一、在application.yml配置中添加数据库根据实体类自动创建数据库表的配置(这里数据库采用MySQL数据库)
jpa: database: MYSQL show-sql: true #Hibernate ddl auto (validate|create|create-drop|update) hibernate: ddl-auto: update naming: physical-strategy: org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl properties: hibernate: dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect enable_lazy_load_no_trans: true启动项目时,系统就会自动创建实体类中的定义的表,创建完之后你会发现数据库里的字段和实体类里的字段顺序是不一样的 是乱序的 这是为什么呢?
二、解决SpringDataJpa实体类中属性顺序与数据库中生成字段顺序不一致的问题
翻了翻源码才发现,很多地方都是使用LinkedHashMap或者是List来传输Entity里面的fields,于是感觉Hibernate应该是考虑到使用Entity里面定义的fields的顺序来实现建表语句里的表字段顺序的。
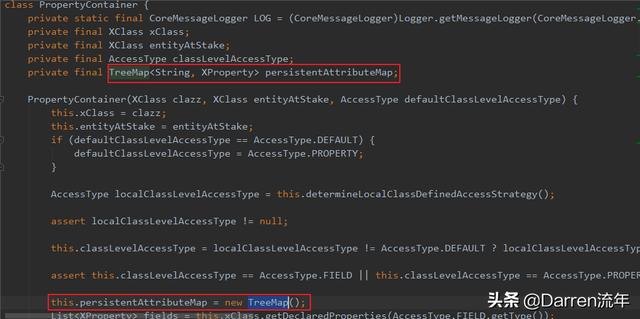
于是就一步步跟踪下去,终于在一个地方发现了一个问题:org.hibernate.cfg包下的PropertyContainer类在取fields的时候是使用TreeMap来保存的,于是试着改了下,将这个里面的所有TreeMap改成了LinkedHashMap,编译通过,打包,测试。
终于,我们期待已久的结果出来了:建表语句里面的字段顺序和Entity里面的fields的顺序一致了。
具体做法如下:
/**
在本项目中创建一个和源码类一样的包结构和一样名字的类,把所有源码中的所有代码复制到你创建的那个类中,
然后,就可以对你创建的类 进行修改了,修改好之后启动项目,你就会发现程序走的是你创建的那个类,
数据库的所有字段都是和实体类排序一样的了。
**/
这里附上修改后的代码,仅供参考(这里的Hibernate版本为hibernate5)
package org.hibernate.cfg;import java.util.*;import javax.persistence.Access;import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;import javax.persistence.OneToMany;import javax.persistence.OneToOne;import javax.persistence.Transient;import org.hibernate.AnnotationException;import org.hibernate.annotations.Any;import org.hibernate.annotations.ManyToAny;import org.hibernate.annotations.Target;import org.hibernate.annotations.Type;import org.hibernate.annotations.common.reflection.XClass;import org.hibernate.annotations.common.reflection.XProperty;import org.hibernate.boot.MappingException;import org.hibernate.boot.jaxb.Origin;import org.hibernate.boot.jaxb.SourceType;import org.hibernate.cfg.annotations.HCANNHelper;import org.hibernate.internal.CoreMessageLogger;import org.hibernate.internal.util.StringHelper;import org.jboss.logging.Logger;/** * 解决SpringDataJpa实体类中属性顺序与数据库中生成字段顺序不一致的问题 */class PropertyContainer { private static final CoreMessageLogger LOG = (CoreMessageLogger)Logger.getMessageLogger(CoreMessageLogger.class, PropertyContainer.class.getName()); private final XClass xClass; private final XClass entityAtStake; private final AccessType classLevelAccessType; private final LinkedHashMap persistentAttributeMap; PropertyContainer(XClass clazz, XClass entityAtStake, AccessType defaultClassLevelAccessType) { this.xClass = clazz; this.entityAtStake = entityAtStake; if (defaultClassLevelAccessType == AccessType.DEFAULT) { defaultClassLevelAccessType = AccessType.PROPERTY; } AccessType localClassLevelAccessType = this.determineLocalClassDefinedAccessStrategy(); assert localClassLevelAccessType != null; this.classLevelAccessType = localClassLevelAccessType != AccessType.DEFAULT ? localClassLevelAccessType : defaultClassLevelAccessType; assert this.classLevelAccessType == AccessType.FIELD || this.classLevelAccessType == AccessType.PROPERTY; this.persistentAttributeMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); List fields = this.xClass.getDeclaredProperties(AccessType.FIELD.getType()); List getters = this.xClass.getDeclaredProperties(AccessType.PROPERTY.getType()); this.preFilter(fields, getters); Map persistentAttributesFromGetters = new HashMap(); this.collectPersistentAttributesUsingLocalAccessType(this.persistentAttributeMap, persistentAttributesFromGetters, fields, getters); this.collectPersistentAttributesUsingClassLevelAccessType(this.persistentAttributeMap, persistentAttributesFromGetters, fields, getters); } private void preFilter(List fields, List getters) { Iterator propertyIterator = fields.iterator(); XProperty property; while(propertyIterator.hasNext()) { property = (XProperty)propertyIterator.next(); if (mustBeSkipped(property)) { propertyIterator.remove(); } } propertyIterator = getters.iterator(); while(propertyIterator.hasNext()) { property = (XProperty)propertyIterator.next(); if (mustBeSkipped(property)) { propertyIterator.remove(); } } } private void collectPersistentAttributesUsingLocalAccessType(LinkedHashMap persistentAttributeMap, Map persistentAttributesFromGetters, List fields, List getters) { Iterator propertyIterator = fields.iterator(); XProperty xProperty; Access localAccessAnnotation; while(propertyIterator.hasNext()) { xProperty = (XProperty)propertyIterator.next(); localAccessAnnotation = (Access)xProperty.getAnnotation(Access.class); if (localAccessAnnotation != null && localAccessAnnotation.value() == javax.persistence.AccessType.FIELD) { propertyIterator.remove(); persistentAttributeMap.put(xProperty.getName(), xProperty); } } propertyIterator = getters.iterator(); while(propertyIterator.hasNext()) { xProperty = (XProperty)propertyIterator.next(); localAccessAnnotation = (Access)xProperty.getAnnotation(Access.class); if (localAccessAnnotation != null && localAccessAnnotation.value() == javax.persistence.AccessType.PROPERTY) { propertyIterator.remove(); String name = xProperty.getName(); XProperty previous = (XProperty)persistentAttributesFromGetters.get(name); if (previous != null) { throw new MappingException(LOG.ambiguousPropertyMethods(this.xClass.getName(), HCANNHelper.annotatedElementSignature(previous), HCANNHelper.annotatedElementSignature(xProperty)), new Origin(SourceType.ANNOTATION, this.xClass.getName())); } persistentAttributeMap.put(name, xProperty); persistentAttributesFromGetters.put(name, xProperty); } } } private void collectPersistentAttributesUsingClassLevelAccessType(LinkedHashMap persistentAttributeMap, Map persistentAttributesFromGetters, List fields, List getters) { Iterator var5; XProperty getter; if (this.classLevelAccessType == AccessType.FIELD) { var5 = fields.iterator(); while(var5.hasNext()) { getter = (XProperty)var5.next(); if (!persistentAttributeMap.containsKey(getter.getName())) { persistentAttributeMap.put(getter.getName(), getter); } } } else { var5 = getters.iterator(); while(var5.hasNext()) { getter = (XProperty)var5.next(); String name = getter.getName(); XProperty previous = (XProperty)persistentAttributesFromGetters.get(name); if (previous != null) { throw new MappingException(LOG.ambiguousPropertyMethods(this.xClass.getName(), HCANNHelper.annotatedElementSignature(previous), HCANNHelper.annotatedElementSignature(getter)), new Origin(SourceType.ANNOTATION, this.xClass.getName())); } if (!persistentAttributeMap.containsKey(name)) { persistentAttributeMap.put(getter.getName(), getter); persistentAttributesFromGetters.put(name, getter); } } } } public XClass getEntityAtStake() { return this.entityAtStake; } public XClass getDeclaringClass() { return this.xClass; } public AccessType getClassLevelAccessType() { return this.classLevelAccessType; } public Collection getProperties() { this.assertTypesAreResolvable(); return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(this.persistentAttributeMap.values()); } private void assertTypesAreResolvable() { Iterator var1 = this.persistentAttributeMap.values().iterator(); XProperty xProperty; do { if (!var1.hasNext()) { return; } xProperty = (XProperty)var1.next(); } while(xProperty.isTypeResolved() || discoverTypeWithoutReflection(xProperty)); String msg = "Property " + StringHelper.qualify(this.xClass.getName(), xProperty.getName()) + " has an unbound type and no explicit target entity. Resolve this Generic usage issue or set an explicit target attribute (eg @OneToMany(target=) or use an explicit @Type"; throw new AnnotationException(msg); } private AccessType determineLocalClassDefinedAccessStrategy() { AccessType hibernateDefinedAccessType = AccessType.DEFAULT; AccessType jpaDefinedAccessType = AccessType.DEFAULT; org.hibernate.annotations.AccessType accessType = (org.hibernate.annotations.AccessType)this.xClass.getAnnotation(org.hibernate.annotations.AccessType.class); if (accessType != null) { hibernateDefinedAccessType = AccessType.getAccessStrategy(accessType.value()); } Access access = (Access)this.xClass.getAnnotation(Access.class); if (access != null) { jpaDefinedAccessType = AccessType.getAccessStrategy(access.value()); } if (hibernateDefinedAccessType != AccessType.DEFAULT && jpaDefinedAccessType != AccessType.DEFAULT && hibernateDefinedAccessType != jpaDefinedAccessType) { throw new org.hibernate.MappingException("@AccessType and @Access specified with contradicting values. Use of @Access only is recommended. "); } else { AccessType classDefinedAccessType; if (hibernateDefinedAccessType != AccessType.DEFAULT) { classDefinedAccessType = hibernateDefinedAccessType; } else { classDefinedAccessType = jpaDefinedAccessType; } return classDefinedAccessType; } } private static boolean discoverTypeWithoutReflection(XProperty p) { if (p.isAnnotationPresent(OneToOne.class) && !((OneToOne)p.getAnnotation(OneToOne.class)).targetEntity().equals(Void.TYPE)) { return true; } else if (p.isAnnotationPresent(OneToMany.class) && !((OneToMany)p.getAnnotation(OneToMany.class)).targetEntity().equals(Void.TYPE)) { return true; } else if (p.isAnnotationPresent(ManyToOne.class) && !((ManyToOne)p.getAnnotation(ManyToOne.class)).targetEntity().equals(Void.TYPE)) { return true; } else if (p.isAnnotationPresent(ManyToMany.class) && !((ManyToMany)p.getAnnotation(ManyToMany.class)).targetEntity().equals(Void.TYPE)) { return true; } else if (p.isAnnotationPresent(Any.class)) { return true; } else if (p.isAnnotationPresent(ManyToAny.class)) { if (!p.isCollection() && !p.isArray()) { throw new AnnotationException("@ManyToAny used on a non collection non array property: " + p.getName()); } else { return true; } } else if (p.isAnnotationPresent(Type.class)) { return true; } else { return p.isAnnotationPresent(Target.class); } } private static boolean mustBeSkipped(XProperty property) { return property.isAnnotationPresent(Transient.class) || "net.sf.cglib.transform.impl.InterceptFieldCallback".equals(property.getType().getName()) || "org.hibernate.bytecode.internal.javassist.FieldHandler".equals(property.getType().getName()); }}



















 965
965











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








