上午为了解44题通配符匹配
又是荒废了一上午
算法能力还是太渣了啊
得加把劲了!!!
编写一个程序,通过已填充的空格来解决数独问题。
一个数独的解法需遵循如下规则:
- 数字
1-9在每一行只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一列只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一个以粗实线分隔的3x3宫内只能出现一次。
空白格用 '.' 表示。
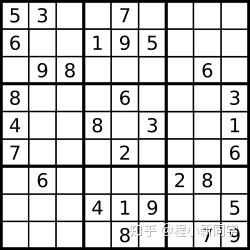
一个数独。
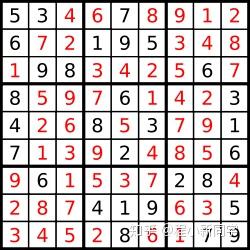
答案被标成红色。
Note:
- 给定的数独序列只包含数字 1-9 和字符 '.' 。
- 你可以假设给定的数独只有唯一解。
- 给定数独永远是 9x9 形式的。
思路:
这道题算是一道非常好的回溯题目了,之前写了一篇关于回溯法的文章,里面写到了关于回溯法比较经典的例题——八皇后问题和迷宫问题
程小新同学:LeetCode--回溯法心得zhuanlan.zhihu.com
而这道解数独题目其实和八皇后问题和迷宫问题的思路是大同小异的,就是在每个空白位置依次尝试着赋予1-9这9个数,首先看赋予的值与其每一行每一列以及所在的3x3小区域的值是否冲突,如果冲突,则换成另一个值;如果不冲突,则可以尝试该值赋值给当前位置,并递归到下一个位置的赋值操作,如果下一个值得到的结果是True,这说明当前位置赋予的值是有效的,不须改变,否则就要初始化并回溯,直到找到有效结果。
代码如下:
import numpy as np
class Solution(object):
# 本题采用回溯法解决
# 当时在area3x3检查时栽了跟头
def solveSudoku(self, board):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
# board = np.array(board)
def back(board, position=[0, 0]):
# 如果当前数独中没有空白元素'.',则说明查找成功了
if position == [-1, -1]:
print("successful")
return True
# 获取当前位置的横纵坐标
pos_x = position[0]
pos_y = position[1]
# 获取当前位置的值
pos_value = board[pos_x][pos_y]
if pos_value == '.':
# 依次给每个位置尝试着赋予1-9这9个数
for index in range(1, 10):
value = str(index)
# 如果当前position位置安放的value这个数是有效的,则可以尝试着将当前position位置的值变成value,并再次检验
if self.isValid(board, position, value) is True:
board[pos_x][pos_y] = value
next_position = self.getNextPosition(board, position)
# 如果当前position位置后面的位置都安放数字成功的话,说明当前position位置放置的value也是对的,则不需改变
# 否则将当前position位置的值初始化,即变成'.',并回溯
if back(board, next_position) is True:
return True
else:
board[pos_x][pos_y] = '.'
else:
next_pos = self.getNextPosition(board, position)
back(board, next_pos)
return False
back(board)
# 获取下一个有效点的坐标位置
def getNextPosition(self, board, position):
next_x = position[0]
next_y = position[1]
while board[next_x][next_y] != '.':
next_y += 1
if next_y >= len(board):
next_x += 1
next_y = 0
if next_x not in range(len(board)) or next_y not in range(len(board)):
return [-1, -1]
return [next_x, next_y]
# 判断当前位置是否有效
def isValid(self, board, position, value):
"""
:param board: array[[]]-->指代所给的数独列表
:param position: List[int x, y]-->指代所给的当前位置
:param value: str-->指代当前位置的值
:return: boolean-->若返回为True,则表示当前位置有效;反之,则无效
"""
board = np.array(board)
# 获取当前位置的横纵坐标
pos_x = position[0]
pos_y = position[1]
# 获取当前位置横纵坐标所对应的每一行每一列元素
pos_row = board[pos_x]
pos_col = board[:, pos_y]
# 如果当前位置的值value与其所在的每一行或者每一列的值重复,则表示当前值无效,返回False
if value in pos_row or value in pos_col:
return False
# 获取当前位置点所在的3x3区域的位置
area3x3_x = pos_x//3*3
area3x3_y = pos_y//3*3
area3x3_batch = board[area3x3_x:area3x3_x+3, area3x3_y:area3x3_y+3]
# 如果当前位置的值value与其所在的3x3区域的值重复,则表示当前值无效,返回False
if value in area3x3_batch:
return False
return True
if __name__ == "__main__":
board = [['5', '3', '.', '.', '7', '.', '.', '.', '.'],
['6', '.', '.', '1', '9', '5', '.', '.', '.'],
['.', '9', '8', '.', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.'],
['8', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '3'],
['4', '.', '.', '8', '.', '3', '.', '.', '1'],
['7', '.', '.', '.', '2', '.', '.', '.', '6'],
['.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '.', '2', '8', '.'],
['.', '.', '.', '4', '1', '9', '.', '.', '5'],
['.', '.', '.', '.', '8', '.', '.', '7', '9']]
这个是我的解法,但很不幸的是:超出时间限制了,我当时看了半天始终是没看到哪儿时间花的比较多,如果各位读者看出了问题,还请不吝赐教!!!
下面是我在网上找到的一种解法,其思想与我的大同小异,但是可以跑出来。
代码如下:
import numpy as np
def isRowAndColValid(x, y, field, num):
for i in range(9):
if field[x][i] == str(num):
return False
for j in range(9):
if field[j][y] == str(num):
return False
return True
def isSquareValid(x, y, field, num):
row, col = (x // 3) * 3, (y // 3) * 3
for i in range(row, row + 3):
for j in range(col, col + 3):
if field[i][j] == str(num):
return False
return True
def getNext(field):
for x in range(9):
for y in range(9):
if field[x][y] == ".":
return [x, y]
return []
class Solution:
def solveSudoku(self, board):
"""
:type board: List[List[str]]
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify board in-place instead.
"""
def DFS(board):
next = getNext(board)
if not next:
# print(board)
return True
for i in range(1, 10):
if isRowAndColValid(next[0], next[1], board, i) and isSquareValid(next[0], next[1], board, i):
board[next[0]][next[1]] = str(i)
if DFS(board):
return True
board[next[0]][next[1]] = "."
DFS(board)
print(np.array(board))
if __name__ == "__main__":
board = [['5', '3', '.', '.', '7', '.', '.', '.', '.'],
['6', '.', '.', '1', '9', '5', '.', '.', '.'],
['.', '9', '8', '.', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.'],
['8', '.', '.', '.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '3'],
['4', '.', '.', '8', '.', '3', '.', '.', '1'],
['7', '.', '.', '.', '2', '.', '.', '.', '6'],
['.', '6', '.', '.', '.', '.', '2', '8', '.'],
['.', '.', '.', '4', '1', '9', '.', '.', '5'],
['.', '.', '.', '.', '8', '.', '.', '7', '9']]
result = Solution().solveSudoku(board)
print(result)
执行效率一般般,在10%左右。




 本文深入探讨了使用回溯法解决数独问题的算法思路,通过详细的代码解析,展示了如何在每个空白位置尝试1-9的数值,确保每行、每列及3x3区域内的数字不重复,实现数独的有效求解。
本文深入探讨了使用回溯法解决数独问题的算法思路,通过详细的代码解析,展示了如何在每个空白位置尝试1-9的数值,确保每行、每列及3x3区域内的数字不重复,实现数独的有效求解。

















 4904
4904

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










