1:介绍基于3.1的版本
2:C层主要相关注解
@Controller:用于标识是处理器类; @RequestMapping:请求到处理器功能方法的映射规则; @RequestParam:请求参数到处理器功能处理方法的方法参数上的绑定 @RequestBody:请求的 body 体的绑定(通过 HttpMessageConverter 进行类型转换); @ResponseBody:处理器功能处理方法的返回值作为响应体(通过 HttpMessageConverter 进行类型转换); @PathVariable:请求 URI 中的模板变量部分到处理器功能处理方法的方法参数上的绑定,从而支持RESTful架构风格的URI @InitBinder:自定义数据绑定注册支持,用于将请求参数转换到命令对象属性的对应类型; @RequestHeader:请求头(header)数据到处理器功能处理方法的方法参数上的绑定; @ResponseStatus:定义处理器功能处理方法/异常处理器返回的状态码和原因; @CookieValue:cookie 数据到处理器功能处理方法的方法参数上的绑定; @ModelAttribute:请求参数到命令对象的绑定; @SessionAttributes:用于声明 session 级别存储的属性,放置在处理器类上,通常列出模型属性(如@ModelAttribute)对应的名称,则这些属性会透明的保存到 session 中; @ExceptionHandler:注解式声明异常处理器; |
3:@RequestMapping
public interface RequestMapping extends Annotation {
public abstract String[] value();
//【GET,POST,HEAD,PUT,PATCH,DELETE,OPTIONS,TRACE;】,我们主要使用get,post
public abstract RequestMethod[] method();
public abstract String[] params();
public abstract String[] headers();
public abstract String[] consumes();
public abstract String[] produces();
} |
-
@RequestMapping(value={"/profile"},method=RequestMethod.GET,consumes="application/json")
method指定请求方法GET, consumes指定处理请求[request]的提交内容类型(Content-Type),请求必须为application/json;
如果请求时使用POST方式,报错如下:

如果请求未指定Content-Type=application/json,报错如下:

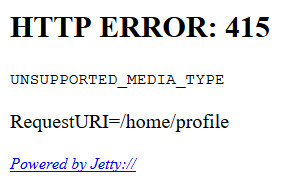
-
@RequestMapping(value="/profile", method=RequestMethod.GET,produces="application/json")
produces:指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回,Accept=application/json;
当我们模拟请求,并指定Headers的Accept=application/xml,报错如下:
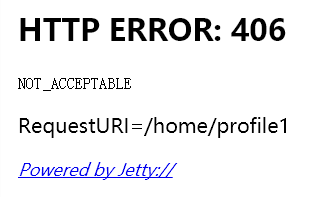
-
@RequestMapping(value="/profile", method=RequestMethod.GET,produces="application/json",params="uid=1",headers="Referer=http://www.test.com/")
params="uid=1",请求里必须包含参数uid=1,headers必须有:Accept:application/json, Referer:http://www.test.com/
当我们的请求里没有参数uid=1时,或者有uid参数,但是值不等于1时,报错如下:
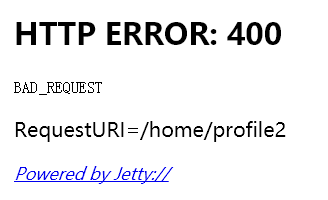
服务端异常:
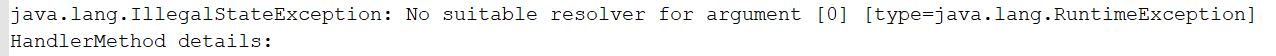
4:@RequestParam
public @ResponseBody String test2(@RequestParam(value="test2", required=true, defaultValue="test2val") String test2) // 如上表示:参数名为test2,为必传参数,默认值test2val,由于设置了默认值,所以请求的时候如果没有这个参数也不会报错 |
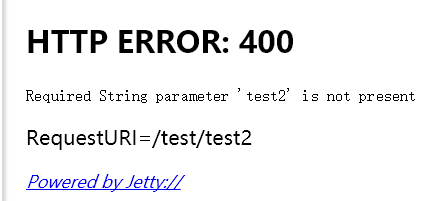
public @ResponseBody String test2(@RequestParam(value="test2") String test2)时,如果请求没有参数test2,报错如下:
5:@RequestBody @ResponseBody
@XmlRootElement(name = "simpleUser")
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
public class SimpleUser extends BaseObject{
@XmlAttribute(name="username")
private String username;
@XmlAttribute(name="password")
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
@RequestMapping(value="/test3", produces = {"application/xml", "application/json"}) //可以按照客户端需求生产JSON格式或者XML格式数据返回
public @ResponseBody SimpleUser test3(@RequestBody SimpleUser simpleUser){
return simpleUser;
} |
-
模拟请求一:
Request:
Headers: Content-Type:application/xml Accept:application/json Body: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <simpleUser username="123" password="123"> </simpleUser>
Response:
Headers: Content-Type →application/json; charset=UTF-8 Server →Jetty(6.1.6) Transfer-Encoding →chunked Body: { "username": "123", "password": "123" } -
模拟请求二:
Request:Headers: Content-Type:application/json Accept:application/xml Body: {"username":"123","password":"123"}Response:
Headers: Content-Type →application/xml; charset=UTF-8 Server →Jetty(6.1.6) Transfer-Encoding →chunked Body: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?> <simpleUser username="123" password="123"/>
6:@PathVariable,restful风格
// request请求 /test4/1/fancyboy
@RequestMapping(value="/test4/{uid}/{username}")
public @ResponseBody String test4(@PathVariable(value="uid") Integer uid, @PathVariable(value="username") String username){
return "uid : "+uid+", username : "+username;
} |
7: @InitBinder, 绑定数据转换或处理
作用域只在当前对象
全局作用域使用,但是需要处理HandlerAdapter的配置,我们默认的配置一般是<mvc:annotation-driven />,该配置默认加载了AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter:
public class GlobalWebBindingInitializer implements WebBindingInitializer{
@Override
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder, WebRequest request) {
binder.registerCustomEditor(String.class, new StringHtmlEscapeEditor());
}
}
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter">
<property name="cacheSeconds" value="0"/>
<property name="webBindingInitializer">
<bean class="xxx.xxx.GlobalWebBindingInitializer"/>
</property>
</bean> |
8:@ExceptionHandler
作用域:方法所在的controller有效,优先级高于@ControllerAdvice,如下:
/**
* 异常页面控制
* @param runtimeException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Throwable.class)
public @ResponseBody Map<String,Object> runtimeExceptionHandler(RuntimeException runtimeException) {
logger.error("ExceptionControllerAdvice get error!", runtimeException);
Map<String, Object> model = new TreeMap<String, Object>();
model.put("status", "ExceptionControllerAdvice");
return model;
} |
作用域:全局有效的使用,如下:
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionControllerAdvice{
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExceptionControllerAdvice.class);
/**
* 异常页面控制
* @param runtimeException
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Throwable.class)
public @ResponseBody Map<String,Object> runtimeExceptionHandler(RuntimeException runtimeException) {
logger.error("ExceptionControllerAdvice get error!", runtimeException);
Map<String, Object> model = new TreeMap<String, Object>();
model.put("status", "ExceptionControllerAdvice");
return model;
}
} |




 本文详细介绍了Spring MVC框架中常用注解的功能与用法,包括@Controller、@RequestMapping、@RequestParam等,并通过实例演示如何实现RESTful风格的服务。
本文详细介绍了Spring MVC框架中常用注解的功能与用法,包括@Controller、@RequestMapping、@RequestParam等,并通过实例演示如何实现RESTful风格的服务。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








