Shiro的架构有3个主要概念:Subject、SecurityManager和Realms. 提供的服务有Authentication(认证),Authorization(授权),Session Management(会话管理),Cryptography(加密) 建议参考 第一章 Shiro简介——《跟我学Shiro》
恰好有时间就学习下shiro,先从一个shiroHelloTest做起
测试代码
<!--pom.xml-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
@Test
public void t(){
//使用的jar版本是1.4.0,`IniSecurityManagerFactory` 已经弃用.
DefaultSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//MyShiroRealm 继承AuthorizingRealm,需要实现用于验证用户和权限的2个方法.
securityManager.setRealm(new MyShiroRealm());
//SecurityUtils存放一个全局的securityManager
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//从ThreadLocal 中获取subject,如果没有则build一个
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("song", "123");
try {
subject.login(token);
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//看是否已验证或者说已登录
Assert.assertEquals(true, subject.isAuthenticated());
subject.logout();
Assert.assertEquals(false, subject.isAuthenticated());
}
小黄鸭的看代码的方法,一行一行的看啊
0. 先附上类图
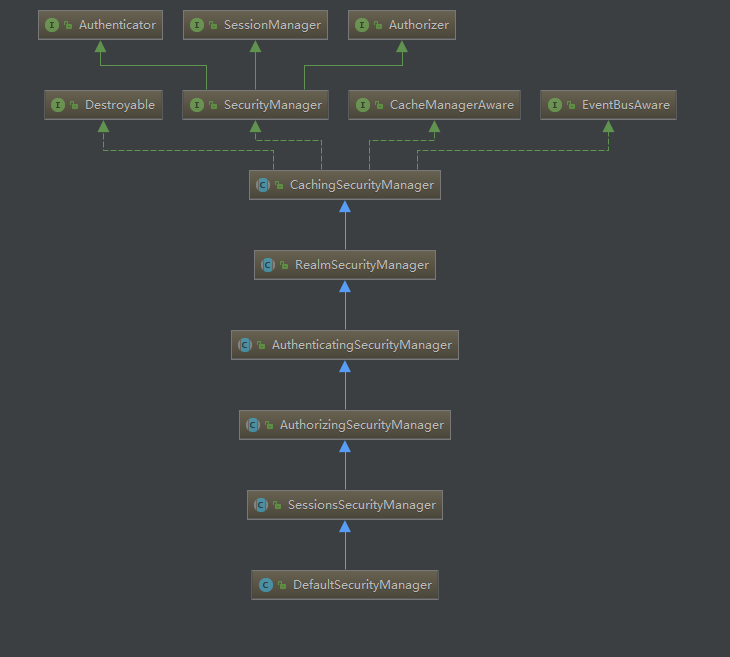
1.第一行代码对应的DefaultSecurityManager的构造方法
public DefaultSecurityManager() {
super();
//以下暂且不看,猜测是一些工厂类和dao的方法,用到时候再看
this.subjectFactory = new DefaultSubjectFactory();
this.subjectDAO = new DefaultSubjectDAO();
}
对super()查看:
//父类SessionsSecurityManager的构造方法
this.sessionManager = new DefaultSessionManager();
applyCacheManagerToSessionManager();
//爷爷AuthorizingSecurityManager的构造方法
//realm的一些实现
this.authorizer = new ModularRealmAuthorizer();
//祖爷爷AuthenticatingSecurityManager的构造方法
this.authenticator = new ModularRealmAuthenticator();
//爷爷的爷爷RealmSecurityManager的构造方法 什么也没做
//祖宗CachingSecurityManager,use a default event bus
setEventBus(new DefaultEventBus());
只知道构造方法初始化了一些默认的东西.具体干嘛的回头看
2. securityManager.setRealm(new MyShiroRealm());
securityManager.setRealm(new MyShiroRealm());
setRealm 是 默认securityManager的爷爷的爷爷 RealmSecurityManager的方法.
在执行完set的语句后,执行以下两个方法
//判断realm是否继承CacheManagerAware,是则CacheManager set realm里,CacheManager是其祖宗的字段
applyCacheManagerToRealms();
//set eventBus 同上
applyEventBusToRealms();
3. Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();进入该方法
public static Subject getSubject() {
Subject subject = ThreadContext.getSubject();
if (subject == null) {
subject = (new Subject.Builder()).buildSubject();
ThreadContext.bind(subject);
}
return subject;
}
Builder 是 Subject的内部类.看其构造方法
public Builder(SecurityManager securityManager) {
if (securityManager == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("SecurityManager method argument cannot be null.");
}
this.securityManager = securityManager;
this.subjectContext = newSubjectContextInstance();
if (this.subjectContext == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Subject instance returned from 'newSubjectContextInstance' " +
"cannot be null.");
}
this.subjectContext.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
}
查看 newSubjectContextInstance() 返回 return new DefaultSubjectContext();
其父类就是一个被封装的map,通过一个map存储着一些键值对,写了一下get的方法
最终调用,好吧又回到了securityManager
public Subject buildSubject() {
return this.securityManager.createSubject(this.subjectContext);
}
默认的securityManager会处理下subjectContext中的session,securityManager,权限管理什么的,不过测试的时候这些都是null. 最后交给DefaultSubjectFactory处理
public Subject createSubject(SubjectContext context) {
SecurityManager securityManager = context.resolveSecurityManager();
Session session = context.resolveSession();
boolean sessionCreationEnabled = context.isSessionCreationEnabled();
PrincipalCollection principals = context.resolvePrincipals();
boolean authenticated = context.resolveAuthenticated();
String host = context.resolveHost();
return new DelegatingSubject(principals, authenticated, host, session, sessionCreationEnabled, securityManager);
}
DelegatingSubject是subject的实现类
5. 看subject.login(token);
通过上面的代码一番跟踪,login方法可以看DelegatingSubject的实现
public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal();
//登录,如果失败一般会抛出异常来进行处理.
Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token);
//-----------
//以下基本是把登录返回的subject的内容赋值给当前的subject
//------------
PrincipalCollection principals;
String host = null;
if (subject instanceof DelegatingSubject) {
DelegatingSubject delegating = (DelegatingSubject) subject;
//we have to do this in case there are assumed identities - we don't want to lose the 'real' principals:
principals = delegating.principals;
host = delegating.host;
} else {
principals = subject.getPrincipals();
}
if (principals == null || principals.isEmpty()) {
String msg = "Principals returned from securityManager.login( token ) returned a null or " +
"empty value. This value must be non null and populated with one or more elements.";
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
this.principals = principals;
this.authenticated = true;
if (token instanceof HostAuthenticationToken) {
host = ((HostAuthenticationToken) token).getHost();
}
if (host != null) {
this.host = host;
}
Session session = subject.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
this.session = decorate(session);
} else {
this.session = null;
}
}
public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
AuthenticationInfo info;
try {
//长辈AuthenticatingSecurityManager中authenticator.authenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)
//实现的方法是AbstractAuthenticator类public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token)
//最后执行securityManager.setRealm(new MyShiroRealm())一步 set进去的realm 的getAuthenticationInfo方法
//如果有多个realm则循环执行,通过实现AuthenticationStrategy.afterAllAttempts()来判断所有的认证结果是否有效
info = authenticate(token);
} catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
try {
onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an " +
"exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", e);
}
}
throw ae; //propagate
}
//生成一个新的subject,并把旧的subject,token,info 添加到其context里
Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject);
//执行记住我的逻辑
onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn);
return loggedIn;
}
6. logout
直接看securityManager的logout处理
beforeLogout(subject);记住我的退出- 如果实现了LogoutAware接口,则执行其onLogout方法
- subjectDao 执行 delete subject
- 最后 stopSession






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








