点击关注公众号,利用碎片时间学习
前言
网上貌似webflux这一套的SpringSecurity操作资料貌似很少。
自己研究了一波,记录下来做一点备忘,如果能帮到也在迷惑的人一点点,就更好了。
新项目是前后端分离的项目,前台vue,后端SpringCloud2.0,采用oauth2.0机制来获得用户,权限框架用的gateway。
一,前台登录
大概思路前台主要是配合项目中配置的clientId,clientSecret去第三方服务器拿授权码code,然后拿这个code去后端交互,后端根据code去第三方拿用户信息,由于第三方只保存用户信息,不管具体的业务权限,所以我会在本地保存一份用户副本,用来做权限关联。
用户登录成功后,会把一些用户基本信息(脱敏)生成jwt返回给前端放到head中当Authorization,同时后端把一些相关联的菜单,权限等数据放到redis里做关联,为后面的权限控制做准备。
二,SpringSecurity的webflux应用
如果用过SpringSecurity,HttpSecurity应该是比较熟悉的,基于Web允许为特定的http请求配置安全性。
WebFlux中ServerHttpSecurity与HttpSecurity提供的相似的类似,但仅适用于WebFlux。默认情况下,它将应用于所有请求,但可以使用securityMatcher(ServerWebExchangeMatcher)或其他类似方法进行限制。
项目比较特殊,就不能全展示了,大概写一写,开启Security如下:
@EnableWebFluxSecurity
public class MyExplicitSecurityConfiguration {
@Bean
SecurityWebFilterChain webFluxSecurityFilterChain(ServerHttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.securityContextRepository(new NoOpServerSecurityContextAutoRepository(tokenProvider)).httpBasic().disable()
.formLogin().disable()
.csrf().disable()
.logout().disable();
http.addFilterAt(corsFilter(), SecurityWebFiltersOrder.CORS)
.authorizeExchange()
.matchers(EndpointRequest.to("health", "info"))
.permitAll()
.and()
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS)
.permitAll()
.and()
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers(HttpMethod.PUT)
.denyAll()
.and()
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers(HttpMethod.DELETE)
.denyAll()
.and()
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers(HttpMethod.HEAD)
.denyAll()
.and()
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers(HttpMethod.PATCH)
.denyAll()
.and()
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers(HttpMethod.TRACE)
.denyAll()
.and()
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers(excludedAuthPages).permitAll()
.and()
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers(authenticatedPages).authenticated()
.and()
.exceptionHandling()
.accessDeniedHandler(new AccessDeniedEntryPointd())
.and()
.authorizeExchange()
.and()
.addFilterAt(webFilter(), SecurityWebFiltersOrder.AUTHORIZATION)
.authorizeExchange()
.pathMatchers("/**").access(new JwtAuthorizationManager(tokenProvider))
.anyExchange().authenticated();
return http.build();
}
}因为是前后端分离项目,所以没有常规的后端的登录操作,把这些disable掉。
securityContextRepository是个用于在请求之间保留SecurityContext策略接口,实现类是WebSessionServerSecurityContextRepository(session存储),还有就是NoOpServerSecurityContextRepository(用于无状态应用),像我们JWT这种就用后者,不能用前者,应该我们是无状态的应用,没有主动clear的操作,会导致内存溢出等问题。
build()方法中会有一个初始化操作。
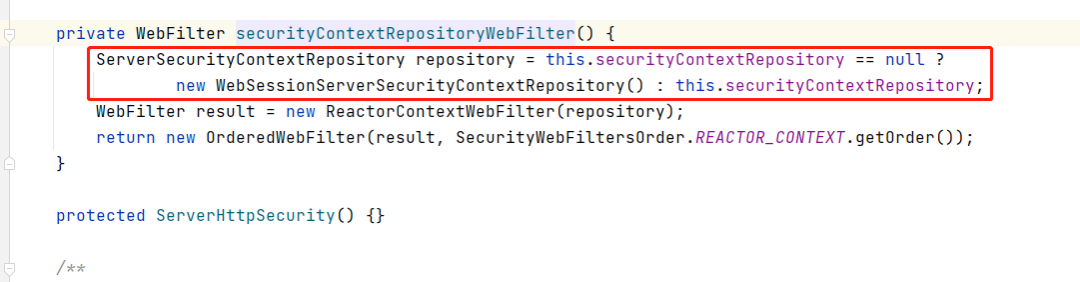
初始化操作就设置成了WebSessionServerSecurityContextRepository,我们就自己在SecurityWebFilterChain中设置成NoOpServerSecurityContextRepository。
接下来我们为了满足自定义认证需求,我们自己配置一个AuthenticationWebFilter。
public AuthenticationWebFilter webFilter() {
AuthenticationWebFilter authenticationWebFilter = new AuthenticationWebFilter(new JWTReactiveAuthenticationManager(userCache, tokenProvider, coreUserApi));
authenticationWebFilter.setServerAuthenticationConverter(new TokenAuthenticationConverter(guestList, tokenProvider));
authenticationWebFilter.setRequiresAuthenticationMatcher(new NegatedServerWebExchangeMatcher(ServerWebExchangeMatchers.pathMatchers(excludedAuthPages)));
authenticationWebFilter.setSecurityContextRepository(new NoOpServerSecurityContextAutoRepository(tokenProvider));
return authenticationWebFilter;
}几个特殊的类,稍微解释下。
AuthenticationWebFilter
一个执行特定请求身份验证的WebFilter,包含了一整套验证的流程操作,具体上源码看一眼基本能了解个大概。
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, WebFilterChain chain) {
return this.requiresAuthenticationMatcher.matches(exchange)
.filter( matchResult -> matchResult.isMatch())
.flatMap( matchResult -> this.authenticationConverter.convert(exchange))
.switchIfEmpty(chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.empty()))
.flatMap( token -> authenticate(exchange, chain, token))
.onErrorResume(AuthenticationException.class, e -> this.authenticationFailureHandler
.onAuthenticationFailure(new WebFilterExchange(exchange, chain), e));
}
private Mono<Void> authenticate(ServerWebExchange exchange, WebFilterChain chain, Authentication token) {
return this.authenticationManagerResolver.resolve(exchange)
.flatMap(authenticationManager -> authenticationManager.authenticate(token))
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.defer(() -> Mono.error(new IllegalStateException("No provider found for " + token.getClass()))))
.flatMap(authentication -> onAuthenticationSuccess(authentication, new WebFilterExchange(exchange, chain)));
}
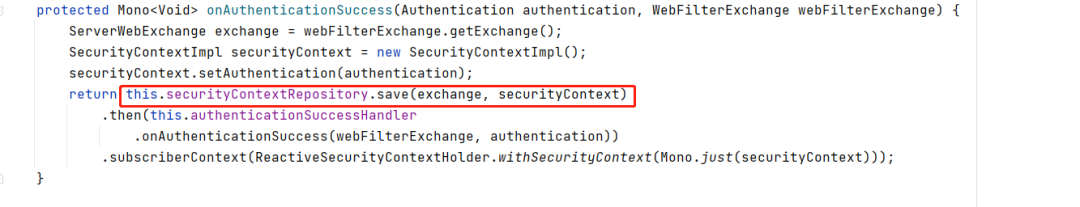
protected Mono<Void> onAuthenticationSuccess(Authentication authentication, WebFilterExchange webFilterExchange) {
ServerWebExchange exchange = webFilterExchange.getExchange();
SecurityContextImpl securityContext = new SecurityContextImpl();
securityContext.setAuthentication(authentication);
return this.securityContextRepository.save(exchange, securityContext)
.then(this.authenticationSuccessHandler
.onAuthenticationSuccess(webFilterExchange, authentication))
.subscriberContext(ReactiveSecurityContextHolder.withSecurityContext(Mono.just(securityContext)));
}
ServerWebExchangeMatcher
一个用来匹配URL用来验证的接口,我代码中用的是他的实现类NegatedServerWebExchangeMatcher,这个类就是指一些我设置的白名单的url就不要验证了,他还有许多实现类,具体可以参见源码,我这就不累述了。
ServerAuthenticationConverter
一个用于从ServerWebExchange转换为用于通过提供的org.springframework.security.authentication.ReactiveAuthenticationManager进行身份验证的Authentication的策略。如果结果为Mono.empty() ,则表明不进行任何身份验证尝试。我这边自己实现了一个TokenAuthenticationConverter,主要功能就是通过JWT转换成Authentication(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)。
ReactiveAuthenticationManager
对提供的Authentication进行身份验证,基本上核心的验证操作就在它提供的唯一方法authenticate里进行操作,根据conver那边转换过来的Authentication当参数进行具体的验证操作,简述如下:
@Override
public Mono<Authentication> authenticate(final Authentication authentication) {
if (authentication.isAuthenticated()) {
return Mono.just(authentication);
}
return Mono.just(authentication)
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.defer(this::raiseBadCredentials))
.cast(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class)
.flatMap(this::authenticateToken)
.publishOn(Schedulers.parallel())
.onErrorResume(e -> raiseBadCredentials())
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.defer(this::raiseBadCredentials))
.map(u -> {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(authentication.getPrincipal(), authentication.getName(), Collections.EMPTY_LIST);
usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.setDetails(u);
return usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
});
}ServerSecurityContextRepository
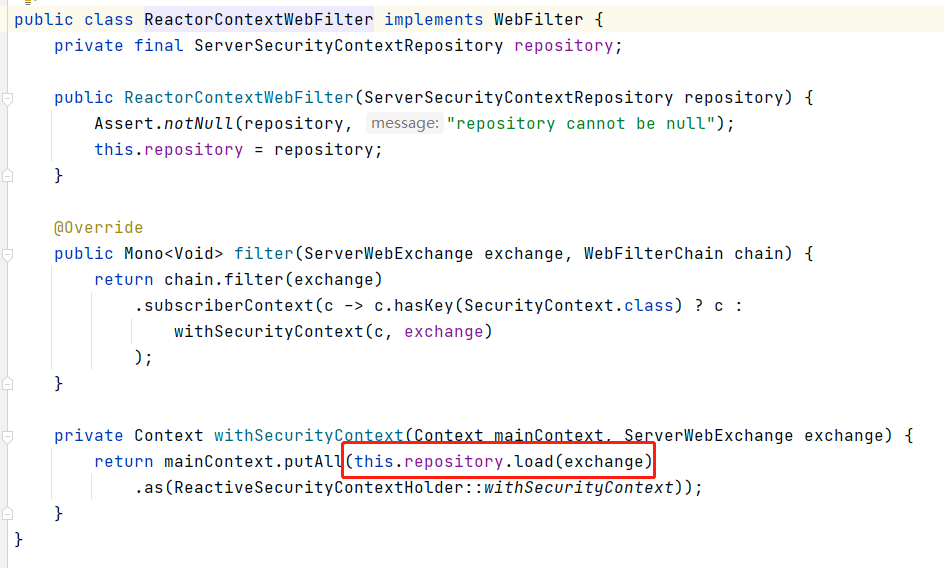
用于在请求之间保留SecurityContext,因为在登录成功后我们是需要保存一个登录的数据,用来后面的请求进行相关的操作。因为我们是无状态的,所以其实NoOpServerSecurityContextRepository是能满足我们的需求,我们不需要进行实际的save,但是load我们稍微要改造下,所以我实现了ServerSecurityContextRepository,仿照NoOpServerSecurityContextRepository,实现了一个自定义的Repository。
为什么load我们要改造,就是因为虽然我们是无状态的,但是实际上每次请求,我们依然要区分到底是谁,为了后面的权限验证做准备,所以我们根据jwt可以生成一个SecurityContext放入ReactiveSecurityContextHolder。
public class NoOpServerSecurityContextAutoRepository
implements ServerSecurityContextRepository {
private TokenProvider tokenProvider;
public NoOpServerSecurityContextAutoRepository(TokenProvider tokenProvider) {
this.tokenProvider = tokenProvider;
}
public Mono<Void> save(ServerWebExchange exchange, SecurityContext context) {
return Mono.empty();
}
public Mono<SecurityContext> load(ServerWebExchange exchange) {
String token = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders().getFirst("Authorization");
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(token)) {
SecurityContext securityContext = new SecurityContextImpl();
securityContext.setAuthentication(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken("password", token, Collections.EMPTY_LIST));
return Mono.justOrEmpty(securityContext);
} else {
return Mono.empty();
}
}
}权限验证

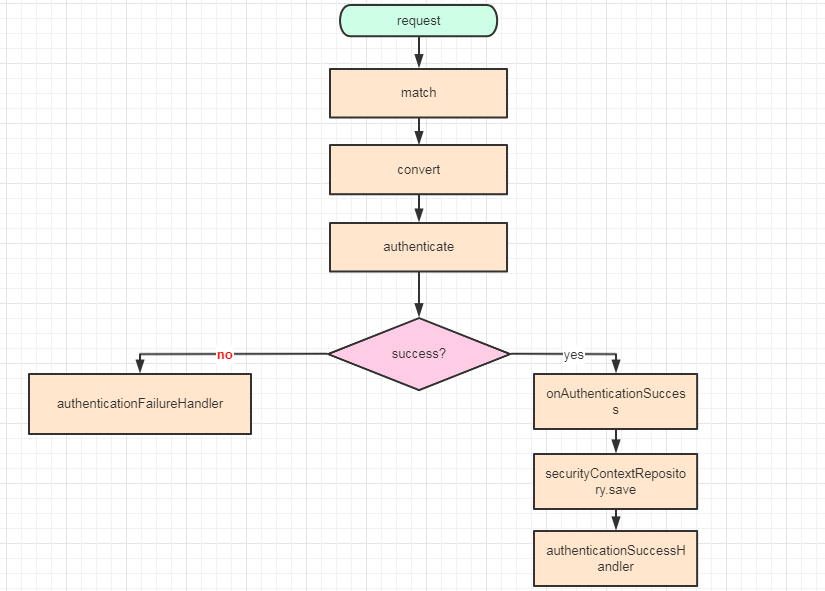
权限验证是在图上配置的。大概的流程,可以看下面的截图。
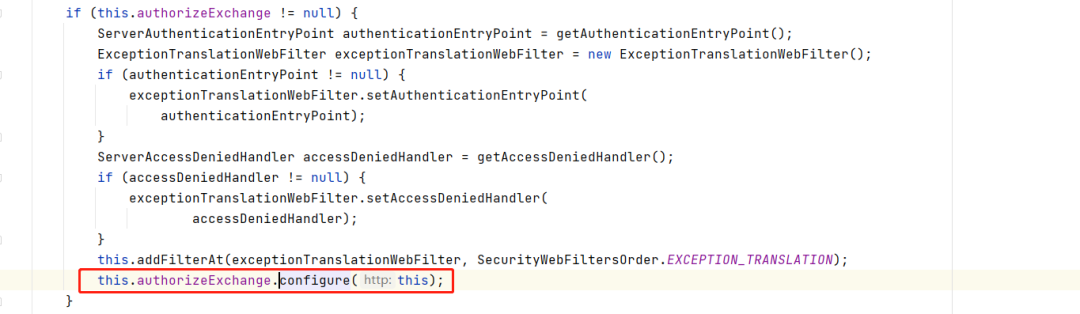
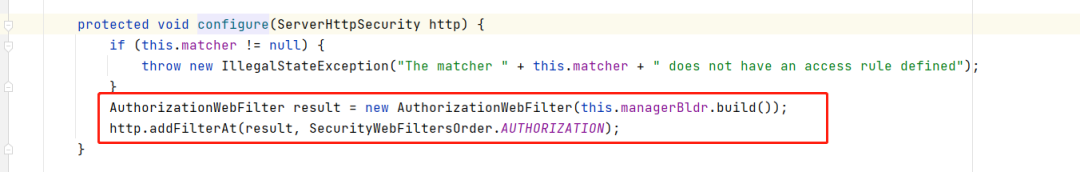
AuthorizationWebFilter
跟到里面,我们发现了最主要的就是这个AuthorizationWebFilter,用来做权限验证的,然后我们在filter方法里面就看得很清楚了,他第一步就是拿的ReactiveSecurityContextHolder.getContext(),然后我们之前在ReactorContextWebFilter里的load操作就是从我们NoOpServerSecurityContextAutoRepository里塞到ReactiveSecurityContextHolder里,因为本质 来说SpringSecurity就是个filter集合,我们从ReactorContextWebFilter里load,然后在AuthorizationWebFilter取,这样就能拿到Authentication来做权限验证了。
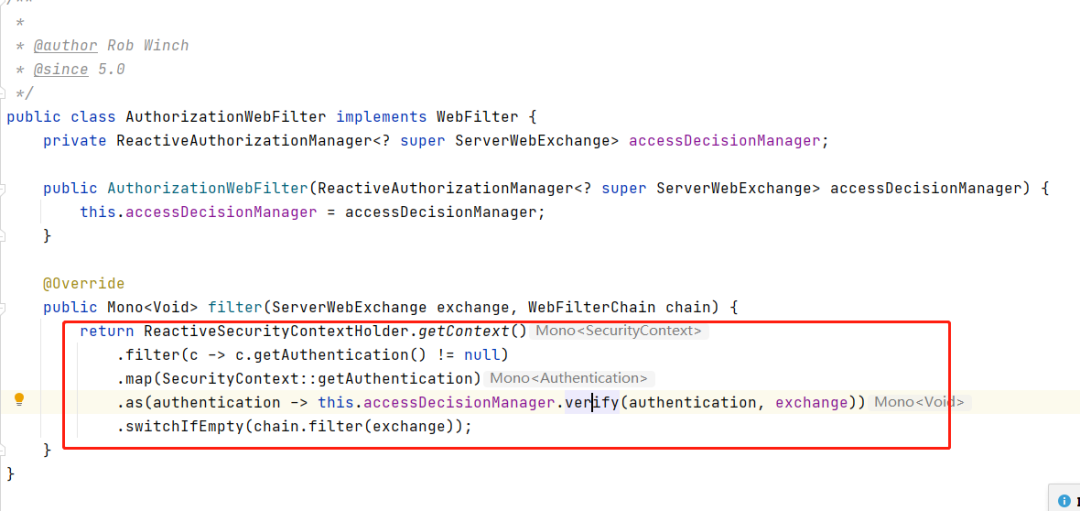
ReactiveAuthorizationManager
反应式授权管理器接口,可以确定Authentication是否有权访问特定对象。其实看源码就很清楚了,就是根据Authentication来做具体的权限验证。
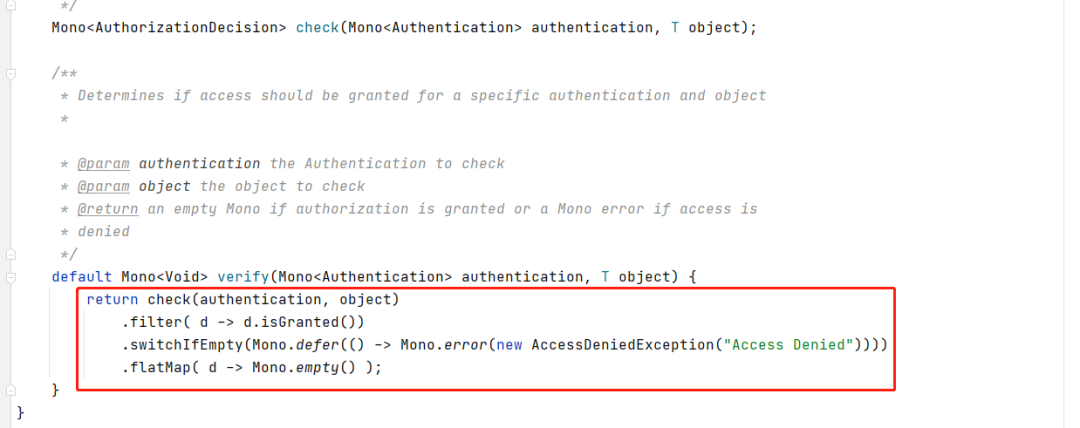
代码很清楚,就不细讲了,我们主要是写check方法。所以我这边自已实现了一个JwtAuthorizationManager类用来做具体的check,内容我就不贴了,简单来说就是拿Authentication里的内容去redis里查对应的菜单权限。
结语
上面就我实际项目中的一些点滴记录,Spring-Security虽是一个博大精深的框架,细研究代码,其实也能大致明白整体的思路,虽然webflux让这一层代码更加了一层迷雾,但是只要努力钻研,总会有茅塞顿开的时候。
感谢阅读,希望对你有所帮助 :)
来源:cnblogs.com/zhou-yuan/p/14472889.html
推荐:
最全的java面试题库
PS:因为公众号平台更改了推送规则,如果不想错过内容,记得读完点一下“在看”,加个“星标”,这样每次新文章推送才会第一时间出现在你的订阅列表里。点“在看”支持我们吧!



















 584
584











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








