Sentinel是阿里巴巴开源的限流器熔断器,并且带有可视化操作界面。在日常开发中,限流功能时常被使用,用于对某些接口进行限流熔断,譬如限制单位时间内接口访问次数;或者按照某种规则进行限流,如限制ip的单位时间访问次数等。
之前我们已经讲过接口限流的工具类ratelimter可以实现令牌桶的限流,很明显sentinel的功能更为全面和完善。来看一下sentinel的简介:
https://github.com/spring-cloud-incubator/spring-cloud-alibaba/wiki/Sentinel
Sentinel 介绍
随着微服务的流行,服务和服务之间的稳定性变得越来越重要。Sentinel 以流量为切入点,从流量控制、熔断降级、系统负载保护等多个维度保护服务的稳定性。
Sentinel 具有以下特征:
-
丰富的应用场景:Sentinel 承接了阿里巴巴近 10 年的双十一大促流量的核心场景,例如秒杀(即突发流量控制在系统容量可以承受的范围)、消息削峰填谷、实时熔断下游不可用应用等。
-
完备的实时监控:Sentinel 同时提供实时的监控功能。您可以在控制台中看到接入应用的单台机器秒级数据,甚至 500 台以下规模的集群的汇总运行情况。
-
广泛的开源生态:Sentinel 提供开箱即用的与其它开源框架/库的整合模块,例如与 Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC 的整合。您只需要引入相应的依赖并进行简单的配置即可快速地接入 Sentinel。
-
完善的 SPI 扩展点:Sentinel 提供简单易用、完善的 SPI 扩展点。您可以通过实现扩展点,快速的定制逻辑。例如定制规则管理、适配数据源等。
来简单使用一下Sentinel。
Sentinel包括服务端和客户端,服务端有可视化界面,客户端需引入jar后即可和服务端通信并完成限流功能。
启动服务端的jar
https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/releases 在这个地址,下载release的jar,然后启动即可。
这个jar是个标准的Springboot应用,可以通过java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.6.0.jar来启动,这样就是默认的设置,启动在8080端口。也可以加上一些自定义配置来启动
java -Dserver.port=8080 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8080 -Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard -jar sentinel-dashboard.jar
具体配置的解释,可以到GitHub上看一下文档。
需要修改账号密码可加上:
-Dsentinel.dashboard.auth.username=sentinel -Dsentinel.dashboard.auth.password=123456
这里我们直接使用默认java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.6.0.jar来启动,之后访问localhost:8080。可以看到界面:
或者使用作者封装的最新docker镜像:docker运行阿里巴巴Sentinel

输入账号密码sentinel后进入主界面
此时因为我们并没有启动客户端,所以界面是空的。
启动客户端
新建一个Springboot项目,pom如下:
-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
-
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
-
xsi:schemaLocation=
"http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
-
<modelVersion>4.0.0
</modelVersion>
-
<parent>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot
</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent
</artifactId>
-
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE
</version>
-
<relativePath/>
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
-
</parent>
-
-
<groupId>com.maimeng.baobanq
</groupId>
-
<artifactId>baobanserver
</artifactId>
-
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
</version>
-
<packaging>jar
</packaging>
-
<name>baobanserver
</name>
-
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot
</description>
-
-
<properties>
-
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8
</project.build.sourceEncoding>
-
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8
</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
-
<java.version>1.8
</java.version>
-
<spring-cloud.version>Finchley.SR1
</spring-cloud.version>
-
</properties>
-
-
<dependencies>
-
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot
</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web
</artifactId>
-
</dependency>
-
-
<!--sentinel-->
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud
</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel
</artifactId>
-
</dependency>
-
<!--sentinel end-->
-
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot
</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test
</artifactId>
-
<scope>test
</scope>
-
</dependency>
-
</dependencies>
-
-
<dependencyManagement>
-
<dependencies>
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud
</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies
</artifactId>
-
<version>${spring-cloud.version}
</version>
-
<type>pom
</type>
-
<scope>import
</scope>
-
</dependency>
-
-
<dependency>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud
</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies
</artifactId>
-
<version>0.2.2.RELEASE
</version>
-
<type>pom
</type>
-
<scope>import
</scope>
-
</dependency>
-
</dependencies>
-
</dependencyManagement>
-
-
<build>
-
<plugins>
-
<plugin>
-
<groupId>org.springframework.boot
</groupId>
-
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin
</artifactId>
-
</plugin>
-
</plugins>
-
</build>
-
-
</project>
需要注意引用的SpringCloud-alibaba的版本是0.2.2,当前的最新版,如果是Springboot2.x的项目,需要引0.2.x的。Springboot1.x的引0.1.x的。
Sentinel的客户端依赖也很简单,spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel加这一个引用即可。
之后在application.yml里添加server的地址配置:
-
spring:
-
application:
-
name: baobanserver
-
cloud:
-
sentinel:
-
transport:
-
dashboard:
localhost:
8080
-
#
eager: true
另外由于8080端口已被占用,自行设置一个端口,如8888。
做完这些,新建一个controller,
-
@RestController
-
public
class TestController {
-
-
@GetMapping(value = "/hello")
-
public String hello() {
-
return
"Hello Sentinel";
-
}
-
}
就是一个普通的controller接口。
之后启动该项目。启动后回到server的控制台界面
发现并没有什么变化。然后我们调用一下hello接口。之后再次刷新server控制台。
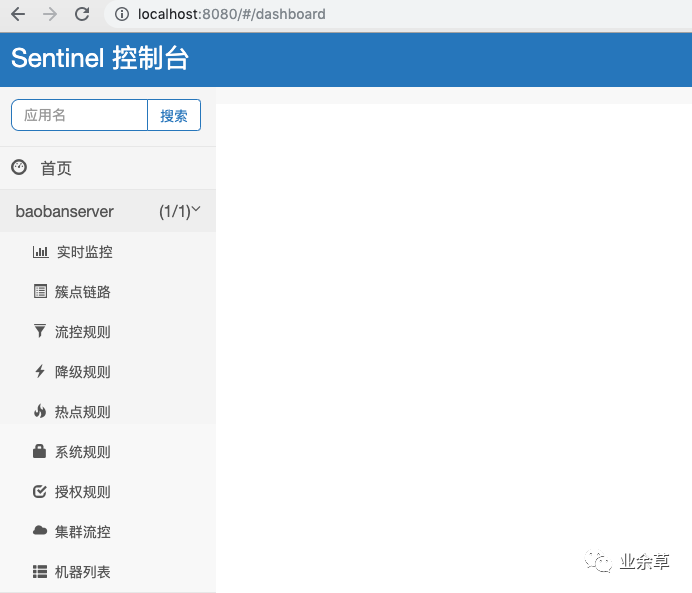
界面已经出现了我们的项目,并且有一堆规则。
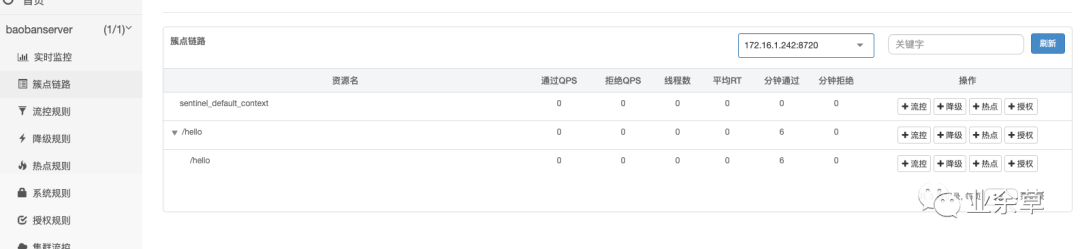
因为Sentinel采用延迟加载,只有在主动发起一次请求后,才会被拦截并发送给服务端。如果想关闭这个延迟,就在上面的yml里把eager的注释放掉。
然后在簇点链路里hello接口的流控那里设置限流规则,将单机阈值设为1.就代表一秒内最多只能通过1次请求到达该hello接口。
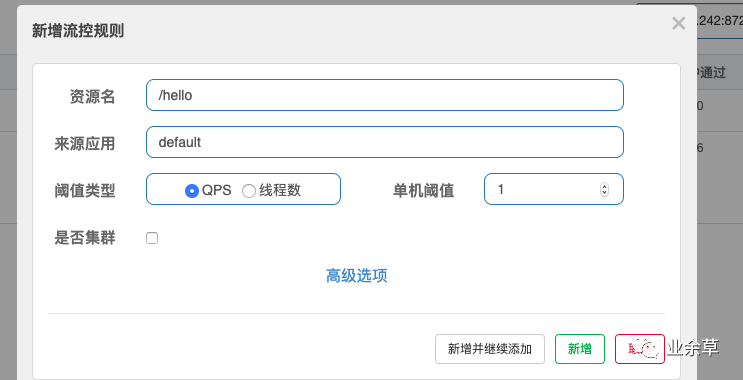
之后再次连续访问hello接口。
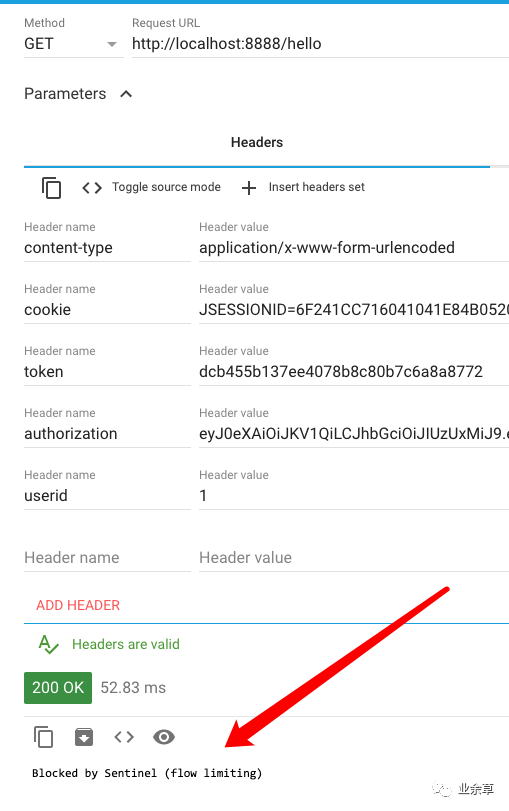
发现已经被拦截了,限流已经生效。
这样就完成了一次简单的限流操作,并且能看到各接口的QPS的统计。
Sentinel 的功能非常强大,这里只是一个入门的demo教程,建议大家阅读官网 get 更多技能!





















 502
502











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








