反射:是动态语言的的关键
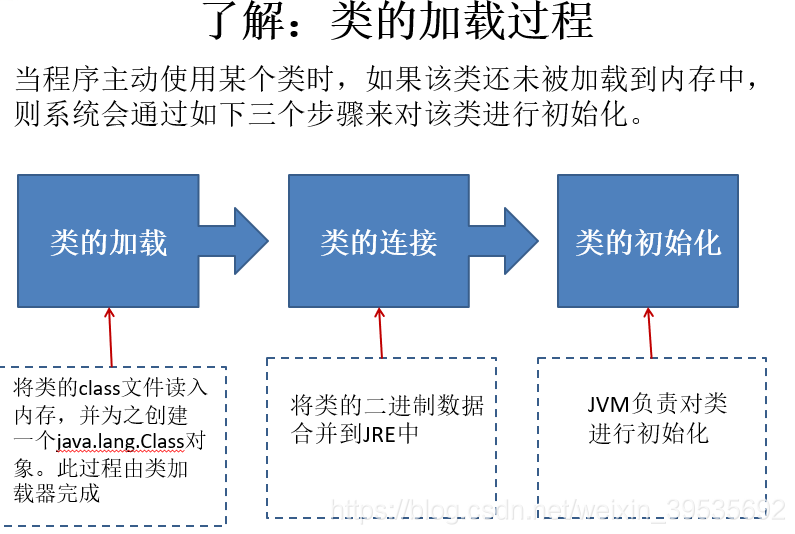
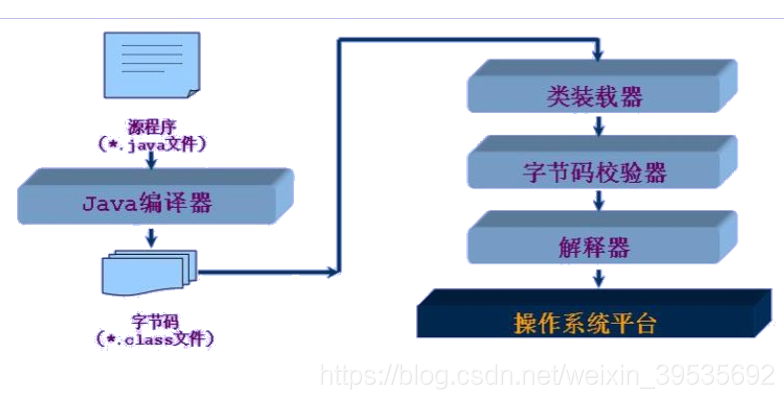
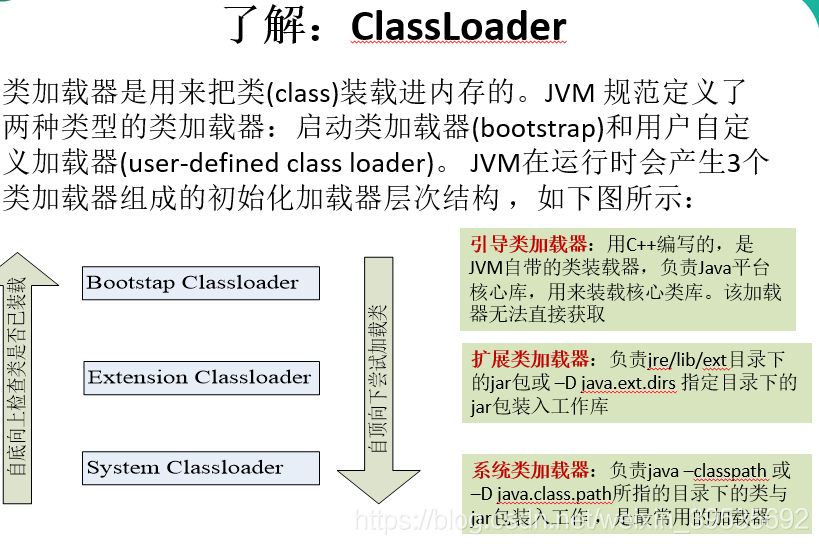
了解类加载器
// 了解类加载器
@Test
public void test1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
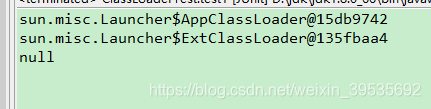
// 系统类加载器 自己编写的的
ClassLoader cl = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
System.out.println(cl);
//扩展类库
ClassLoader cl2 = cl.getParent();
System.out.println(cl2);
//核心类库无法拿到
ClassLoader cl3 = cl2.getParent();
System.out.println(cl3);
}
重要:
// 【重要】通过类加载器加载属性文件
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
Properties pros = new Properties();
// pros.load(new FileInputStream("./hello.properties"));
/*
* ClassLoader cl = this.getClass().getClassLoader(); InputStream in =
* cl.getResourceAsStream("com/atguigu/java/hello.properties");
* pros.load(in);
*/
pros.load(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("com/atguigu/java/hello.properties"));
String userName = pros.getProperty("userName");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(userName);
System.out.println(password);
}
1 Class类描述类的类
clazz通过描述的对应类的构造器获取实例
/*
* 1. Java 程序的运行分为两种状态:
* 编译时:通过 javac 命令,生成零个或多个 .class 字节码文件。(每个 .class 对应一个类)
* 运行时:通过 java 命令,将零个或多个 .class 字节码文件加载到内存中。(由 JVM 提供的类加载器)
*
* 2. 类用于描述现实生活中的一类事物,类是抽象的,若需要具体到某一个事物,通过 new 关键字创建对象。
* 可以操作对象的属性,调用对象的方法。
* (因为在编译时可以确定创建什么类的对象,操作什么属性,调用什么方法)
* 在某种情况下,我们需要得知并使用一个在编译时完全未知的类,创建其对象,操作其属性,调用其方法
*
* 一、反射机制(Reflection):被视为动态语言的关键,在运行时创建任意类的对象,获取并操作任意对象的属性和方法。
*
* Class 是开启反射的源头!
*
* 如何获取 Class 的实例?
* //1. 通过运行时类的属性 class
* //2. 通过运行时类对象的 getClass()
* //3. 通过 Class 静态方法 forName(String className)
* //4. 通过类加载器(了解)
*
* 二、反射的功能:
* ①在运行时判断任意类的对象
* ②在运行时判断任意类的结构
* ③在运行时获取任意类的属性和方法
* ④在运行时调用任意类对象的属性和方法
* ⑤生成动态代理
*
*/
public class ReflectionTest {
//
/*public <T> T get(Class<T> clazz){
//---
return clazz.newInstance();
}*/
@Test
public void test2() throws ClassNotFoundException{
//1. 通过运行时类的属性 class
Class clazz = Person.class;
System.out.println(clazz);
//2. 通过运行时类对象的 getClass()
Person p = new Person();
Class clazz2 = p.getClass();
System.out.println(clazz2);
//3. 通过 Class 静态方法 forName(String className)
String className = "com.atguigu.java.Person";
Class clazz3 = Class.forName(className);
System.out.println(clazz3);
//4. 通过类加载器(了解)
ClassLoader cl = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
Class clazz4 = cl.loadClass(className);
System.out.println(clazz4);
}
//反射之前
@Test
public void test1(){
Person p = new Person();
p.setName("张三");
}
public class InstanceTest {
//1.在运行时创建类的对象 : newInstance() 方法,该方法默认调用运行时类的无参构造器
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
/*Class clazz = Person.class;
Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
System.out.println(p);*/
Class<Person> clazz = Person.class;
Person p = clazz.newInstance();
System.out.println(p);
}
//1. 在运行时获取运行时类的属性
@Test
public void test1(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
//getFields() : 获取所有 public 修饰的属性,包括父类的
//Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();
//getDeclaredFields() : 获取本类所有声明的属性,包括私有的,不包括父类的
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field.getName());
}
}
}
//2. 在运行时获取运行时类属性的完整结构:修饰符 数据类型 属性名
@Test
public void test2(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
//①修饰符
int mod = field.getModifiers();
String strMod = Modifier.toString(mod);
System.out.print(strMod + "\t");
//②数据类型
Class type = field.getType();
System.out.print(type + "\t");
//③属性名
System.out.println(field.getName());
}
}
//7. 在运行时获取运行时类的包
@Test
public void test7(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Package pk = clazz.getPackage();
System.out.println(pk);
}
//6. 在运行时获取运行时类的注解
@Test
public void test6(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
// System.out.println(annotation);
MyAnnotation ma = (MyAnnotation) annotation;
System.out.println(ma.value());
}
}
//5. 在运行时获取运行时类的内部类
@Test
public void test5(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
// Class[] clazzes = clazz.getClasses();
Class[] clazzes = clazz.getDeclaredClasses();
for (Class class1 : clazzes) {
System.out.println(class1);
}
}
//4. 在运行时获取运行时类的接口
@Test
public void test4(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Class[] clazzes = clazz.getInterfaces();
for (Class class1 : clazzes) {
System.out.println(class1);
}
}
//3. 【重要】在运行时获取运行时类带泛型父类的泛型类型
@Test
public void test3(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
//1. 获取带泛型的父类类型
Type type = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
//2. 参数化类型 com.atguigu.java.Creature<java.lang.String>
ParameterizedType pt = (ParameterizedType) type;
//3. 获取参数类型
Type[] types = pt.getActualTypeArguments();
Class cl = (Class) types[0];
System.out.println(cl.getName());
}
//2. 在运行时获取运行时类带泛型父类的类型: Creature<String> c = new Creature<>();
@Test
public void test2(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Type type = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
System.out.println(type);//com.atguigu.java.Creature<java.lang.String>
}
//1. 在运行时获取运行时类的父类
@Test
public void test1(){
Class clazz = Person.class;
Class superClazz = clazz.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(superClazz);
}
动态代理
1 什么是动态代理。
/*
* 动态代理需要实现接口:InvocationHandler
*
* public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
*
* proxy : 生成的代理对象
* method : 代理对象需要执行方法的 Method 的实例
* args : 执行方法需要的参数
*/
public class DynaProxyHandler implements InvocationHandler{
//目标对象
private Object target;
//生成动态代理对象
public Object getProxyInstance(Object target){
this.target = target;
/*
* 第一个参数:通常与目标对象的类加载器一致
* 第二个参数:通常与目标对象实现的接口一致(实现哪些接收说明有什么方法)
* 第三个参数:实现了 InvocationHandler 接口实现类的实例(目的是执行 invoke() 方法)
*/
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("---------代理开始---------");//面向切面编程
Object obj = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("---------代理结束---------");
return obj;
}
}





















 82
82











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








