
Hystrix官网的原理介绍以及使用介绍非常详细,非常建议看一遍,地址见参考文档部分。
一、Hystrix原理
1. Hystrix能做什么
通过hystrix可以解决雪崩效应问题,它提供了资源隔离、降级机制、融断、缓存等功能。
- 资源隔离:包括线程池隔离和信号量隔离,限制调用分布式服务的资源使用,某一个调用的服务出现问题不会影响其他服务调用。
- 降级机制:超时降级、资源不足时(线程或信号量)降级,降级后可以配合降级接口返回托底数据。
- 融断:当失败率达到阀值自动触发降级(如因网络故障/超时造成的失败率高),熔断器触发的快速失败会进行快速恢复。
- 缓存:返回结果缓存,后续请求可以直接走缓存。
- 请求合并:可以实现将一段时间内的请求(一般是对同一个接口的请求)合并,然后只对服务提供者发送一次请求。
2. 隔离模式
Hystrix提供了两种隔离模式:线程池隔离模式、信号量隔离模式。
- 线程池隔离模式:使用一个线程池来存储当前请求,线程池对请求作处理,设置任务返回处理超时时间,堆积的请求先入线程池队列。这种方式要为每个依赖服务申请线程池,有一定的资源消耗,好处是可以应对突发流量(流量洪峰来临时,处理不完可将数据存储到线程池队里慢慢处理)
- 信号量隔离模式:使用一个原子计数器(或信号量)记录当前有多少个线程在运行,请求来先判断计数器的数值,若超过设置的最大线程个数则丢弃该类型的新请求,若不超过则执行计数操作请求来计数器+1,请求返回计数器-1。这种方式是严格的控制线程且立即返回模式,无法应对突发流量(流量洪峰来临时,处理的线程超过数量,其他的请求会直接返回,不继续去请求依赖的服务)
3. 降级
服务降级的目的保证上游服务的稳定性,当整体资源快不够了,将某些服务先关掉,待渡过难关,再开启回来。
①. 快速模式
如果调用服务失败了,那么立即失败并返回。
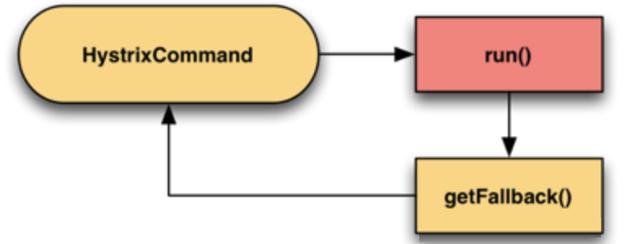
②. 故障转移
如果调用服务失败了,那么调用备用服务,因为备用服务也可能失败,所以也可能有再下一级的备用服务,如此形成一个级联。例如:如果服务提供者不响应,则从缓存中取默认数据。
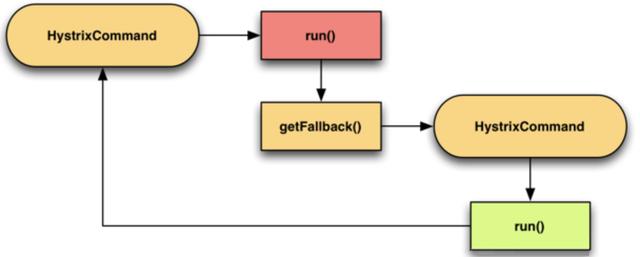
③. 主次模式
举个例子:开发中需要上线一个新功能,但为了防止新功能上线失败可以回退到老的代码,我们会做一个开关比做一个配置开关,可以动态切换到老代码功能。那么Hystrix它是使用通过一个配置来在两个command中进行切换。
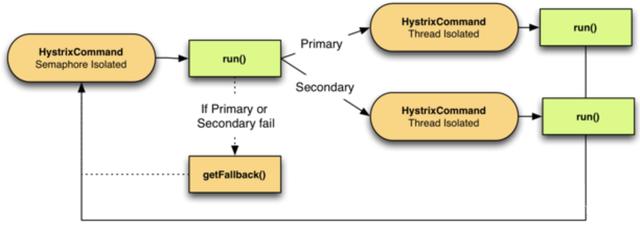
4. 熔断器
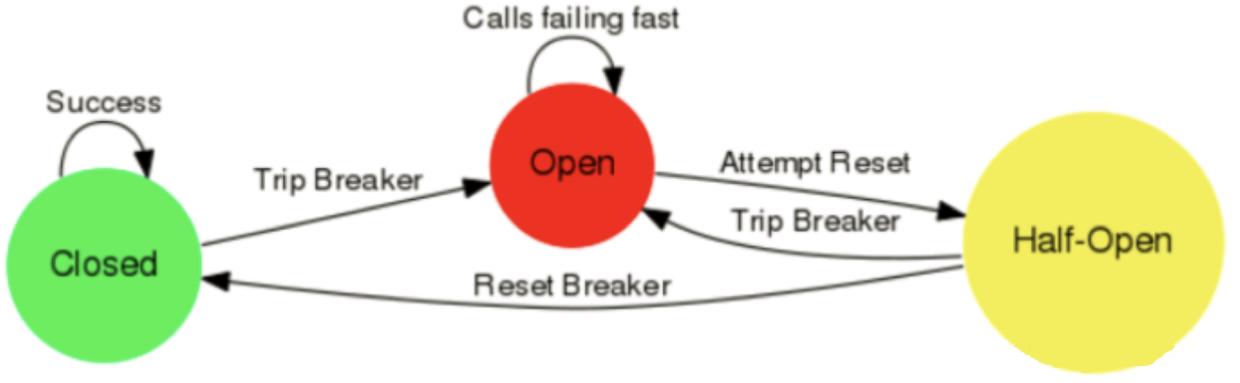
①. 熔断器流程
下图是Hystrix官网提供的熔断器工作流程。
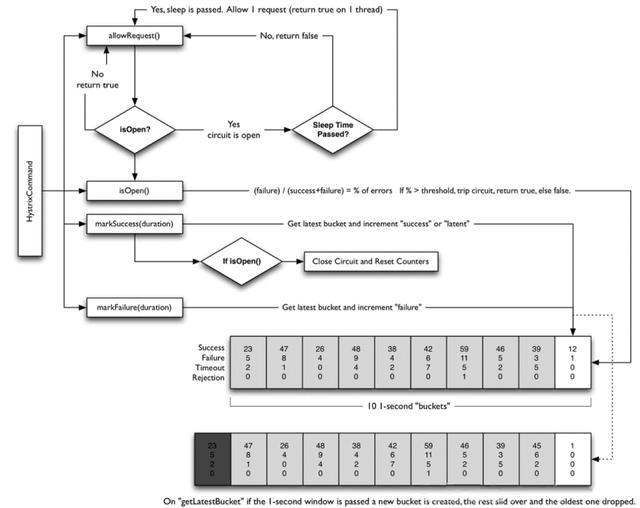
②. 熔断器原理
- 开始时断路器处于关闭状态(Closed)。
- 如果调用持续出错、超时或失败率超过一定限制,断路器打开进入熔断状态,后续一段时间内的所有请求都会被直接拒绝。
- 一段时间以后,保护器会尝试进入半熔断状态(Half-Open),允许少量请求进来尝试;如果调用仍然失败,则回到熔断状态,如果调用成功,则回到电路闭合状态;
5. 请求合并器
①. HystrixCollapser
微服务架构中通常需要依赖多个远程的微服务,而远程调用中最常见的问题就是通信消耗与连接数占用。在高并发的情况之下,因通信次数的增加,总的通信时间消耗将会变得越来越长。同时,因为依赖服务的线程池资源有限,将出现排队等待与响应延迟的清况。
为了优化这两个问题,Hystrix 提供了HystrixCollapser来实现请求的合并,以减少通信消耗和线程数的占用。
HystrixCollapser实现了在 HystrixCommand之前放置一个合并处理器,将处于一个很短的时间窗(默认10毫秒)内对同一依赖服务的多个请求进行整合,并以批量方式发起请求的功能(前提是服务提供方提供相应的批量接口)。HystrixCollapser的封装多个请求合并发送的具体细节,开发者只需关注将业务上将单次请求合并成多次请求即可。
②. 合并请求的开销
需要注意请求合并的额外开销:用于请求合并的延迟时间窗会使得依赖服务的请求延迟增高。比如,某个请求不通过请求合并器访问的平均耗时为5ms,请求合并的延迟时间窗为lOms (默认值), 那么当该请求设置了请求合并器之后,最坏情况下(在延迟时间 窗结束时才发起请求)该请求需要15ms才能完成。
③. 什么时候使用合并请求的功能?
合并请求存在额外开销,所以需要根据依赖服务调用的实际情况决定是否使用此功能,主要考虑下面两个方面:
a) 请求命令本身的延迟
对于单次请求而言,如果[单次请求平均时间/时间窗口]越小,对于单次请求的性能形象越小。如果依赖服务的请求命令本身是一个高延迟的命令,那么可以使用请求合并器,因为延迟时间窗的时间消耗显得微不足道了。
b) 并发量
时间窗口内并发量越大,合并求情的性能提升越明显。如果一个时间窗内只有少数几个请求,那么就不适合使用请求合并器。相反,如果一个时间窗内具有很高的并发量,那么使用请求合并器可以有效减少网络连接数量并极大提升系统吞吐量,此时延迟时间窗所增加的消耗就可以忽略不计了。
6. Hystrix工作流程
下图来自Hystrix官网,其描述了Hystrix的工作流程。
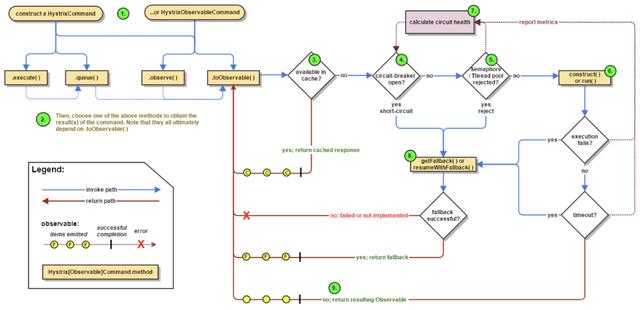
转换成流程图,如下所示:
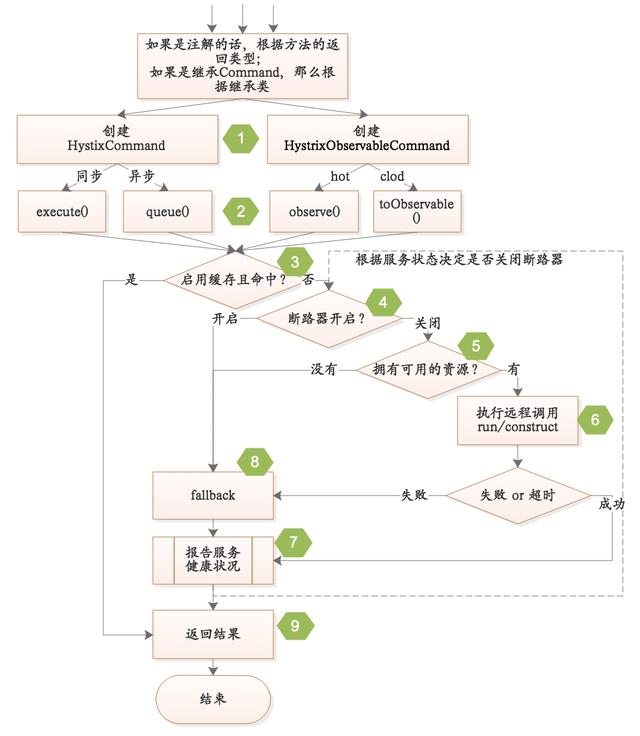
接下来详细介绍一下这次流程图,以及其中的9步操作。

二、Hystrix工作流程详解
1. 创建Command对象
①. 说明
HystrixCommand:用在依赖的服务返回单个操作结果的时候。HystrixObservableCommand:用在依赖的服务返回多个操作结果的时候。通过以下方式创建Command对象。
HystrixCommand command =newHystrixCommand(arg1, arg2); HystrixObservableCommand command =newHystrixObservableCommand(arg1, arg2);如果通过注解的方式使用HystrixCommand,那么在请求被拦截时,将会在HystrixCommandAspect中创建Command对象。
②. 代码
HystrixCommandAspect #methodsAnnotatedWithHystrixCommand方法
HystrixInvokable invokable = HystrixCommandFactory.getInstance().create(metaHolder);ExecutionType executionType = metaHolder.isCollapserAnnotationPresent() ?metaHolder.getCollapserExecutionType() : metaHolder.getExecutionType();Object result;try { result = CommandExecutor.execute(invokable, executionType, metaHolder);}catch (HystrixBadRequestException e) { throw e.getCause();}HystrixCommandFactory#create方法
public HystrixInvokable create(MetaHolder metaHolder) { HystrixInvokable executable; if (metaHolder.isCollapserAnnotationPresent()) { executable = new CommandCollapser(metaHolder); } else if (metaHolder.isObservable()) { executable = new GenericObservableCommand (HystrixCommandBuilderFactory. getInstance().create(metaHolder)); } else { executable = new GenericCommand(HystrixCommandBuilderFactory. getInstance().create(metaHolder)); } return executable;}2. 命令执行
①. 代码
通过以下代码我们可以看到Command对象根据方法返回结果类型,决定如何执行命令。
public static Object execute(HystrixInvokable invokable, ExecutionType executionType, MetaHolder metaHolder) throws RuntimeException { Validate.notNull(invokable); Validate.notNull(metaHolder); switch (executionType) { case SYNCHRONOUS: { return castToExecutable(invokable, executionType).execute(); } case ASYNCHRONOUS: { HystrixExecutable executable = castToExecutable(invokable, executionType); if (metaHolder.hasFallbackMethodCommand() && ExecutionType.ASYNCHRONOUS == metaHolder.getFallbackExecutionType()) { return new FutureDecorator(executable.queue()); } return executable.queue(); } case OBSERVABLE: { HystrixObservable observable = castToObservable(invokable); return ObservableExecutionMode.EAGER == metaHolder.getObservableExecutionMode() ? observable.observe() : observable.toObservable(); } default: throw new RuntimeException("unsupported execution type: " + executionType); }}其中ExecutionType是根据方法的返回结果的类型决定的,代码如下:
CollapserMetaHolderFactory#create方法
ExecutionType.getExecutionType(batchCommandMethod .getReturnType())ExecutionType#getExecutionType方法
public static ExecutionType getExecutionType(Class> type) { if (Future.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) { return ExecutionType.ASYNCHRONOUS; } else if (Observable.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) { return ExecutionType.OBSERVABLE; } else { return ExecutionType.SYNCHRONOUS; }}HystrixCommand#execute方法
这是Command的同步执行方法。和下面异步方法对比可知仅仅是多了一个Future.get()调用。
public R execute() { try { return queue().get(); } catch (Exception e) { throw decomposeException(e); }}HystrixCommand#queue方法如下所示。这是Command的异步执行方法。
public Future queue() { final Observable o = toObservable(); final Future f = o.toBlocking().toFuture(); /* special handling of error states that throw immediately */ if (f.isDone()) { try { f.get(); return f; } catch (Exception e) { // 略去 } } return f;}②, 分析
a) HystrixComrnand执行方式
execute():同步执行,从依赖的服务返回一个单一的结果对象,或是在发生错误的时候抛出异常。
queue():异步执行,直接返回一个Future对象,其中包含了服务执行结束时要返回的单一结果对象。
value = command.execute();Future fValue = command.queue();b) HystrixObservableCommand执行方式
- observe():返回Observable对象,它代表了操作的多个结果,它一个Hot Observable。
- toObservable():同样会返回Observable对象,也代表了操作的多个结果,但它返回的是一个Cold Observable。
Observable ohValue = command.observe();//hot observableObservable ocValue = command.toObservable();//cold observable不论事件源是否有订阅者,Hot Observable都会在创建后对事件进行发布,所以对于Hot Observable的“订阅者”都有可能是从“事件源”的中途开始的,并可能只是看到了整个操作的局部过程。而Cold Observable在没有订阅者的时候并不会发布事件,而是进行等待,直到有订阅者之后才发布事件,所以对于Cold Observable的订阅者,它可以保证从一开始看到整个操作的全部过程。
3. 从缓存中取结果?
①. 分析
当前Command是否启用缓存功能(即hystrix.command.default.requestCache.enabled是否为true),启用缓存,并且缓存命中时,立即返回;当返回数据后丢入缓存中去。
②. 代码
AbstractCommand#toObservable中
public Observable toObservable() { //省略 final Boolean requestCacheEnabled = isRequestCachingEnabled(); final String cacheKey = getCacheKey(); final AbstractCommand _cmd = this; /* try from cache first */ if (requestCacheEnabled) { HystrixCommandResponseFromCache fromCache = (HystrixCommandResponseFromCache) requestCache.get(cacheKey); if (fromCache != null) { isResponseFromCache = true; return handleRequestCacheHitAndEmitValues(fromCache, _cmd); } } //省略 // put in cache if (requestCacheEnabled && cacheKey != null) { // wrap it for caching HystrixCachedObservable toCache = HystrixCachedObservable.from(hystrixObservable, this); HystrixCommandResponseFromCache fromCache = (HystrixCommandResponseFromCache) requestCache.putIfAbsent(cacheKey, toCache); if (fromCache != null) { // another thread beat us so we'll use the cached value instead toCache.unsubscribe(); isResponseFromCache = true; return handleRequestCacheHitAndEmitValues(fromCache, _cmd); } else { // we just created an ObservableCommand so we cast and return it afterCache = toCache.toObservable(); } } else { afterCache = hystrixObservable; } //省略}4. 断路器是否打开?
如果断路器是打开的,那么进入fallback处理流程;如果断路器是关闭的,那么进入下一步。
AbstractCommand#applyHystrixSemantics中
private Observable applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand _cmd) { executionHook.onStart(_cmd); /* determine if we're allowed to execute */ if (circuitBreaker.allowRequest()) { //省略 } else { return handleShortCircuitViaFallback(); }}5. 是否有资源可用?
如果此Command相关的线程池的请求队列或信号量已满,那么进入fallback处理流程,否则进入下一步。以下是信号量检查相关的代码:
AbstractCommand#applyHystrixSemantics中
private Observable applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand _cmd) { executionHook.onStart(_cmd); /* determine if we're allowed to execute */ if (circuitBreaker.allowRequest()) { final TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore = getExecutionSemaphore(); final AtomicBoolean semaphoreHasBeenReleased = new AtomicBoolean(false); final Action0 singleSemaphoreRelease = new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (semaphoreHasBeenReleased.compareAndSet (false, true)) { executionSemaphore.release(); } } } ; final Action1 markExceptionThrown = new Action1() { @Override public void call(Throwable t) { eventNotifier.markEvent (HystrixEventType.EXCEPTION_THROWN, commandKey); } } ; if (executionSemaphore.tryAcquire()) { try { /* used to track userThreadExecutionTime */ executionResult = executionResult. setInvocationStartTime (System.currentTimeMillis()); return executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd) .doOnError(markExceptionThrown) .doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease) .doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease); } catch (RuntimeException e) { return Observable.error(e); } } else { return handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback(); } } else { return handleShortCircuitViaFallback(); }}
6. 发送请求
①. 说明
这一步是真正调用消费者提供服务的过程。这一步在HystrixObservableCommand#construct()或HystrixCommand#run()中实现,这两个类是抽象类,提供了多种不同的子类实现方式。HystrixCommand#run():返回单一结果或抛出异常。HystrixObservableCommand#construct():返回Observable对象,通过Observable对象可以发送多个结果,或通过onError发送错误通知。
如果run()或construct ()方法的执行时间超过了命令设置的超时阙值,当前处理线程将会抛出一个TimeoutException(如果该命令不在其自身的线程中执行,则会通过单独的计时线程来抛出),此时进入fallback流程。如果当前命令没有被取消或中断,那么它最终会忽略run()或者construct ()方法的返回。
如果命令没有抛出异常并返回了结果,那么Hystrix在记录一些日志并采集监控报告之后将该结果返回。在使用run()的情况下,Hystrix会返回一个Observable,它发射单个结果并产生onCompleted的结束通知;而在使用construct()的情况下,Hystrix会直接返回该方法产生的Observable对象。
②. 代码
HttpClientRibbonCommand#run代码如下所示:
protected ClientHttpResponse run() throws Exception { return forward();}protected ClientHttpResponse forward() throws Exception { final RequestContext context = RequestContext.getCurrentContext(); long contentLength = null; String contentLengthHeader = context.getRequest().getHeader("Content-Length"); if (StringUtils.hasText(contentLengthHeader)) { contentLength = new long(contentLengthHeader); } URI uriInstance = new URI(this.uri); RibbonApacheHttpRequest request = new RibbonApacheHttpRequest(this.method, uriInstance, this.retryable, this.headers, this.params, this.requestEntity, contentLength); final RibbonApacheHttpResponse response = this.client .executeWithLoadBalancer(request); context.set("ribbonResponse



















 61
61











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








