
nodejs 的 zlib 模块提供了资源压缩功能。例如在 http 传输过程当中经常使用的 gzip,能大幅度减小网络传输流量,提升速度。本文将从下面几个方面介绍 zlib 模块和相关知识点:node
文件压缩 / 解压
HTTP 中的压缩/解压
压缩算法:RLE
压缩算法:哈夫曼树
文件的压缩/解压
以 gzip 压缩为例,压缩代码以下:git
const zlib = require("zlib");
const fs = require("fs");
const gzip = zlib.createGzip();
const rs = fs.createReadStream("./db.json");
const ws = fs.createWriteStream("./db.json.gz");
rs.pipe(gzip).pipe(ws);
以下图所示,4.7Mb 大小的文件被压缩到了 575Kb。程序员

解压刚才压缩后的文件,代码以下:github
const zlib = require("zlib");
const fs = require("fs");
const gunzip = zlib.createGunzip();
const rs = fs.createReadStream("./db.json.gz");
const ws = fs.createWriteStream("./db.json");
rs.pipe(gunzip).pipe(ws);
HTTP 中的压缩/解压
在服务器中和客户端的传输过程当中,浏览器(客户端)经过 Accept-Encoding 消息头来告诉服务端接受的压缩编码,服务器经过 Content-Encoding 消息头来告诉浏览器(客户端)实际用于编码的算法。web
服务器代码示例以下:算法
const zlib = require("zlib");
const fs = require("fs");
const http = require("http");
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const rs = fs.createReadStream("./index.html");
// 防止缓存错乱
res.setHeader("Vary", "Accept-Encoding");
// 获取客户端支持的编码
let acceptEncoding = req.headers["accept-encoding"];
if (!acceptEncoding) {
acceptEncoding = "";
}
// 匹配支持的压缩格式
if (/\bdeflate\b/.test(acceptEncoding)) {
res.writeHead(200, { "Content-Encoding": "deflate" });
rs.pipe(zlib.createDeflate()).pipe(res);
} else if (/\bgzip\b/.test(acceptEncoding)) {
res.writeHead(200, { "Content-Encoding": "gzip" });
rs.pipe(zlib.createGzip()).pipe(res);
} else if (/\bbr\b/.test(acceptEncoding)) {
res.writeHead(200, { "Content-Encoding": "br" });
rs.pipe(zlib.createBrotliCompress()).pipe(res);
} else {
res.writeHead(200, {});
rs.pipe(res);
}
});
server.listen(4000);
客户端代码就很简单了,识别 Accept-Encoding 字段,并进行解压:json
const zlib = require("zlib");
const http = require("http");
const fs = require("fs");
const request = http.get({
host: "localhost",
path: "/index.html",
port: 4000,
headers: { "Accept-Encoding": "br,gzip,deflate" }
});
request.on("response", response => {
const output = fs.createWriteStream("example.com_index.html");
switch (response.headers["content-encoding"]) {
case "br":
response.pipe(zlib.createBrotliDecompress()).pipe(output);
break;
// 或者, 只是使用 zlib.createUnzip() 方法去处理这两种状况:
case "gzip":
response.pipe(zlib.createGunzip()).pipe(output);
break;
case "deflate":
response.pipe(zlib.createInflate()).pipe(output);
break;
default:
response.pipe(output);
break;
}
});
从上面的例子能够看出来,3 种对应的解压/压缩 API:api
zlib.createInflate() 和
zlib.createDeflate()
zlib.createGunzip() 和
zlib.createGzip()
zlib.createBrotliDecompress() 和
zlib.createBrotliCompress()
压缩算法:RLE
RLE 全称是 Run Length Encoding, 行程长度编码,也称为游程编码。它的原理是:记录连续重复数据的出现次数。它的公式是:字符 * 出现次数。
例如原数据是 AAAAACCPPPPPPPPERRPPP,一共 18 个字节。按照 RLE 的规则,压缩后的结果是:A5C2P8E1R2P3,一共 12 个字节。压缩比例是:12 / 17 = 70.6%
RLE 的优势是压缩和解压很是快,针对连续出现的多个字符的数据压缩率更高。但对于ABCDE相似的数据,压缩后数据会更大。
压缩算法:哈夫曼树
哈夫曼树的原理是:出现频率越高的字符,用尽可能更少的编码来表示。按照这个原理,以数据ABBCCCDDDD为例:
字符
编码(二进制)
D
0
C
1
B
10
A
11
原来的数据是 10 个字节。那么编码后的数据是:1110101110000,一共 13bit,在计算机中须要 2 个字节来存储。这样的压缩率是:2 / 10 = 20%。
可是仅仅按照这个原理编码后的数据,没法正确还原。之前 4bit 为例,1110能够理解成:
11 + 10
1 + 1 + 1 + 0
1 + 1 + 10
...
而哈夫曼树的设计就很巧妙,能正确还原。哈夫曼树的构造过程以下:
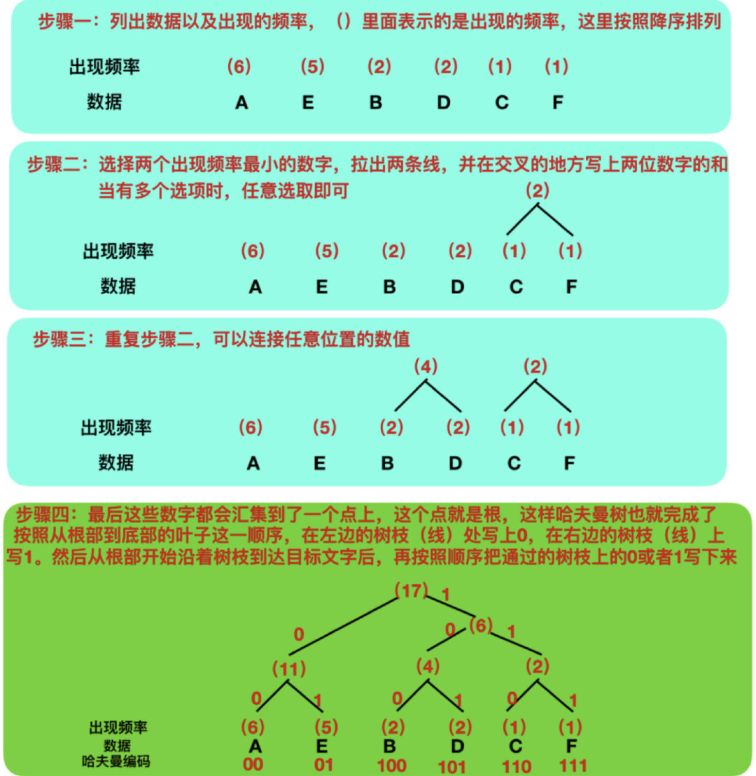
不管哪一种数据类型(文本文件、图像文件、EXE 文件),均可以采用哈夫曼树进行压缩。
参考连接
👇扫码关注「心谭博客」,查看「前端图谱」&「算法题解」,坚持分享,共同成长👇





















 605
605











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








