
目录结构:
1.全文检索
2.Lucene入门
3.Lucene进阶
全文检索
一, 生活中的搜索:
1.Windows系统中的有搜索功能:打开“我的电脑”,按“F3”就可以使用查找的功能,查找指定的文件或文件夹。搜索的范围是整个电脑中的文件资源。
2.Eclipse中的帮助子系统:点击HelpHelp Contents,可以查找出相关的帮助信息。搜索的范围是Eclipse的所有帮助文件。
搜索引擎,如Baidu或Google等,可以查询到互联网中的网页、PDF、DOC、PPT、图片、音乐、视频等。
3.Mac中的Spotlight搜索
4.数据库中检索检查某一个关键字的例子。
select * from topic where content like '%java%'
文本检索,会使索引失效
存在问题:
1.搜索速度慢
2.搜索效果不好.
3.没有相关度排序
二, 什么是全文检索?
全文检索是指计算机索引程序通过扫描文章中的每一个词,对每一个词建立一个索引,指明该词在文章中出现的次数和位置,当用户查询时,检索程序就根据事先建立的索引进行查找,并将查找的结果反馈给用户的检索方式。这个过程类似于通过字典中的检索字表查字的过程。
在说全文检索之前我们先来了解一下数据分类
结构化数据:指具有固定格式或有限长度的数据,如数据库,元数据等;
半结构化数据:半结构化数据
非结构化数据:指不定长或无固定格式的数据,如邮件,word文档等;
非结构化数据又一种叫法叫全文数据。从全文数据中进行检索就叫全文检索。
特点:只关注文本不考虑语义
三, 为什么使用 ?
搜索速度:将数据源中的数据都通过全文索引
匹配效果:过词元(term)进行匹配,通过语言分析接口的实现,可以实现对中文等非英语的支持。
相关度:有匹配度算法,将匹配程度(相似度)比较高的结果排在前面。
适用场景:关系数据库中进行模糊查询时,数据库自带的索引将不起作用,此时需要通过全文检索来提高速度;比如:
网站系统中针对内容的模糊查询;
select * from article where content like '%上海平安%'
ERP系统中产品等数据的模糊查询,BBS、BLOG中的文章搜索等;
各种搜索引擎运行依赖于全文检索;
只对指定领域的网站进行索引与搜索(即垂直搜索,如“818工作搜索”、“有道购物搜索”)
要在word、pdf等各种各样的数据格式中检索内容;
其它场合:比如搜狐拼音输入法、Google输入法等。
四, 工作原理
1.如何查询全文数据?
顺序扫描法(Serial Scanning):所谓顺序扫描,比如要找内容包含某一个字符串的文件,就是一个文档一个文档的看,对于每一个文档,从头看到尾,如果此文档包含此字符串,则此文档为我们要找的文件,接着看下一个文件,直到扫描完所有的文件。比如Window自带的搜索。
如何提升全文检索的速度?
对非结构化数据顺序扫描很慢,对结构化数据的搜索却相对较快(由于结构化数据有一定的结构可以采取一定的搜索算法加快速度),那么把我们的非结构化数据想办法弄得有一定结构不就行了吗?关系数据库中存储的都是结构化数据,因此很检索都比较快。
从非结构化数据中提取出的然后重新组织的信息,我们称之索引。
字典及图书目录的原理。
2.全文检索的过程
索引创建:将现实世界中所有的结构化和非结构化数据提取信息,创建索引的过程。
搜索索引:就是得到用户的查询请求,搜索创建的索引,然后返回结果的过程。
3.案例分析
索引文件中应该存放什么?
索引文件中只需要存放单词及文档编号即可
要查出即包含is,又包括 shanghai及pingan的文档,先获得包含is的文档列表,再获得包含shanghai及pingan的文档列表,最合做一个集合并运算,就得出文档1及文档3。
文档0
What is your name?
文档1
My name is shanghai pingan!
文档2
What is that?
文档3
It is shanghai pingan, ShangHai Pingan
首先将我们非结构化数据存储到文档区
| 文档编号 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 0 | What is your name? |
| 1 | My name is shanghai pingan! |
| 2 | What is that? |
| 3 | It is shanghai pingan, ShangHai Pingan |
如何建立索引?
第一步:分词组件(Tokenizer)对文档进行处理,此过程称为Tokenize。
- 将文档分成一个一个单独的单词。(用空格分开)
- 去除标点符号。
- 去除停词(Stop word)。大量出现的助词,比如is,it等。中文:的,了,呢
经过分词(Tokenizer)后得到的结果称为词元(Token)。词元(Token)如下:
shanghai,ShangHai,pingan,My,name,What,your,pingan
第二步:将得到的词元(Token)传给语言处理组件(Linguistic Processor),对于英语,处理大致如下:
- 变为小写(Lowercase)。
- 将单词缩减为词根形式,如“cars”到“car”等。这种操作称为:stemming。
- 将单词转变为词根形式,如“drove”到“drive”等。这种操作称为:lemmatization。
语言处理组件(linguistic processor)的结果称为词(Term)。结果如下:
shanghai,pingan,my,name,what,your
第三步:把得到的词Term传给索引组件(Indexer)处理,处理过程如下:
1、把得到的词创建一个字典表
| 词term | 文档Document |
|---|---|
| what | 0 |
| name | 0 |
| My | 1 |
| name | 1 |
| shanghai | 1 |
| pingan | 1 |
| what | 2 |
| that | 2 |
| shanghai | 3 |
| pingan | 3 |
| shanghai | 3 |
| pingan | 3 |
2、对字典按字母顺序进行排序
| 词term | 文档Document |
|---|---|
| shanghai | 1 |
| shanghai | 3 |
| shanghai | 3 |
| pingan | 1 |
| pingan | 3 |
| pingan | 3 |
| my | 1 |
| name | 0 |
| name | 1 |
| what | 0 |
| what | 2 |
| your | 0 |
3、合并相同的词(Term)成为文档倒排(Posting List)链表。
| 词term | 出现次数 | 文档 | Frequency | 文档 | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shanghai | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| pingan | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| my | 1 | 1 | 1 | ~ | ~ |
| name | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| what | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| your | 1 | 0 | 1 | ~ | ~ |
最终会存储两部分一个文档区和一个索引区
| 词元 | 文档编号 |
|---|---|
| what | 0,2 |
| your | 0 |
| name | 0,1 |
| my | 1 |
| shanghai | 1,3,3 |
| pingan | 1,3,3 |
| that | 2 |
搜索处理的大致流程:
1、接收用户输入的搜索词及关键字并作简单处理;
2、对查询语句进行词法分析,语法分析,及语言处理;
3、查询到包含输出词的文档列表,并进行相关逻辑运算;
4、根据文档的相关性进行排序,把相关性最高的文档返回出来。
4.文档相关性
计算词的权重:
1、找出词(Term)对文档的重要性的过程称为计算词的权重(Term weight)的过程。主要有两个因素:
A、Term Frequency (tf):即此Term在此文档中出现了多少次。tf 越大说明越重要。
B、 Document Frequency (df):即有多少文档包含该Term。df 越大说明越不重要。
2、判断Term之间的关系从而得到文档相关性的过程,也即向量空间模型的算法(VSM)。
实现方式:把文档看作一系列词(Term),每一个词(Term)都有一个权重(Term weight),不同的词(Term)根据自己在文档中的权重来影响文档相关性的打分计算
5.全文检索应用架构
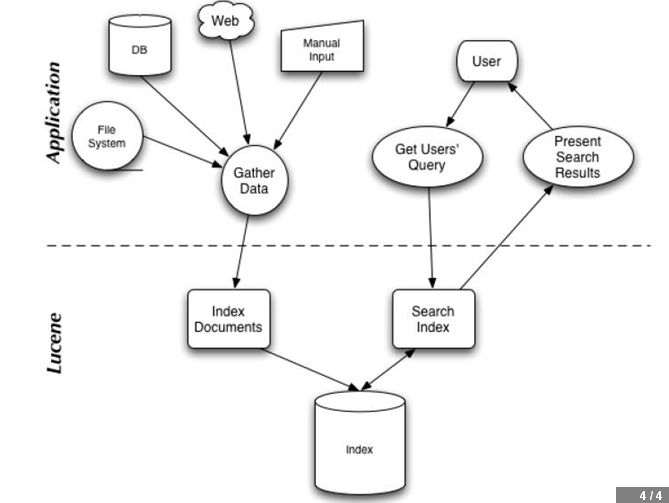
6.全文检索的流程对应的Lucene 实现的包结构
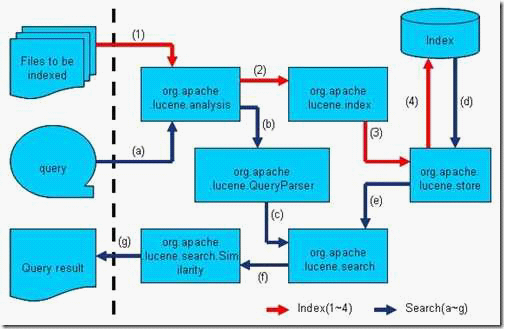
Lucene 的analysis 模块主要负责词法分析及语言处理而形成Term。
Lucene的index模块主要负责索引的创建,里面有IndexWriter。
Lucene的store模块主要负责索引的读写。
Lucene 的QueryParser主要负责语法分析。
Lucene的search模块主要负责对索引的搜索。
Lucene入门
Lucene是什么?
Lucene是一个用Java写的高性能、可伸缩的全文检索引擎工具包,它可以方便的嵌入到各种应用中实现针对应用的全文索引/检索功能。Lucene的目标是为各种中小型应用程序加入全文检索功能。
开发步骤
建立索引文件
1,创建一个测试类LuceneTest
2,导入jar包
lucene-core-4.10.4.jar 核心包
lucene-analyzers-common-4.10.4.jar 分词器包
3,创建索引写入器IndexWriter 传入对应的参数:索引需要存放的位置,索引写入器配置对象(配置版本,分词器)
4.内容写入之后,写入到二进制文件中不方便查看,使用工具(lukeall-4.10.0.jar)查看索引库
public class LuceneTest {
String content1 = "hello world";
String content2 = "hello java world";
String content3 = "hello lucene world";
String indexPath = "hello";
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();//分词器
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() throws Exception {
//1.创建索引写入器
Directory d = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexPath));//索引需要存放的位置
//创建索引写入器配置对象
IndexWriterConfig conf = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_4_10_4, analyzer);
IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(d, conf);
//2.写入文档信息
//添加文档 定义字段的存储规则
FieldType type = new FieldType();
type.setIndexed(true);//是否要索引
type.setStored(true);//是否需要存储
Document document1 = new Document();//数据库中的一条数据
//new Field("字段名","字段内容","字段的配置属性")
document1.add(new Field("title", "doc1", type));//该条记录中的字段 title:doc1
document1.add(new Field("content", content1, type));//content: hello world
writer.addDocument(document1);
Document document2 = new Document();
document2.add(new Field("title", "doc2", type));
document2.add(new Field("content", content2, type));
writer.addDocument(document2);
Document document3 = new Document();
document3.add(new Field("title", "doc3", type));
document3.add(new Field("content", content3, type));
writer.addDocument(document3);
//需要把添加的记录保存
writer.commit();
writer.close();
}
}
运行测试类会在该项目目录下生成一个hello文件夹
打开_0.xfs文件,这时我们看不出一个所以然
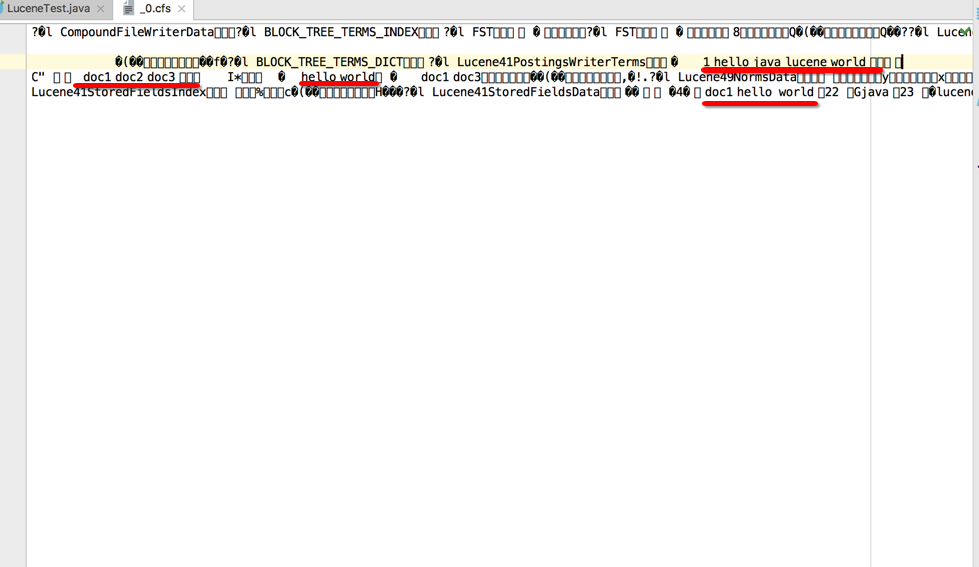
使用工具(lukeall-4.10.0.jar)查看索引库
只需在终端通过命令行 java -jar lukeall-4.10.0.jar 即可
需要在Path路径上找到hello索引库的绝对路径
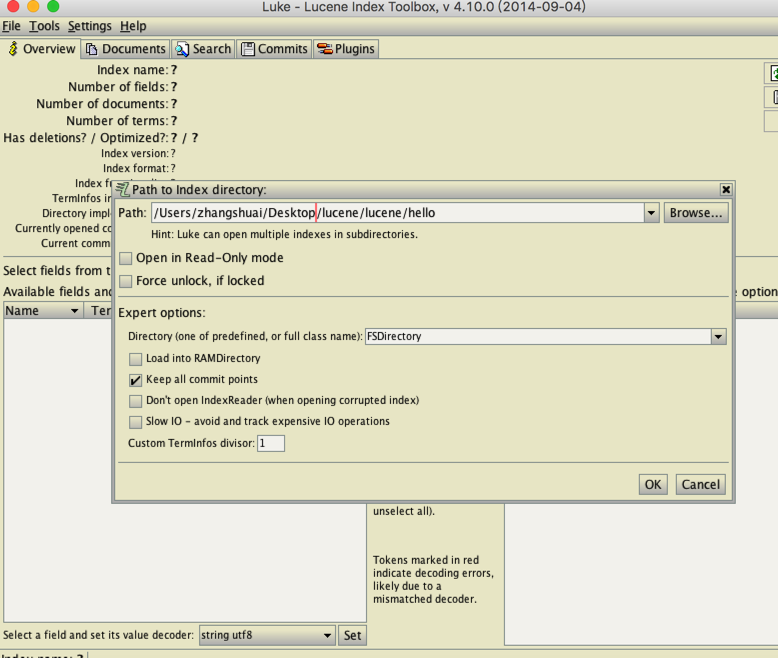
点击OK即可看到索引库
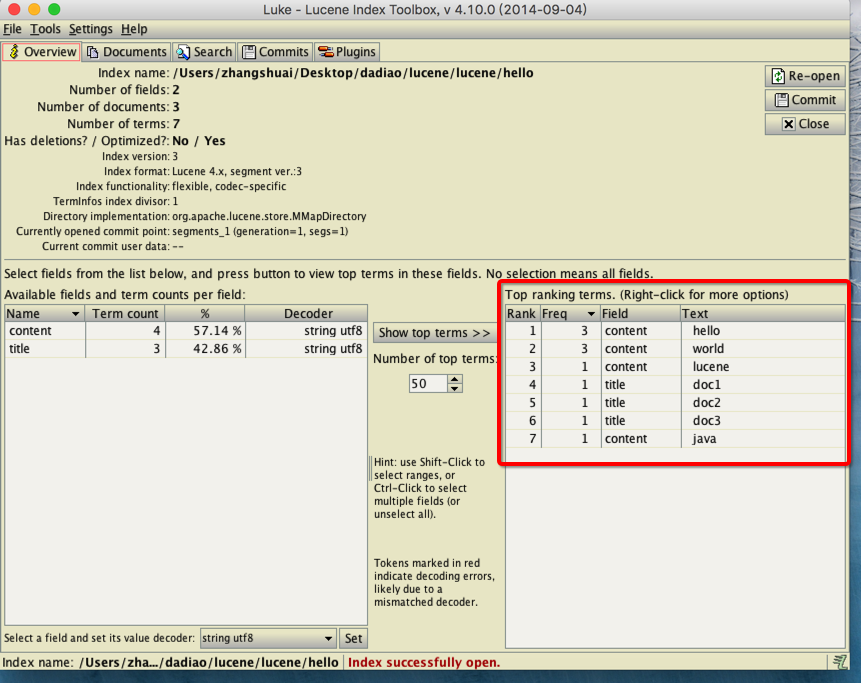
查询索引库
0.导入jar包lucene-queryparser-4.10.4.jar(将字符串变成Query对象)
1.创建测试方法searchIndex()
2.创建索引查询对象IndexSearcher
3.根据查询的文本内容解析成Query查询对象(导入jar包lucene-queryparser-4.10.4.jar)设置查询字段,分词器
4.根据查询器查询到文档编号
5.通过文档编号查询对应的文档内容
//索引查询过程
@Test
public void searchIndex() throws Exception {
//1.创建索引写入器
Directory d = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexPath));
//创建分词器
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();
//打开索引目录
IndexReader r = DirectoryReader.open(d);
//创建索引查询对象
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(r);
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser("content", analyzer);
Query query = parser.parse("hello");//查询hello
//search(查询对象,符合条件的前n条记录)
TopDocs search = searcher.search(query, 10000);//n:前几个结果
System.out.println("符合条件的记录有多少个:" + search.totalHits);
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = search.scoreDocs;
for (int i = 0; i < scoreDocs.length; i++) {
System.out.println("*******************************");
System.out.println("分数:" + scoreDocs[i].score);//相关度的排序
int docId = scoreDocs[i].doc;//文档编号
Document document = searcher.doc(docId);
System.out.println("文档编号 docId--->" + docId);
System.out.println("标题内容 title:--->" + document.get("content"));
}
}
打印结果:
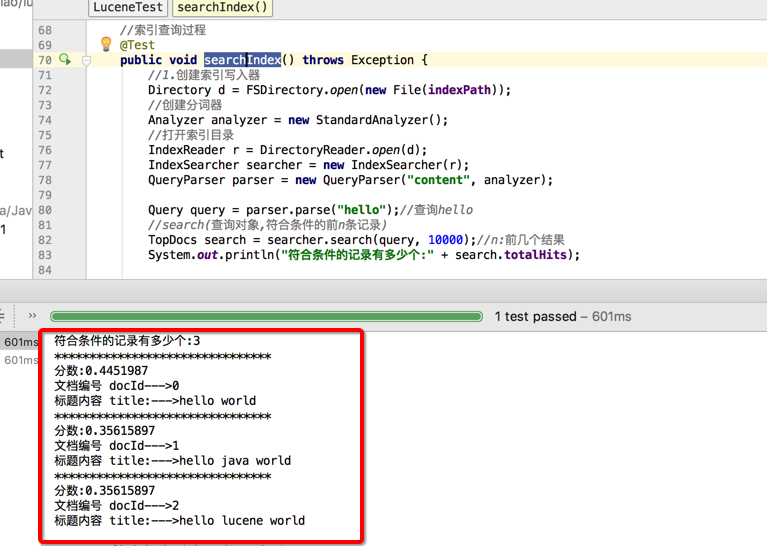
常用API
Directory:索引目录用于存放lucene索引文件
Directory是一个对索引目录的一个抽象,索引目录可以存放在普通的文件中,也可以位于数据库,或其它的远程服务中;一般情况下均使用文件来索引目录,这时一个Directory就相当于一个文件夹。
SimpleFSDirectory:直接使用java.io.RandomAccessFile类来操作索引文件,在普通的Lucene应用中,可以直接使用SimpleFSDirectory。
SimpleFSDirectory类:直接使用java.io.RandomAccessFile类来操作索引文件,在普通的Lucene应用中,这是最简单的用法。
构造函数:
SimpleFSDirectory(File path) :直接根据一个文件夹地址来创建索引目录;
MMapDirectory(File path) :让OS把整个索引文件映射到虚拟地址空间,这样Lucene就会觉得索引在内存中。
Document:当往索引中加入内容的时候,每一条信息用一个子Document来表示,Document的意思表示文档,也可以理解成记录,与关系数据表中的一行数据记录类似;
在Document创建完以后,直接调用其提供的字段操作方法来操作其中的字段对象。
Document提供的方法主要包括:
字段添加:add(Field field)
字段删除:removeField、removeFields
获取字段或值:get、getBinaryValue、getField、getFields等
Field:Field代表Document中的一行数据,相当于一条Lucene记录中的一列。
Lucene提供了一个接口Fieldable,其它的API大多针对这个接口编程,因此Lucene中的列对象实际上是由Fieldable来定义,实现该接口的除了Field类,还包括NumericField等。在实际开发中,主要使用的是Field类。
Field类提供的常用构造方法:
1、Field(String name, String value, Field.Store store, Field.Index index) -通过字段名称,字段值,存储类型及索引方式来创建一个字段;
2、Field(String name, byte[] value, Field.Store store) -通过字段名称、字段值(字节码)及字段存储方式创建字段对象;
3、Field(String name, Reader reader) -根据字段名称及Reader对象创建字段对象;
4、其它构造方法,详情查看API。
new Field("title", "中国太平", Store.NO, Index.ANALYZED);
new Field("content", "比较好的保险公司", Store.YES, Index.ANALYZED);
FieldType:Lucene中,在创建Field的时候,可以指定Field的store及index属性;
store属性:表示字段值是否存储,True表示要存储,而False则表示不存储;
type.setStored(true);//是否需要存储在文档区中
indexed属性:表示字段的是否需要建立索引,即是否支持搜索。tokenized属性:表示字段是否需要根据Analyzer规则进行分词
创建FieldTest测试类(复制上面的类修改类名)
定义字段的存储规则
FieldType type2 = new FieldType();
type2.setIndexed(true);//该字段是否要索引
type2.setStored(true);//是否需要存储在文档区中
type2.setTokenized(false);//字段是否分词
type2.setTokenized(false);//字段是否分词
设置所有的字段的配置属性为type2
document1.add(new Field("content", content1, type2));
document2.add(new Field("content", content2, type2));
document3.add(new Field("content", content3, type2));
public class FieldTest {
String content1 = "hello world";
String content2 = "hello java world";
String content3 = "hello lucene world";
String indexPath = "fieldType";
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();//分词器
//创建索引
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() throws Exception {
//1.创建索引写入器
Directory d = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexPath));//索引需要存放的位置
//创建索引写入器配置对象
IndexWriterConfig confg = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_4_10_4, analyzer);
confg.setOpenMode(IndexWriterConfig.OpenMode.CREATE);//索引每次重新创建
IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(d, confg);
//2.写入文档信息
//添加文档 定义字段的存储规则
FieldType type = new FieldType();
type.setIndexed(true);//该字段是否要索引
type.setStored(true);//是否需要存储
type.setTokenized(true);
FieldType type2 = new FieldType();
type2.setIndexed(true);//该字段是否要索引
type2.setStored(true);//是否需要存储
type2.setTokenized(false);//字段是否分词
Document document1 = new Document();//数据库中的一条数据
//new Field("字段名","字段内容","字段的配置属性")
document1.add(new Field("title", "doc1", type));//该条记录中的字段 title:doc1
document1.add(new Field("content", content1, type2));//content: hello world
writer.addDocument(document1);
Document document2 = new Document();
document2.add(new Field("title", "doc2", type));
document2.add(new Field("content", content2, type2));
writer.addDocument(document2);
Document document3 = new Document();
document3.add(new Field("title", "doc3", type));
document3.add(new Field("content", content3, type2));
writer.addDocument(document3);
//需要把添加的记录保存
writer.commit();
writer.close();
}
}
运行测试类
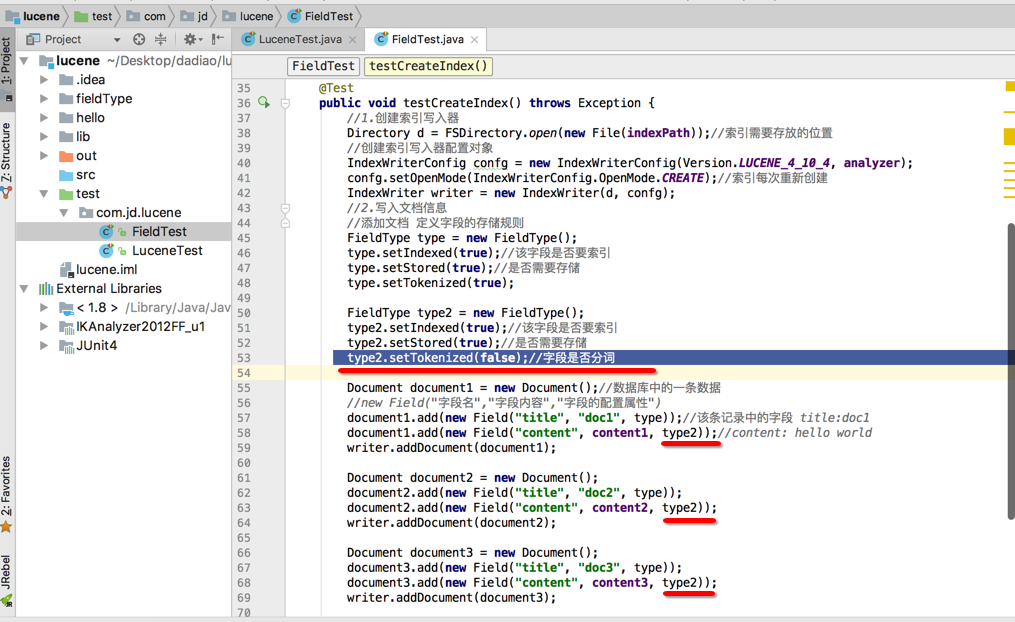
查看索引库
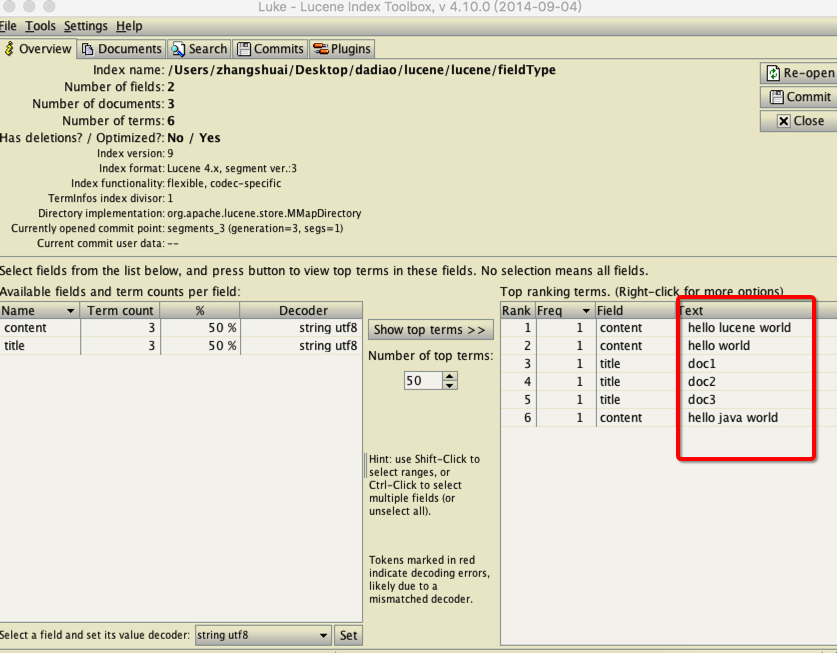
当我们搜索用户名或者地名希望是完整的词元,不希望被分割,此时就可以设置该字段的tokenize属性为false,设置不进行分词
在索引库中:
1.标题和内容都通过分词器进行索引了.
2.标题是完整储存在文档区中,内容值截取前30个字符存储在存储区
3.文章ID只是存储在文档区但是没有进行分词
4.时间,作者,阅读量,评论数,来源是没索引也没存储的
Analyzer(词法分析器)
创建一个测试类AnalyzerTest
封装一个测试各个分词器的方法analyzerMethod(Analyzer analyzer, String content);
public class AnalyzerTest {
String en = "good morning boy";
String ch = "你好 恭喜发财 东方明珠三生三世十里桃花";
@Test
public void analyzerMethod(Analyzer analyzer, String content) throws Exception {
TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("content", content);
tokenStream.reset();
while (tokenStream.incrementToken()) {
System.out.println(tokenStream);
}
}
//英文分词器SimpleAnalyzer测试
@Test
public void testSimpleAnalyzer() throws Exception {
analyzerMethod(new SimpleAnalyzer(), en);
}
}
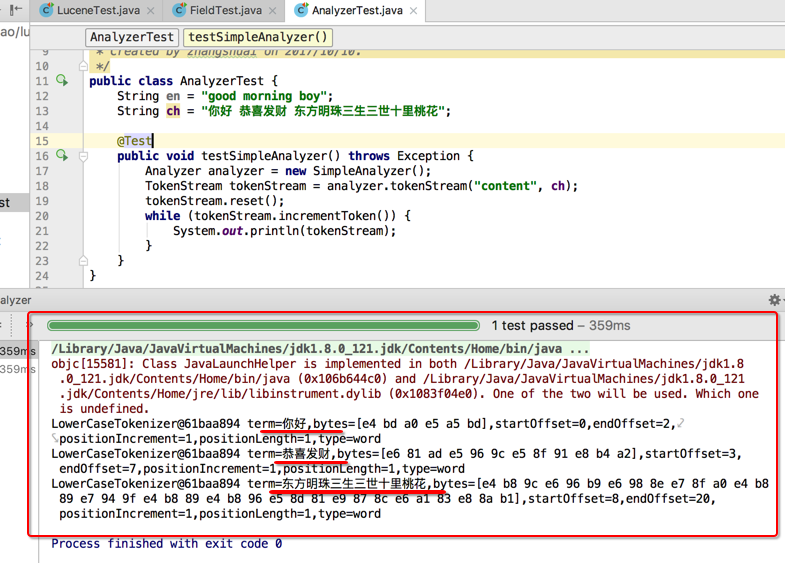
英文分词:
SimpleAnalyzer:最简单的词法分析器,按英文单词建立索引,以空格为分隔符;
//英文分词器SimpleAnalyzer测试
@Test
public void testSimpleAnalyzer() throws Exception {
analyzerMethod(new SimpleAnalyzer(), en);
}
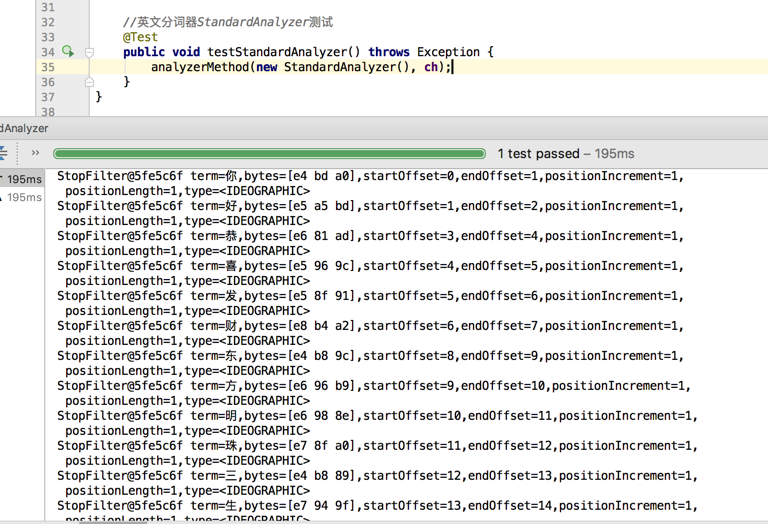
StandardAnalyzer:按英文单词及中文字符来进行分析。
//英文分词器StandardAnalyzer测试
@Test
public void testStandardAnalyzer() throws Exception {
analyzerMethod(new StandardAnalyzer(), en);
}
对于英文StandardAnalyzer也是采取空格进行分词
下面对中文进行分词测试(对于中文他是单字分词)
//英文分词器StandardAnalyzer测试
@Test
public void testStandardAnalyzer() throws Exception {
analyzerMethod(new StandardAnalyzer(), ch);
}
PerFieldAnalyzerWrapper:
public void testPerFieldAnalyzerWrapper() throws Exception {
Map<String, Analyzer> analyzerMap = new HashMap<>();
analyzerMap.put("en", new SimpleAnalyzer());//使用SimpleAnalyzer分词器
analyzerMap.put("ch", new StandardAnalyzer());//使用StandardAnalyzer
//设置默认分词器
PerFieldAnalyzerWrapper wrapper = new PerFieldAnalyzerWrapper(new SimpleAnalyzer(), analyzerMap);
//会根据传入的字段名在PerFieldAnalyzerWrapper找到这个字段对应的分词器
//如果PerFieldAnalyzerWrapper没有该字段对应的分词器就会应用默认的的分词器
//tokenStream("content", xxxxxxxxx);根据xxxxxx来判断选择的分词器
TokenStream tokenStream = wrapper.tokenStream("content", ch);
tokenStream.reset();
while (tokenStream.incrementToken()) {
System.out.println(tokenStream);
}
}
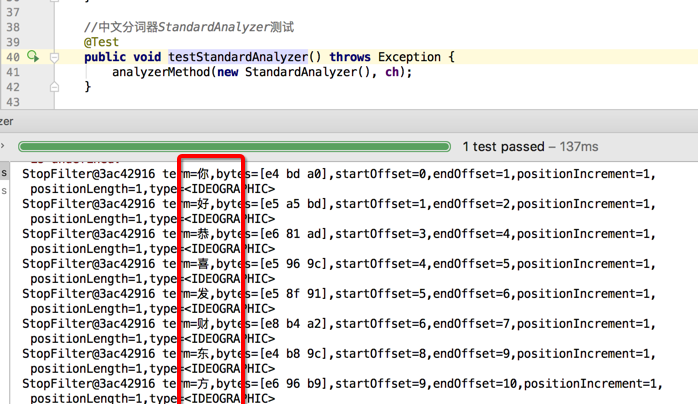
中文分词:
StandardAnalyzer:单字分词,把每一个字当成一个词
//中文分词器StandardAnalyzer测试
@Test
public void testStandardAnalyzer() throws Exception {
analyzerMethod(new StandardAnalyzer(), ch);
}
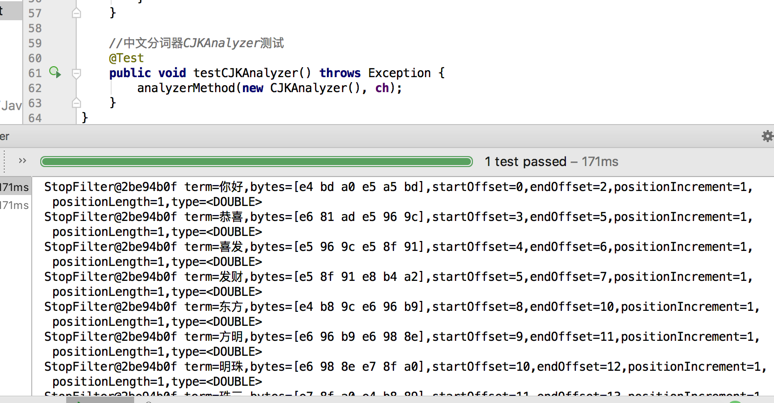
CJKAnalyzer:二分法分词,把相临的两个字当成一个词,比如我们是中国人;我们,们是,是中,中国,国人等
//中文分词器CJKAnalyzer测试
@Test
public void testCJKAnalyzer() throws Exception {
analyzerMethod(new CJKAnalyzer(), ch);
}
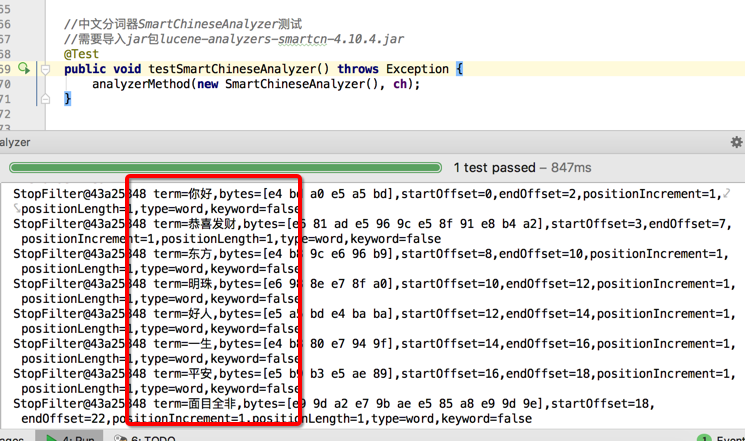
SmartChineseAnalyzer:字典分词,也叫词库分词;把中文的词全部放置到一个词库中,按某种算法来维护词库内容;如果匹配到就切分出来成为词语。通常词库分词被认为是最理想的中文分词算法。如:“我们是中国人”,效果为:“我们”、“中国人”。(可以使用SmartChineseAnalyzer,“极易分词” MMAnalyzer ,或者是“庖丁分词”分词器、IKAnalyzer。推荐使用IKAnalyzer )
//中文分词器SmartChineseAnalyzer测试
//需要导入jar包lucene-analyzers-smartcn-4.10.4.jar
@Test
public void testSmartChineseAnalyzer() throws Exception {
analyzerMethod(new SmartChineseAnalyzer(), ch);
}
}
IKAnalyzer:第三方的
1.导入jar包 IKAnalyzer2012FF_u1.jar(这个包在中央仓库是没有的)支持停词和自定义拓展词
2.添加停词词典stopword.dic
3.添加拓展词典ext.dic
//中文分词器IKAnalyzer测试
//需要导入jar包IKAnalyzer2012FF_u1.jar
@Test
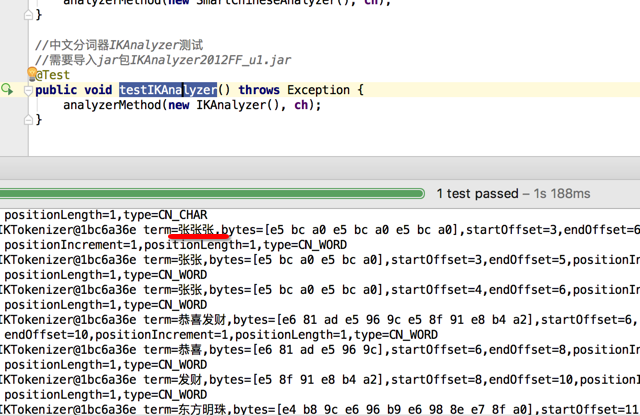
public void testIKAnalyzer() throws Exception {
analyzerMethod(new IKAnalyzer(), ch);
}
如果想去掉"的","了","吗".....的语气词我们可以加入配置文件
IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml和stopword.dic
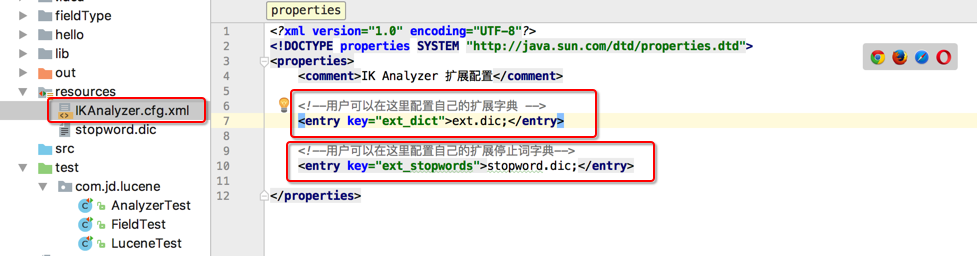
在stopword.dic文件里添加我们不需要的分词即可,这样拆分词元就不会把这些停词作为分词了
我们如果想加入一些我们自己需要的词元则需要在配置文件IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml中配置一个额外分词文件 拓展词典ext.dic
在拓展词典ext.dic中设置我们自定义的词元
索引库的更新
public class CRUDTest {
String content1 = "hello world";
String content2 = "hello java world";
String content3 = "hello lucene world";
String indexPath = "luncecrud";
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();//分词器
//创建索引
@Test
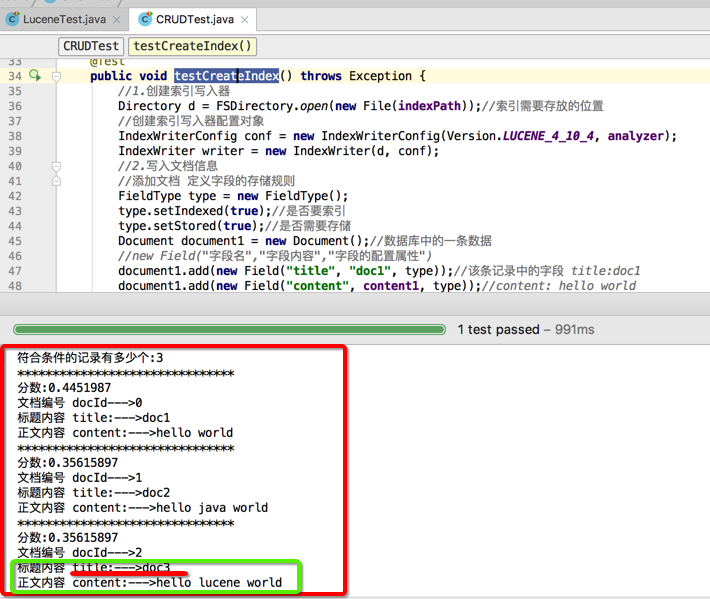
public void testCreateIndex() throws Exception {
//1.创建索引写入器
Directory d = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexPath));//索引需要存放的位置
//创建索引写入器配置对象
IndexWriterConfig conf = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_4_10_4, analyzer);
IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(d, conf);
//2.写入文档信息
//添加文档 定义字段的存储规则
FieldType type = new FieldType();
type.setIndexed(true);//是否要索引
type.setStored(true);//是否需要存储
Document document1 = new Document();//数据库中的一条数据
//new Field("字段名","字段内容","字段的配置属性")
document1.add(new Field("title", "doc1", type));//该条记录中的字段 title:doc1
document1.add(new Field("content", content1, type));//content: hello world
writer.addDocument(document1);
Document document2 = new Document();
document2.add(new Field("title", "doc2", type));
document2.add(new Field("content", content2, type));
writer.addDocument(document2);
Document document3 = new Document();
document3.add(new Field("title", "doc3", type));
document3.add(new Field("content", content3, type));
writer.addDocument(document3);
//需要把添加的记录保存
writer.commit();
writer.close();
testSearch();
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
//创建索引写入器
Directory d = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexPath));
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_4_10_4, analyzer);
IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(d, config);
//更新对象
Term term = new Term("title", "doc2");//更新的条件
Document updateDoc = new Document();//更新之后的文档对象
FieldType type = new FieldType();
type.setIndexed(true);
type.setStored(true);
updateDoc.add(new Field("title", "doc2", type));
updateDoc.add(new Field("content", "hello黄河之水天上来吧我要更新内容啦", type));
writer.updateDocument(term, updateDoc);
//提交更新内容 释放资源
writer.commit();
writer.close();
testSearch();
}
//索引查询过程
@Test
public void testSearch() throws Exception {
//1.创建索引写入器
Directory d = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexPath));
//打开索引目录
IndexReader r = DirectoryReader.open(d);
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(r);
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser("content", analyzer);
Query query = parser.parse("hello");//查询hello
//search(查询对象,符合条件的前n条记录)
TopDocs search = searcher.search(query, 10000);//n:前几个结果
System.out.println("符合条件的记录有多少个:" + search.totalHits);
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = search.scoreDocs;
Document doc = null;
for (int i = 0; i < scoreDocs.length; i++) {
System.out.println("*******************************");
System.out.println("分数:" + scoreDocs[i].score);//相关度的排序
int docId = scoreDocs[i].doc;//文档编号
Document document = searcher.doc(docId);
System.out.println("文档编号 docId--->" + docId);
System.out.println("标题内容 title:--->" + document.get("title"));
System.out.println("正文内容 content:--->" + document.get("content"));
}
}
}
先创建一个创建索引的方法testCreateIndex()和索引查询的方法testSearch()然后创建一个索引更新的方法testUpdate();
先执行testCreateIndex()
在执行testUpdate();
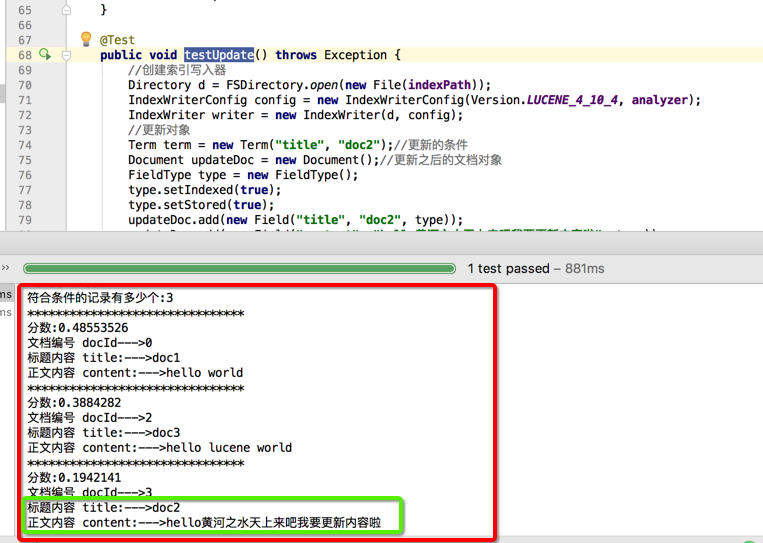
把文档标题为doc2 的内容更新为新的内容,同时文档编号发生变化,文档编号为1的被删除,增加类文档编号3.说明更新的操作是先删除后添加
删除索引库
@Test
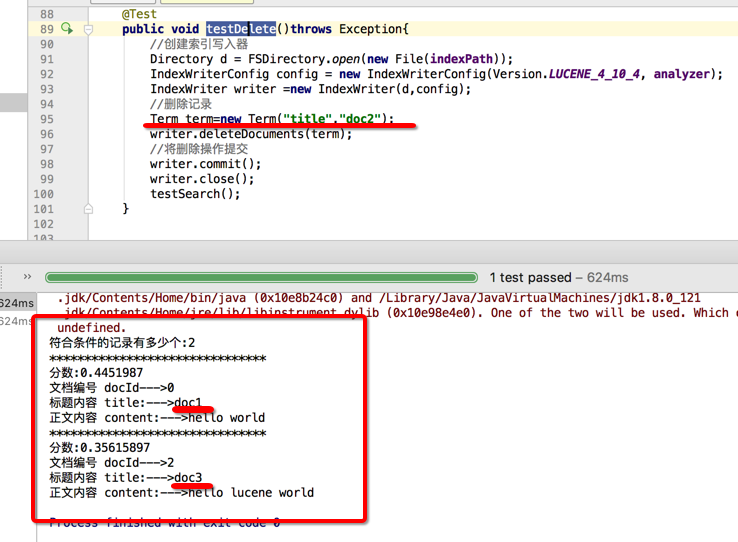
public void testDelete()throws Exception{
//创建索引写入器
Directory d = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexPath));
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_4_10_4, analyzer);
IndexWriter writer = new IndexWriter(d, config);
//删除记录
/**
* 方式一
Term term=new Term("title","doc2");
writer.deleteDocuments(term);
*/
//方式二
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser("title", analyzer);
Query query = parser.parse("doc3");
writer.deleteDocuments(query);
//将删除操作提交
writer.commit();
writer.close();
testSearch();
}
Lucene进阶
查询所有
//索引查询过程1
public void search1(String content) throws Exception {
//1.创建索引写入器
Directory d = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexPath));
//创建分词器
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();
//打开索引目录
IndexReader r = DirectoryReader.open(d);
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(r);
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser("content", analyzer);
Query query = parser.parse(content);//查询hello
//search(查询对象,符合条件的前n条记录)
TopDocs search = searcher.search(query, 10000);//n:前几个结果
System.out.println("符合条件的记录有多少个:" + search.totalHits);
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = search.scoreDocs;
for (int i = 0; i < scoreDocs.length; i++) {
System.out.println("*******************************");
System.out.println("分数:" + scoreDocs[i].score);//相关度的排序
int docId = scoreDocs[i].doc;//文档编号
Document document = searcher.doc(docId);
System.out.println("文档编号 docId--->" + docId);
System.out.println("标题内容 title:--->" + document.get("title"));
System.out.println("正文内容 content:--->" + document.get("content"));
}
}
//索引查询过程2
public void search2(Query query) throws Exception {
//1.创建索引写入器
Directory d = FSDirectory.open(new File(indexPath));
//创建分词器
Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer();
//打开索引目录
IndexReader r = DirectoryReader.open(d);
IndexSearcher searcher = new IndexSearcher(r);
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser("content", analyzer);
//search(查询对象,符合条件的前n条记录)
TopDocs search = searcher.search(query, 10000);//n:前几个结果
System.out.println("符合条件的记录有多少个:" + search.totalHits);
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = search.scoreDocs;
for (int i = 0; i < scoreDocs.length; i++) {
System.out.println("*******************************");
System.out.println("分数:" + scoreDocs[i].score);//相关度的排序
int docId = scoreDocs[i].doc;//文档编号
Document document = searcher.doc(docId);
System.out.println("文档编号 docId--->" + docId);
System.out.println("标题内容 title:--->" + document.get("title"));
System.out.println("正文内容 content:--->" + document.get("content"));
}
}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
search1("*:*");//查询所有,匹配所有字段
search2(new MatchAllDocsQuery());
}
单词搜索
/**
* 单词搜索
*
* @throws Exception
*/
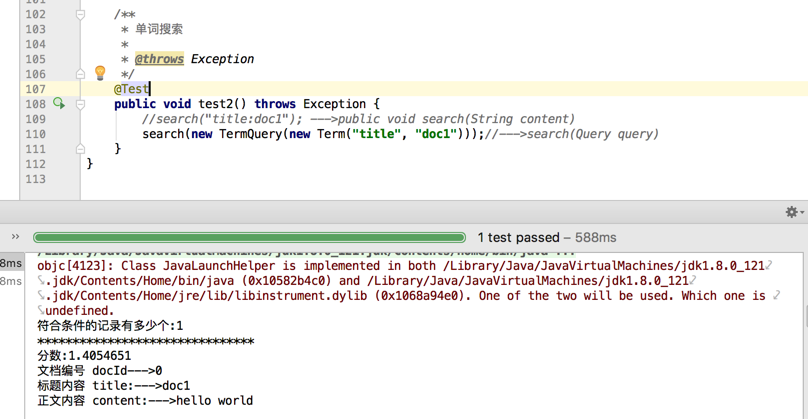
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
//search("title:doc1"); --->public void search(String content)
search(new TermQuery(new Term("title", "doc1")));//--->search(Query query)
}
段落查询
/**
* 段落查询
* @throws Exception
*/
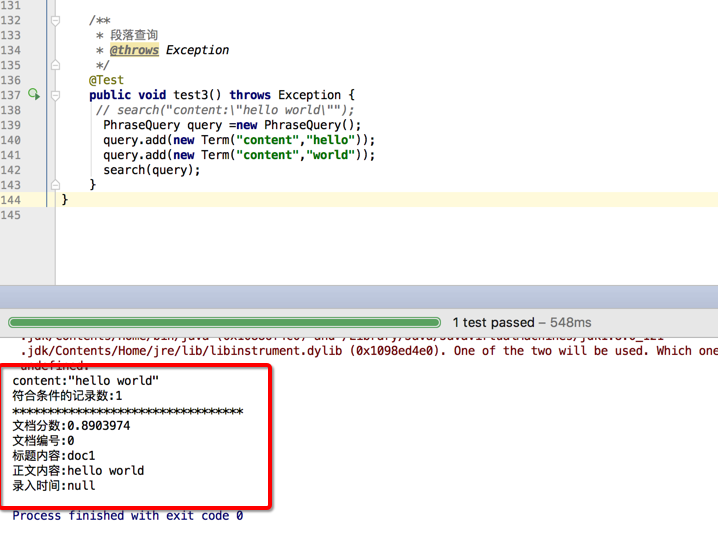
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
// search("content:\"hello world\"");
PhraseQuery query =new PhraseQuery();
query.add(new Term("content","hello"));
query.add(new Term("content","world"));
search(query);
}
通配符检索
/**
* 通配符检索
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception {
//查询所有
//方式1
search("l*ne");
//方式2
search("luenc?");
//方式3
WildcardQuery query = new WildcardQuery(new Term("content","l*ne"));
search(query);
}
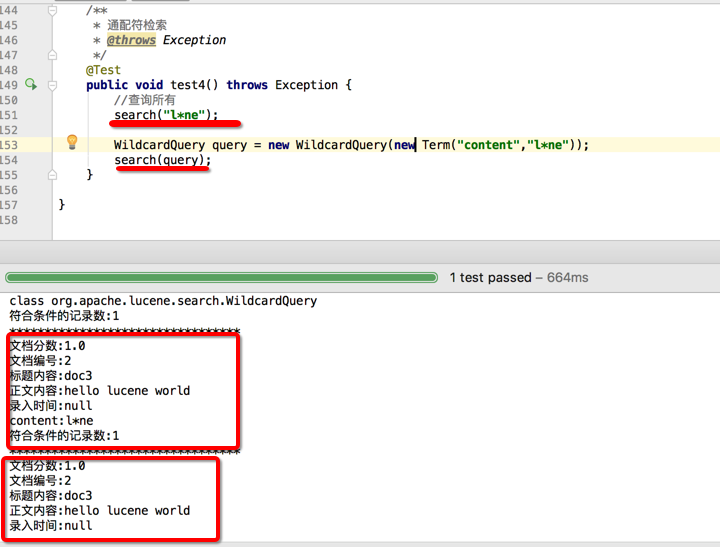
search("l**ne");中的 *表示多个字符
search("luenc?");中的?表示一个字符
单词模糊查询
Lucene支持单词容错content:lucenx ~1 表示支持单词容错一个字母,content:lucenx~N N最大值为2
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception{
search("content:lxcenX~2");
FuzzyQuery query = new FuzzyQuery(new Term("content","lucenx"),1);
search(query);
}
相似查询在关键字后面使用 ~ ( 波浪线)符号,后面可以跟一个表示相似度的数字,比如~0.85 , ~ 0.3 , ~1,值在0-1之间,1表示非常相似度最高,默认为0.5。
@Test
public void test6() throws Exception{
search("lqcenX~1");
FuzzyQuery query = new FuzzyQuery(new Term("content","lqcenX"));
search(query);
}
段落查询 (临近查询)
content:"hello world"~1 表示这个段落中间可以插入1个单词
content:"hello world"~N 表示这个段落中间可以插入N个单词
/**
* 段落查询 (临近查询)
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void test7() throws Exception{
//~1 表示这个段落中间可以插入一个单词
//content:\"hello world\"~N 表示这个段落中间可以插入N个单词
//search("content:\"hello world\"~1");
PhraseQuery query = new PhraseQuery();
query.add(new Term("content","hello"));
query.add(new Term("content","world"));
query.setSlop(1);//设置中间有一个停词
search(query);
}
范围检索
/**
* 范围检索
*/
@Test
public void test8() throws Exception {
// {:左开区间
// }:右开区间
// [:左闭区间
// ]:右闭区间
//search("inputtime:{20101010 TO 20101012}");
//TermRangeQuery(查询字段,左边的值,右边的值,是否左闭区间,是否右闭区间);
TermRangeQuery query = new TermRangeQuery("inputtime", new BytesRef("20101010"), new BytesRef("20101012"), false, false);
search(query);
}
组合查询
AND和&&:目标-->查询出标题中包括One及内容中包括java的文档;
下面两种情况均可:
title:one && content:java
title:one AND content:java
/**
* 组合查询AND和&&
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void test9() throws Exception {
//search("content:hello AND inputtime:{20101010 TO 20101012}");
search("content:hello && inputtime:{20101010 TO 20101012}");
/*
BooleanQuery query = new BooleanQuery();
query.add(new TermQuery(new Term("content","hello")), BooleanClause.Occur.MUST);
query.add(new TermRangeQuery("inputtime",new BytesRef("20101010"),new BytesRef("20101012"),false,false), BooleanClause.Occur.MUST);
search(query);
*/
}
OR和||:查询出标题中包括One但内容中不包括java的文档;
默认情况下分词组合即为逻辑或(OR)方式。
下面三种情况均可:
title:one || content:java
title:one OR content:java
title:one content:java
/**
* 组合查询OR和||
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void test10() throws Exception {
//search("content:lucene OR inputtime:{20101010 TO 20101012}");
//search("content:lucene || inputtime:{20101010 TO 20101012}");
BooleanQuery query = new BooleanQuery();
query.add(new TermQuery(new Term("content","lucene")), BooleanClause.Occur.SHOULD);
query.add(new TermRangeQuery("inputtime",new BytesRef("20101010"),new BytesRef("20101012"),false,false), BooleanClause.Occur.SHOULD);
search(query);
}
Not或!:查询出标题中包括One但内容中不包括java的文档;
下面两种情况均可:
title:one ! content:java
title:one NOT content:java
/**
* 组合查询OR和||
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void test10() throws Exception {
//search("content:lucene OR inputtime:{20101010 TO 20101012}");
//search("content:lucene || inputtime:{20101010 TO 20101012}");
BooleanQuery query = new BooleanQuery();
query.add(new TermQuery(new Term("content","lucene")), BooleanClause.Occur.SHOULD);
query.add(new TermRangeQuery("inputtime",new BytesRef("20101010"),new BytesRef("20101012"),false,false), BooleanClause.Occur.SHOULD);
search(query);
}
必须包括(+)及排除(-):目标--->查询出标题中包括One但内容中不包括java的文档;
+title:one -content:title
增加权重
Luence允许我们在组合查询中,指定某一个词的相关性权重值,从而可以让得到相关性高的结果;
要提升一个词的相关性权重,则可以在关键词的后面添加^n来实现。
比如查询jakarta apache,如果要把jakarta 的相关性提高,则可以改为jakarta^4 apache
相关性权重也可以用于词组查询,比如"jakarta apache"^4 "Apache Lucene" 将把与jakarta apache词组最相关的优先排列出来;
相关性权重值默认为1,一般要提升权重时均设置为大于1的整数;该值也可以为0-1的小数,但不能为负数。
/**
* 增加权重
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void test12() throws Exception {
//search("content:lucene^10 java");
BooleanQuery query = new BooleanQuery();
TermQuery termQuery = new TermQuery(new Term("content", "lucene"));
termQuery.setBoost(10);//该查询对象添加权重
query.add(termQuery, BooleanClause.Occur.SHOULD);
query.add(new TermQuery(new Term("content","java")), BooleanClause.Occur.SHOULD);
search(query);
}
特殊字符
由于| & ! + - ( ) 等符号在查询表达式中被用做关键字,因此要查询这些字符必须使用\来进行转义处理。
当前Lucene查询中的特殊字符:+ - && || ! ( ) { } [ ] ^ " ~ * ? :
比如,要查询包括(1+1):2 的文档,需要使用到如下表达式:
(1+1):2
分组
使用括号()对查询表示式分组Grouping
Lucene查询语法中支持通过()来对查询表达式进行分组,从而组合出各种复杂的查询。
1、查询出标题中包括one或two,但内容中不包括java的文档;
Query query=parser.parse("title:(one OR two) NOT content:java");
高亮实现
1、高亮的概述:从搜索结果中截取一部分摘要,并把符合条件的记录添加高亮显示;
高亮需要使用jar包lucene-highlighter-4.10.4.jar
2、高亮涉及的功能包括两部分:A、截取摘要,B、高亮显示
Formatter formatter = new SimpleHTMLFormatter("<font color=\"red\">","</font>");
Scorer scorer = new QueryScorer(query);
Highlighter hl = new Highlighter(formatter,scorer);
hl.setMaxDocCharsToAnalyze(20);
String str=hl.getBestFragment(new StandardAnalyzer(), "content",doc.get("content"));





















 1013
1013

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








