1.0. 安装
1.1.1. 下载
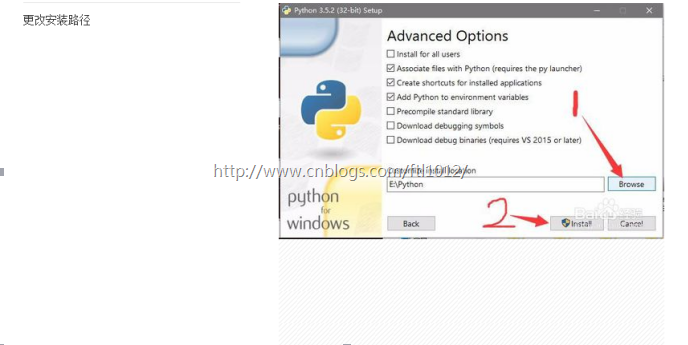
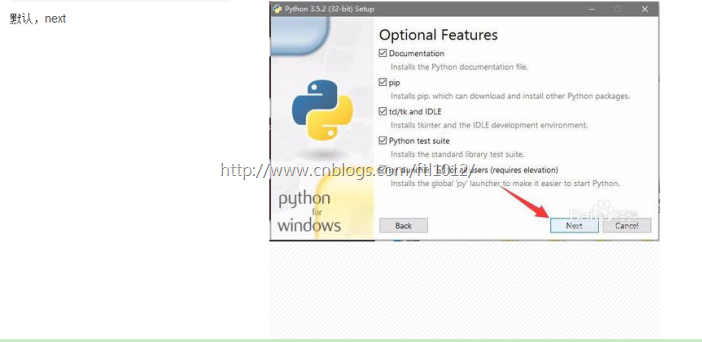
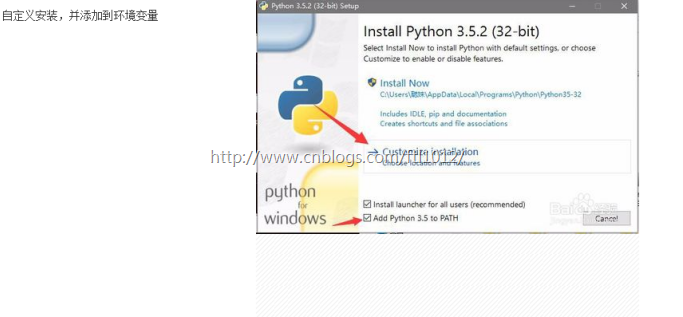
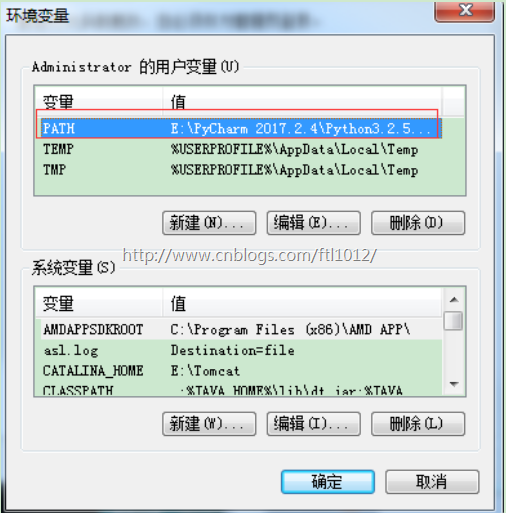
1.1.2. 配置环境变量
因为在安装的时候我们选择了添加python到环境变量,所以默认安装好的,没有的可以手动更改。
环境变量,添加路径到path即可,注意封号
1.1.3. python 2 vs 3
1. 默认支持中文
2. 不兼容2.x
3. 核心语法调整,更易学
4. 新特性默认只在3.x上有
2.x = 默认编码 =ASSIC =不支持
3.x = 默认编码 =UNICODE =默认支持中文
Py2中只有2种数据类型:str unicode [其中str中保存的是bytes, unicode里面保存的是unicode]
Py3中只有2种数据类型:str bytes
Py3中合并Py2中的int和long int类型为int类型
1.1.4. 系统位数
32bit =内存的最大寻址空间是2**32, 4GB
64bit, =2**64 但实际上支持不到这莫大的内存,2**4x, 目前主板支持的最大的内存是100多GB
4gb ==64位系统 会不会比32位系统快? = 一样的
1.1.5. 硬盘:
5400转 = 每分钟 =骑自行车
7200转 = 每分钟 =骑电动车
10000转 = 每分钟 =骑快速电动车
15000转 = 每分钟 =骑摩托车 机械硬盘最快的
SSD = Tesla
1.1. 执行py程序方式为:
1. 交互器,缺点程序不能永久保存,主要用与简单的语法测试相关
2. 文件执行
1.2. Python特征
1.简单主义思想的语言,伪代码是最大的优点,让你专注于解决问题,而不是代码本身
2.直接源代码运行,不需要解释器,类似Java
3.即支持面向过程也支持面向对象编程
4.使用Python编程,不需要考虑底层的,因为底层有自动化的内存管理
5.可扩展性以及可嵌入性,可以把部分程序用C或者C++写,在Python中使用,同理也可以在C中调用Python
6.开源,免费,可移植性,丰富的库
1.3. python变量

跟JAVA一样,更改的是地址的指引
1.4. 变量/常量的命名规则
变量:是为了存储 程序运算过程中的一些中间 结果,为了方便日后调用
1. 要具有描述性
2. 变量名只能_,数字,字母组成,不可以是空格或特殊字符(#?<.,¥$*!~)
3. 不能以中文为变量名
4. 不能以数字开头
5. 保留字符是不能被使用
6. 变量的命名应该有意义
常量:不变的量 pie = 3.141592653....
在py里面所有的变量都是可变的 ,所以用全部大写的变量名来代表次变量为常量
1.5. 内存何时释放
1.自动释放:Python有自己的PVM机制,会定期清理内存
2.手动释放:del name (清空了堆栈直接的指引,变量找不到索引),PVM会自动回收内存

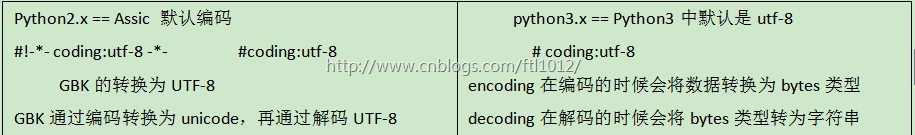
1.6. 字符编码
ASCII: 将二进制翻译成我们能看懂的字符,共计255个符号,所有字符占用8个比特1个字节
支持中文的第一张表就叫 GB2312
unicode 万国码 支持所有国家和地区的编码且向下兼容gb2312 , gbk
2**16 = 65535 = 存一个字符 统一占用2个字节
UTF-8 = unicode 的扩展集,可变长的字符编码集
Assic -->Gb2312 ->gbk1.0-->gb18030
Assic -->unicode -->utf-8(支持所有国家语言,支持中文) /utf-16
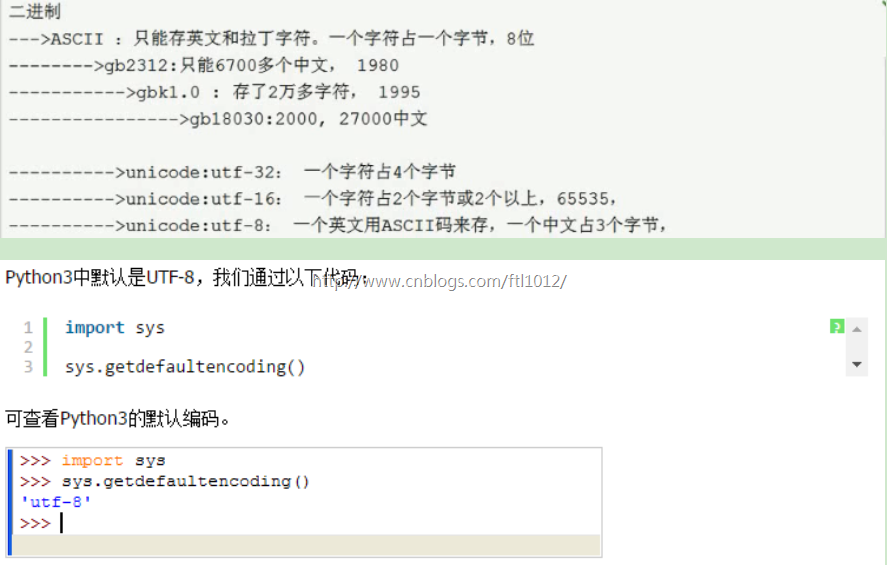
Py3中只有2种数据类型:str[unicode编码] bytes[十六进制编码], 2者可以相互转换,其他的转换需要中间转
bytes-->int: int(str(bytes('123', 'utf-8'),'utf-8')) # 编码
Py3中合并Py2中的int和long int类型为int类型
1.7. 注释及简单的用户输入输出
中文编码:#coding:utf-8
单行注释: 用#
# print ("hello world")
多行注释:三个单引号或者双引号(单双引号效果相同),有变量的时候,可以用作多行的输入
''' print ("hello world") '''
注意:单双引号效果同,但是为了有时候英文的需要,例如my='it's me'里面的缩写,程序会认为是变量而终止,所以最好用双引号my="it's me"
用户输入:
input/raw_input 接受的所有数据都是字符串,即便你输入的是数字,但依然会被当成字符串来处理
int(age):将字符串转化为整数类型
str(age):将整数转化为字符串类型
death_age = 80
max_age=90
name = raw_input("your name:")
age = raw_input("your age:")
#print( type(age) )
print ("your name is :",name)
print ("your age is :",age)
print ("your grandpa is older than you :",max_age-int(age))

print的使用:
有逗号(","),会按照2个单独的字符集处理
需要一起处理,则需要"+"做字符串的拼接,不同类型之间需要转型
3个单/双引号也可以用于多行的输入
print是一个函数,所以print和括号直接不需要空格
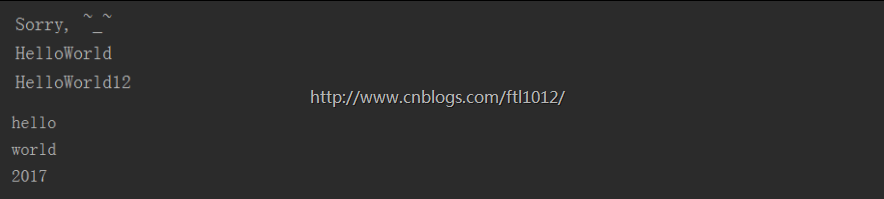
print("Sorry, ~_~")
print "Hello"+"World"
print "Hello"+"World"+str(12)
print ("hello",end="___") #end 默认是换行的
print () #等价于换行,end 默认是换行的
msg="""hello
world
2017"""
print (msg)
1.8. if语句实现猜年龄
python通过缩进来是实现的语法判断,而且缩进级别必须相同,否则会报错
if...else是一个整体,不一定需要同时出现,但是有else必须有if
# if int(guess_age) == max_age: 注意等号2边的空格
while面的True必须大写
break可以退出循环,exit(0)也可以退出循环,也可以设置标志位来结束循环
max_age = 90
#flag=True
#True必须是大写的哈
#while flag
while True:
guess_age = raw_input("input the age of you guess>>:")
if int(guess_age) == max_age:
print ("Congratulation^_^")
break; # 终止循环
#exit(0)
#flag=false
elif int(guess_age) > max_age:
print ("please try small")
elif int(guess_age) < max_age:
print ("please try bigger")
else:
print("Sorry,~_~")
print "END"
1.9. 算术运算符
除法计算
print (5/2) # 2.5
print (5//2) # 2
Python特殊的判断:连续的大小判断
a=100
b=90
c=200
if b
print "OK" # OK
判断三个数字中的最大值
a=int (raw_input("input the first num:"))
b=int (raw_input("input the first num:"))
c=int (raw_input("input the first num:"))
max =a
if max < b:
max = b;
if max < c:
max = c;
print max
else:
print max
py内置数学函数
# abs(x) 返回数字的绝对值,如abs(-10) 返回 10
# ceil(x) 返回数字的上入整数,如math.ceil(4.1) 返回 5
# cmp(x, y) 如果 x < y 返回 -1, 如果 x == y 返回 0, 如果 x > y 返回 1
# exp(x) 返回e的x次幂(ex),如math.exp(1) 返回2.718281828459045
# fabs(x) 返回数字的绝对值,如math.fabs(-10) 返回10.0
# floor(x) 返回数字的下舍整数,如math.floor(4.9)返回 4
# log(x) 如math.log(math.e)返回1.0,math.log(100,10)返回2.0
# log10(x) 返回以10为基数的x的对数,如math.log10(100)返回 2.0
# max(x1, x2,...) 返回给定参数的最大值,参数可以为序列。
# min(x1, x2,...) 返回给定参数的最小值,参数可以为序列。
# modf(x) 返回x的整数部分与小数部分,两部分的数值符号与x相同,整数部分以浮点型表示。
# pow(x, y) x**y 运算后的值。
# round(x [,n]) 返回浮点数x的四舍五入值,如给出n值,则代表舍入到小数点后的位数。
# sqrt(x) 返回数字x的平方根,数字可以为负数,返回类型为实数,如math.sqrt(4)返回 2+0j
特殊的赋值运算符:
num += 1 等价于 num = num + 1
num -= 1 等价于 num = num - 1
num *= 2 等价于 num = num * 2
num /= 2 等价于 num = num / 2
num //= 2 等价于 num = num // 2
num %= 2 等价于 num = num % 2
num **= 2 等价于 num = num ** 2
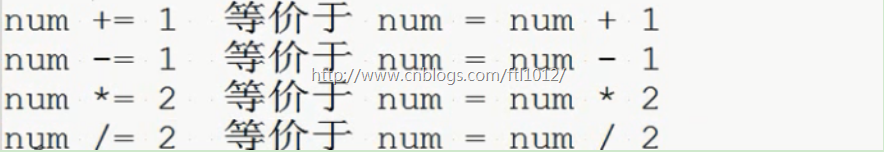
短路原则:类似Java中的 &&,||
对于and 如果前面的第一个条件为假,那么这个and前后两个条件组成的表达式 的计算结果就一定为假,第二个条件就不会被计算
对于or 如果前面的第一个条件为真,那么这个or前后两个条件组成的表达式 的计算结果就一定为真,第二个条件就不会被计算
not not True or False and not True ==> (not (not True) )or( False and (not True ))
--》True

1.10. break/continue
break: 退出本次循环
continue: 退出当前的循环
注意:Python的while语句中也可以由else的语法
num=1
while num<=9:
num += 1
if num == 3:
continue
print (num)
else:
print "while also has else syndex"
1.11. 编码规范
常量 : 大写加下划线
USER_CONSTANT
对于不会发生改变的全局变量,使用大写加下划线。私有变量 : 小写和一个前导下划线
_private_value
Python 中不存在私有变量一说,若是遇到需要保护的变量,使用小写和一个前导下划线。但这只是程序员之间的一个约定,用于警告说明这是一个私有变量,外部类不要去访问它。但实际上,外部类还是可以访问到这个变量。
内置变量 : 小写,两个前导下划线和两个后置下划线
__class__
两个前导下划线会导致变量在解释期间被更名。这是为了避免内置变量和其他变量产生冲突。用户定义的变量要严格避免这种风格。以免导致混乱。
2 函数和方法总体而言应该使用,小写和下划线。但有些比较老的库使用的是混合大小写,即首单词小写,之后每个单词第一个字母大写,其余小写。但现在,小写和下划线已成为规范。
私有方法 : 小写和一个前导下划线
def _secrete(self):
print "don't test me."
这里和私有变量一样,并不是真正的私有访问权限。同时也应该注意一般函数不要使用两个前导下划线(当遇到两个前导下划线时,Python 的名称改编特性将发挥作用)。特殊函数后面会提及。
特殊方法 : 小写和两个前导下划线,两个后置下划线
def __add__(self, other):
return int.__add__(other)
这种风格只应用于特殊函数,比如操作符重载等。
函数参数 : 小写和下划线,缺省值等号两边无空格
def connect(self, user=None):
self._user = user
3 类
类总是使用驼峰格式命名,即所有单词首字母大写其余字母小写。类名应该简明,精确,并足以从中理解类所完成的工作。常见的一个方法是使用表示其类型或者特性的后缀,例如:
SQLEngine
MimeTypes
对于基类而言,可以使用一个 Base 或者 Abstract 前缀
BaseCookie
AbstractGroup
class UserProfile(object):
def __init__(self, profile):
return self._profile = profile
def profile(self):
return self._profile
4 模块和包
除特殊模块 __init__ 之外,模块名称都使用不带下划线的小写字母。
若是它们实现一个协议,那么通常使用lib为后缀,例如:
import smtplib
import os
import sys
5 关于参数
5.1 不要用断言来实现静态类型检测
断言可以用于检查参数,但不应仅仅是进行静态类型检测。 Python 是动态类型语言,静态类型检测违背了其设计思想。断言应该用于避免函数不被毫无意义的调用。
5.2 不要滥用 *args 和 **kwargs
*args 和 **kwargs 参数可能会破坏函数的健壮性。它们使签名变得模糊,而且代码常常开始在不应该的地方构建小的参数解析器。
6 其他
6.1 使用 has 或 is 前缀命名布尔元素
is_connect = True
has_member = False
6.2 用复数形式命名序列
members = ['user_1', 'user_2']
6.3 用显式名称命名字典
person_address = {'user_1':'10 road WD', 'user_2' : '20 street huafu'}
6.4 避免通用名称
诸如 list, dict, sequence 或者 element 这样的名称应该避免。
6.5 避免现有名称
诸如 os, sys 这种系统已经存在的名称应该避免。
7 一些数字
一行列数 : PEP 8 规定为 79 列,这有些苛刻了。根据自己的情况,比如不要超过满屏时编辑器的显示列数。这样就可以在不动水平游标的情况下,方便的查看代码。
一个函数 : 不要超过 30 行代码, 即可显示在一个屏幕类,可以不使用垂直游标即可看到整个函数。
一个类 : 不要超过 200 行代码,不要有超过 10 个方法。
一个模块 不要超过 500 行。
1.12. 打印直角三角形
#coding:utf-8
#Python 3.5.2
lines = int(input("please input the lines:"))
while lines > 0:
tmp = lines
while tmp > 0:
print ("*",end="")#不换行
tmp -= 1
print ()
lines -= 1
1.13打印9*9
#Python 3.5.2
first = 9
while first > 0:
sec = 1
while sec <= first:
print (str(sec)+"*"+str(first)+"="+str(first * sec),end=" ")#不换行
sec += 1
print ()
first -= 1




















 1161
1161











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








