14
XSLT Processor for C
This chapter contains the following sections:
Accessing XSLT for C
XSLT for C is provided with Oracle9i and Oracle9i Application Server. It is also available for download from the OTN site:
It is located in $ORACLE_HOME/xdk/c/parser.
XSLT for C Features
readme.html in the root directory of the software archive contains release specific information including bug fixes and API additions.
You can post questions, comments, or bug reports to the XML Discussion Forum at
Specifications
See the following:
XML XSLT for C (DOM Interface) Usage
Figure 14-1 shows the XSLT for C functionality.
There are two inputs to xmlparse():
The stylesheet to be applied to the XML document
XML document
xmlinit() initializes the XSLT processing. xmlinit() initializes the xslprocess() result.
xslprocess()optionally calls other functions, such as print functions. You can see the list of available functions either on OTN or in the
The resultant document (XML, HTML, VML, and so on) is typically sent to an application for further processing.
The application terminates the XSLT process by declaring xmlterm() for the XML document, stylesheet, and final result.
XML Parser for C's XSLT functionality is illustrated with the following examples:
Figure 14-1 XSLT for C (DOM Interface) Usage
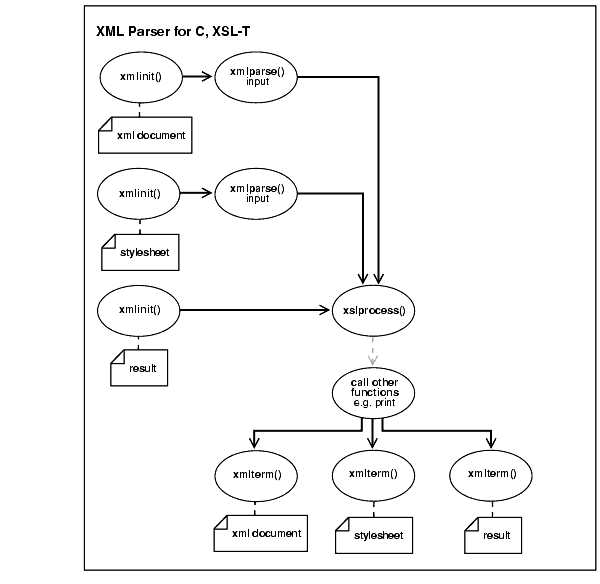 Text description of the illustration adxml056.gif
Text description of the illustration adxml056.gif
Invoking XSLT for C
XSLT for C can be invoked in two ways:
By invoking the executable on the command line
By writing C code and using the supplied APIs
Command Line Usage
The XSLT for C can be called as an executable by invoking bin/xml
Table 14-1 lists the command line options.
Table 14-1 XML Parser for C: Command Line Options
Option
Description
-e encoding
Specify input file encoding
-h
Help - show this usage help
-v
Version - display parser version then exit
-w
Whitespace - preserve all whitespace
-s
Stylesheet
Using the Sample Files Included with the Software
$ORACLE_HOME/xdk/c/parser/sample directory contains several XML applications to illustrate how to use the XSLT for C.
Table 14-2 lists the sample files in sample/ directory.
Table 14-2 XSLT for C sample/ Files
sample/ File Name
Description
XSLSample.c
Source for XSLSample program
XSLSample.std
Expected output from XSLSample
class.xml
XML file that may be used with XSLSample
iden.xsl
Stylesheet that may be used with XSLSample
cleo.xml
XML version of Shakespeare's play
--
Running the XSLT for C Sample Programs
Building the Sample Programs
Change directories to the sample directory and read the README file. This will explain how to build the sample programs according to your platform.
Sample Programs
Table 14-3 lists the programs built by the sample files in the sample directory.
Table 14-3 XSLT for C: Sample Built Programs in sample/
Built Program
Description
XSLSample
Sample usage of XSL processor. It takes two filenames as input, the XML file and XSL stylesheet
XSLT for C Example1: XSL -- iden.xsl
This example stylesheet can be used to input XSLSample.c.
select="*|@*|comment()|processing-instruction()|text()"/>
XSLT for C Example 2: C -- XSLSample.c
This example contains C source code for XSLSample.c.
/* Copyright (c) Oracle Corporation 1999. All Rights Reserved. */
/*
NAME
XSLSample.c - Sample function for XSL
DESCRIPTION
Sample usage of C XSL Processor
*/
#include
#ifndef ORATYPES
# include
#endif
#ifndef ORAXML_ORACLE
# include
#endif
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
xmlctx *xctx, *xslctx, *resctx;
xmlnode *result;
uword ecode;
/* Check for correct usage */
if (argc < 3)
{
puts("Usage is XSLSample \n");
return 1;
}
/* Parse the XML document */
if (!(xctx = xmlinit(&ecode, (const oratext *) 0,
(void (*)(void *, const oratext *, uword)) 0,
(void *) 0, (const xmlsaxcb *) 0, (void *) 0,
(const xmlmemcb *) 0, (void *) 0,
(const oratext *) 0)))
{
printf("Failed to initialze XML parser, error %u\n", (unsigned) ecode);
return 1;
}
printf("Parsing '%s' ...\n", argv[1]);
if (ecode = xmlparse(xctx, (oratext *)argv[1], (oratext *) 0,
XML_FLAG_VALIDATE | XML_FLAG_DISCARD_WHITESPACE))
{
printf("Parse failed, error %u\n", (unsigned) ecode);
return 1;
}
/* Parse the XSL document */
if (!(xslctx = xmlinit(&ecode, (const oratext *) 0,
(void (*)(void *, const oratext *, uword)) 0,
(void *) 0, (const xmlsaxcb *) 0, (void *) 0,
(const xmlmemcb *) 0, (void *) 0,
(const oratext *) 0)))
{
printf("Failed to initialze XML parser, error %u\n", (unsigned) ecode);
return 1;
}
printf("Parsing '%s' ...\n", argv[2]);
if (ecode = xmlparse(xslctx, (oratext *)argv[2], (oratext *) 0,
XML_FLAG_VALIDATE | XML_FLAG_DISCARD_WHITESPACE))
{
printf("Parse failed, error %u\n", (unsigned) ecode);
return 1;
}
/* Initialize the result context */
if (!(resctx = xmlinit(&ecode, (const oratext *) 0,
(void (*)(void *, const oratext *, uword)) 0,
(void *) 0, (const xmlsaxcb *) 0, (void *) 0,
(const xmlmemcb *) 0, (void *) 0,
(const oratext *) 0)))
{
printf("Failed to initialze XML parser, error %u\n", (unsigned) ecode);
return 1;
}
/* XSL processing */
printf("XSL Processing\n");
if (ecode = xslprocess(xctx, xslctx, resctx, &result))
{
printf("Parse failed, error %u\n", (unsigned) ecode);
return 1;
}
/* Print the result tree */
printres(resctx, result);
/* Call the terminate functions */
(void)xmlterm(xctx);
(void)xmlterm(xslctx);
(void)xmlterm(resctx);
return 0;
}
XSLT for C Example 3: C -- XSLSample.std
XSLSample.std shows the expected output from XSLSample.c.
Parsing 'class.xml' ...
Parsing 'iden.xsl' ...
XSL Processing
Calculus
Math
Jim Green
Jack
Mary
Paul





















 700
700











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








