecurityConfig(url_resource.getRole_Name());
for(String resource:url_resource.getRole_url()){
configAttributes.add(configAttribute);
resourceMap.put(resource, configAttributes);
}
}
//以权限名封装为Spring的security Object
}
Gson gson =new Gson();
log.info("权限资源对应关系:"+gson.toJson(resourceMap));
Set<Entry<String, Collection<ConfigAttribute>>> resourceSet = resourceMap.entrySet();
Iterator<Entry<String, Collection<ConfigAttribute>>> iterator = resourceSet.iterator();
}
//返回所请求资源所需要的权限
public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object) throws IllegalArgumentException {
String requestUrl = ((FilterInvocation) object).getRequestUrl();
log.info("requestUrl is " + requestUrl);
if(resourceMap == null) {
loadResourceDefine();
}
log.info("通过资源定位到的权限:"+resourceMap.get(requestUrl));
return resourceMap.get(requestUrl);
}
}dao类中的方法有所改变:
package com.ucs.security.dao;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowCallbackHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.ucs.security.face.SecurityTestInterface;
import com.ucs.security.pojo.URLResource;
import com.ucs.security.pojo.Users;
@Repository("SecurityTestDao")
public class SecurityTestDao implements SecurityTestInterface{
Logger log=Logger.getLogger(SecurityTestDao.class);
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTamplate;
public boolean getinput() {
log.info("getinput");
return true;
}
public boolean geoutput() {
log.info("geoutput");
return true;
}
public boolean addreport_admin() {
log.info("addreport_admin");
return true;
}
public boolean deletereport_admin() {
log.info("deletereport_admin");
return true;
}
public Users findbyUsername(String name) {
final Users users = new Users();
jdbcTamplate.query("SELECT * FROM USER WHERE logname = ?",
new Object[] {name},
new RowCallbackHandler() {
@Override
public void processRow(java.sql.ResultSet rs)
throws SQLException {
users.setName(rs.getString("logname"));
users.setPassword(rs.getString("password"));
users.setRole(rs.getString("role_ids"));
}
});
log.info(users.getName()+" "+users.getPassword()+" "+users.getRole());
return users;
}
@Override
public void user_login() {
log.info("拥有ROLE_USER权限的方法访问:user_login");
}
@Override
//获取所有资源链接
public List<URLResource> findResource() {
List<URLResource> uRLResources =Lists.newArrayList();
Map<String,Integer[]> role_types=new HashMap<String, Integer[]>();
List<String> role_Names=Lists.newArrayList();
List list_role=jdbcTamplate.queryForList("select role_type,power_ids from role");
Iterator it_role = list_role.iterator();
while(it_role.hasNext()){
Map role_map=(Map)it_role.next();
String object = (String)role_map.get("power_ids");
String type = (String)role_map.get("role_type");
role_Names.add(type);
String[] power_ids = object.split(",");
Integer[] int_pow_ids=new Integer[power_ids.length];
for(int i=0;i<power_ids.length;i++){
int_pow_ids[i]=Integer.parseInt(power_ids[i]);
}
role_types.put(type, int_pow_ids);
}
for(String name:role_Names){
URLResource resource=new URLResource();
Integer[] ids=role_types.get(name);//更具角色获取权限id
List<Integer> all_res_ids=Lists.newArrayList();
List<String> urls=Lists.newArrayList();
for(Integer id:ids){//更具权限id获取资源id
List resource_ids=jdbcTamplate.queryForList("select resource_ids from power where id =?",new Object[]{id});
Iterator it_resource_ids = resource_ids.iterator();
while(it_resource_ids.hasNext()){
Map resource_ids_map=(Map)it_resource_ids.next();
String[] ids_str=((String)resource_ids_map.get("resource_ids")).split(",");
for(int i=0;i<ids_str.length;i++){
all_res_ids.add(Integer.parseInt(ids_str[i]));
}
}
}
for(Integer id:all_res_ids){
List resource_urls=jdbcTamplate.queryForList("select resource_url from resource where id=?",new Object[]{id});
Iterator it_res_urls = resource_urls.iterator();
while(it_res_urls.hasNext()){
Map res_url_map=(Map)it_res_urls.next();
urls.add(((String)res_url_map.get("resource_url")));
}
}
//将对应的权限关系添加到URLRsource
resource.setRole_Name(name);
resource.setRole_url(urls);
uRLResources.add(resource);
}
Gson gson =new Gson();
log.info("权限资源对应关系:"+gson.toJson(uRLResources));
return uRLResources;
}
}package com.ucs.security.face;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.security.RolesAllowed;
import com.ucs.security.pojo.URLResource;
import com.ucs.security.pojo.Users;
public interface SecurityTestInterface {
boolean getinput();
boolean geoutput();
//@RolesAllowed("ROLE_ADMIN")//拥有ROLE_ADMIN权限的用户才可进入此方法
boolean addreport_admin();
//@RolesAllowed("ROLE_ADMIN")
boolean deletereport_admin();
Users findbyUsername(String name);
//@RolesAllowed("ROLE_USER")
void user_login();
List<URLResource> findResource();
}首先用户没有登录的时候可以访问一些公共的资源,但是必须把<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')" requires-channel="any"/> 配置删掉,不拦截,任何资源都可以访问,这样公共资源可以任意访问。
对于需要权限的资源已经在数据库配置,如果去访问会直接跳到登录界面。需要登录。
根据登录用户不同分配到的角色就不一样,根据角色不同来获取该角色可以访问的资源。
拥有ROLE_USER角色用户去访问ROLE_ADMIN的资源会返回到403.jsp页面。拥有ROLE_USER和ROLE_ADMIN角色的用户可以去访问两种角色的资源。公共的资源两种角色都可以访问。
security提供了默认的登出地址。登出后用户在spring中的缓存就清除了。






















 1846
1846

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








