概述:
数组类型:AtomicIntegerArray, AtomicLongArray, AtomicReferenceArray原子类的原理和用法基本一致 本文章基于jdk:1.8.0_66版的AtomicIntegerArray进行介绍
AtomicIntegerArray:
函数列表
//构造方法 创建给定长度的AtomicIntegerArray
AtomicIntegerArray(int length)
//构造方法 给定数组复制到创建的AtomicIntegerArray this.array = array.clone();
AtomicIntegerArray(int[] array)
//获取数组长度
final int length()
//获取 i 位置的值
final int get(int i)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值为newValue
final void set(int i, int newValue)
//最后原子方式设置 i 位置的值为定值,因为调用了nsafe.putOrderedLong非堵塞的写入 修改结果不会立刻被线程看到 通常是几纳秒后被线程看到,延时设置变量值.
final void lazySet(int i, int newValue)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值为newValue 返回原值
final int getAndSet(int i, int newValue)
//如果期望值expect==i位置的原值 则原子方式修改i位置值为updata
final boolean compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update)
//等同于compareAndSet方法,里面就是调用compareAndSet方法
final boolean weakCompareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值加1 返回原值
final int getAndIncrement(int i)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值减1 返回原值
final int getAndDecrement(int i)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值加delta 返回原值
final int getAndAdd(int i, int delta)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值加1 返回新值
final int incrementAndGet(int i)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值减1 返回新值
final int decrementAndGet(int i)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值加delta 返回新值
final int addAndGet(int i, int delta)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值为函式数接口返回值 ,返回原值
final int getAndUpdate(int i, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值为函式数接口返回值 ,返回新值
final int updateAndGet(int i, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值为函数式接口返回值 ,返回原值 函数式接口返回处理原值和给定值x结果
final int getAndAccumulate(int i, int x,IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction)
//原子方式设置 i 位置的值为函数式接口返回值 ,返回新值 函数式接口返回处理原值和给定值x结果
final int accumulateAndGet(int i, int x,IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction)AtomicIntegerArray示例
package com.cn.cy.start.juc.array;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;
import java.util.function.IntBinaryOperator;
import java.util.function.IntUnaryOperator;
/**
* 本测试演示 getAndUpdate getAndAccumulate
* 其他的请自行测试
* @author yingchen
* @date 2019/7/16
*/
public class AtomicArrayTest {
private static Unsafe unsafe;
static {
try {
Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
field.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe)field.get(null);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(2);
atomicIntegerArray.set(0,0);
atomicIntegerArray.set(1,1);
IntUnaryOperator unaryOperator = new IntUnaryOperator() {
@Override
public int applyAsInt(int operand) {
return 36;
}
};
System.out.printf("%20s 数组[%s]原值:%s,当前值:%sn","getAndUpdate()",0,atomicIntegerArray.getAndUpdate(0,unaryOperator),atomicIntegerArray.get(0));
IntBinaryOperator binaryOperator = new IntBinaryOperator() {
@Override
public int applyAsInt(int left, int right) {
return left+right;
}
};
System.out.printf("%20s 数组[%s]原值:%s,当前值:%sn","getAndAccumulate()",1,atomicIntegerArray.getAndAccumulate(1,20,binaryOperator),atomicIntegerArray.get(1));
//这里反射获取 atomicIntegerArray 中数组 使用unsaf获取数组里面的值
Field field = atomicIntegerArray.getClass().getDeclaredField("array");
field.setAccessible(true);
int[] array = (int[])field.get(atomicIntegerArray);
int base = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(int[].class);
int scale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(int[].class);
System.out.printf("%20s 元素大小:%sn","Array",scale);
int shift = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale);
System.out.printf("%20s 偏移量:%sn","Array",shift);
System.out.printf("%20s 数组第一个元素偏移地址:%sn","Array",base);
int one = unsafe.getIntVolatile(array, base);
System.out.printf("%20s 数组第一个元素值:%sn","Array",one);
Long anInt = ((long) 1 << shift) + base;
System.out.printf("%20s 数组第二个元素偏地址:%sn","Array",anInt);
int intVolatile = unsafe.getIntVolatile(array, anInt);
System.out.printf("%20s 数组第二个元素值:%sn","Array",intVolatile);
}
}
运行结果:
getAndUpdate() 数组[0]原值:0,当前值:36
getAndAccumulate() 数组[1]原值:1,当前值:21
Array 元素大小:4
Array 偏移量:2
Array 数组第一个元素偏移地址:16
Array 数组第一个元素值:36
Array 数组第二个元素偏地址:20
Array 数组第二个元素值:21
AtomicIntegerArray源码
AtomicIntegerArray的代码很简单,下面仅以getAndIncrement()为例,对AtomicIntegerArray的原理进行说明。 getAndIncrement()源码:
public final int getAndIncrement(int i) {
return getAndAdd(i, 1);
}
public final int getAndAdd(int i, int delta) {
//原子方式设置 array数组中 i 位置的值为delta
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(array, checkedByteOffset(i), delta);
}
private long checkedByteOffset(int i) {
//校验i 位置是否越界
if (i < 0 || i >= array.length)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index " + i);
//返回 i 位置的地址
return byteOffset(i);
}
private static long byteOffset(int i) {
// i 左移shift 加上 数组初始偏移 等于 i 位置的偏移
return ((long) i << shift) + base;
}以上是getAndIncrement 源码的调用链 其中涉及到了 数组寻址 数组寻址[i]位置地址 = 数组初始偏移+元素大小*i;(数组是连续的内存空间) 下面代码是 AtomicIntegerArray中获取比例值 数据初始偏移的代码
static {
//获取比例值 即数组中单个元素的长度
int scale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(int[].class);
if ((scale & (scale - 1)) != 0)
throw new Error("data type scale not a power of two");
//数组偏移量 是获取例如 scale = 4 二进制位数是3 shift= 31 -29=2
//Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros 返回无符号整型i的最高非零位前面的0的个数 4的二进制 0100 1前面还有29个0
shift = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale);
}
//获取数组的初始偏移
private static final int base = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(int[].class);下图是简单的解释数组寻址 是怎么操作的
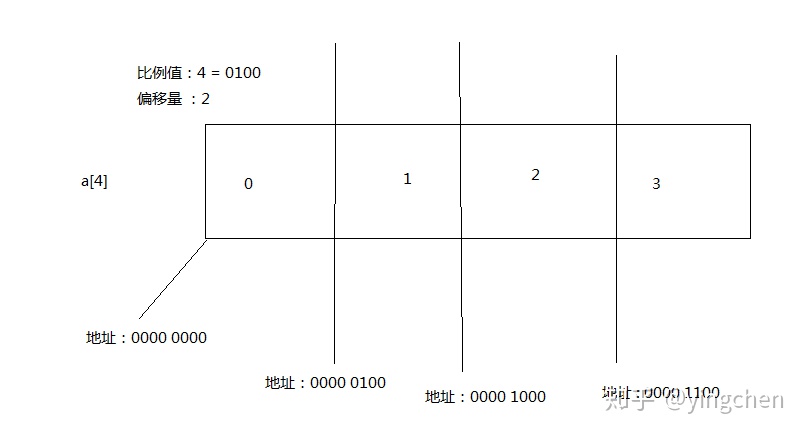
比例值即数组长度,a[0]首地址+比例值 =a[1]首地址= 0000 0100
代码中是使用偏移量计算的:
a[i]首地址=i<<偏移量 + a[0]首地址
a[1]=1 <<2 +0000 0000 = 0000 0100 +0000 0000 =0000 0100
a[2]=2 <<2 +0000 0000 = 0000 1000 +0000 0000 =0000 1000
a[2]=3 <<2 +0000 0000 = 0000 1100 +0000 0000 =0000 1100
/*
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/
/*
*
*
*
*
*
* Written by Doug Lea with assistance from members of JCP JSR-166
* Expert Group and released to the public domain, as explained at
* http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/
*/
package java.util.concurrent.atomic;
import java.util.function.IntUnaryOperator;
import java.util.function.IntBinaryOperator;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
/**
* An {@code int} array in which elements may be updated atomically.
* See the {@link java.util.concurrent.atomic} package
* specification for description of the properties of atomic
* variables.
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
*/
public class AtomicIntegerArray implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2862133569453604235L;
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final int base = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(int[].class);
private static final int shift;
private final int[] array;
static {
int scale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(int[].class);
if ((scale & (scale - 1)) != 0)
throw new Error("data type scale not a power of two");
shift = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale);
}
private long checkedByteOffset(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= array.length)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index " + i);
return byteOffset(i);
}
private static long byteOffset(int i) {
return ((long) i << shift) + base;
}
/**
* Creates a new AtomicIntegerArray of the given length, with all
* elements initially zero.
*
* @param length the length of the array
*/
public AtomicIntegerArray(int length) {
array = new int[length];
}
/**
* Creates a new AtomicIntegerArray with the same length as, and
* all elements copied from, the given array.
*
* @param array the array to copy elements from
* @throws NullPointerException if array is null
*/
public AtomicIntegerArray(int[] array) {
// Visibility guaranteed by final field guarantees
this.array = array.clone();
}
/**
* Returns the length of the array.
*
* @return the length of the array
*/
public final int length() {
return array.length;
}
/**
* Gets the current value at position {@code i}.
*
* @param i the index
* @return the current value
*/
public final int get(int i) {
return getRaw(checkedByteOffset(i));
}
private int getRaw(long offset) {
return unsafe.getIntVolatile(array, offset);
}
/**
* Sets the element at position {@code i} to the given value.
*
* @param i the index
* @param newValue the new value
*/
public final void set(int i, int newValue) {
unsafe.putIntVolatile(array, checkedByteOffset(i), newValue);
}
/**
* Eventually sets the element at position {@code i} to the given value.
*
* @param i the index
* @param newValue the new value
* @since 1.6
*/
public final void lazySet(int i, int newValue) {
unsafe.putOrderedInt(array, checkedByteOffset(i), newValue);
}
/**
* Atomically sets the element at position {@code i} to the given
* value and returns the old value.
*
* @param i the index
* @param newValue the new value
* @return the previous value
*/
public final int getAndSet(int i, int newValue) {
return unsafe.getAndSetInt(array, checkedByteOffset(i), newValue);
}
/**
* Atomically sets the element at position {@code i} to the given
* updated value if the current value {@code ==} the expected value.
*
* @param i the index
* @param expect the expected value
* @param update the new value
* @return {@code true} if successful. False return indicates that
* the actual value was not equal to the expected value.
*/
public final boolean compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update) {
return compareAndSetRaw(checkedByteOffset(i), expect, update);
}
private boolean compareAndSetRaw(long offset, int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(array, offset, expect, update);
}
/**
* Atomically sets the element at position {@code i} to the given
* updated value if the current value {@code ==} the expected value.
*
* <p><a href="package-summary.html#weakCompareAndSet">May fail
* spuriously and does not provide ordering guarantees</a>, so is
* only rarely an appropriate alternative to {@code compareAndSet}.
*
* @param i the index
* @param expect the expected value
* @param update the new value
* @return {@code true} if successful
*/
public final boolean weakCompareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update) {
return compareAndSet(i, expect, update);
}
/**
* Atomically increments by one the element at index {@code i}.
*
* @param i the index
* @return the previous value
*/
public final int getAndIncrement(int i) {
return getAndAdd(i, 1);
}
/**
* Atomically decrements by one the element at index {@code i}.
*
* @param i the index
* @return the previous value
*/
public final int getAndDecrement(int i) {
return getAndAdd(i, -1);
}
/**
* Atomically adds the given value to the element at index {@code i}.
*
* @param i the index
* @param delta the value to add
* @return the previous value
*/
public final int getAndAdd(int i, int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(array, checkedByteOffset(i), delta);
}
/**
* Atomically increments by one the element at index {@code i}.
*
* @param i the index
* @return the updated value
*/
public final int incrementAndGet(int i) {
return getAndAdd(i, 1) + 1;
}
/**
* Atomically decrements by one the element at index {@code i}.
*
* @param i the index
* @return the updated value
*/
public final int decrementAndGet(int i) {
return getAndAdd(i, -1) - 1;
}
/**
* Atomically adds the given value to the element at index {@code i}.
*
* @param i the index
* @param delta the value to add
* @return the updated value
*/
public final int addAndGet(int i, int delta) {
return getAndAdd(i, delta) + delta;
}
/**
* Atomically updates the element at index {@code i} with the results
* of applying the given function, returning the previous value. The
* function should be side-effect-free, since it may be re-applied
* when attempted updates fail due to contention among threads.
*
* @param i the index
* @param updateFunction a side-effect-free function
* @return the previous value
* @since 1.8
*/
public final int getAndUpdate(int i, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
long offset = checkedByteOffset(i);
int prev, next;
do {
prev = getRaw(offset);
next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
} while (!compareAndSetRaw(offset, prev, next));
return prev;
}
/**
* Atomically updates the element at index {@code i} with the results
* of applying the given function, returning the updated value. The
* function should be side-effect-free, since it may be re-applied
* when attempted updates fail due to contention among threads.
*
* @param i the index
* @param updateFunction a side-effect-free function
* @return the updated value
* @since 1.8
*/
public final int updateAndGet(int i, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
long offset = checkedByteOffset(i);
int prev, next;
do {
prev = getRaw(offset);
next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
} while (!compareAndSetRaw(offset, prev, next));
return next;
}
/**
* Atomically updates the element at index {@code i} with the
* results of applying the given function to the current and
* given values, returning the previous value. The function should
* be side-effect-free, since it may be re-applied when attempted
* updates fail due to contention among threads. The function is
* applied with the current value at index {@code i} as its first
* argument, and the given update as the second argument.
*
* @param i the index
* @param x the update value
* @param accumulatorFunction a side-effect-free function of two arguments
* @return the previous value
* @since 1.8
*/
public final int getAndAccumulate(int i, int x,
IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
long offset = checkedByteOffset(i);
int prev, next;
do {
prev = getRaw(offset);
next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSetRaw(offset, prev, next));
return prev;
}
/**
* Atomically updates the element at index {@code i} with the
* results of applying the given function to the current and
* given values, returning the updated value. The function should
* be side-effect-free, since it may be re-applied when attempted
* updates fail due to contention among threads. The function is
* applied with the current value at index {@code i} as its first
* argument, and the given update as the second argument.
*
* @param i the index
* @param x the update value
* @param accumulatorFunction a side-effect-free function of two arguments
* @return the updated value
* @since 1.8
*/
public final int accumulateAndGet(int i, int x,
IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
long offset = checkedByteOffset(i);
int prev, next;
do {
prev = getRaw(offset);
next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSetRaw(offset, prev, next));
return next;
}
/**
* Returns the String representation of the current values of array.
* @return the String representation of the current values of array
*/
public String toString() {
int iMax = array.length - 1;
if (iMax == -1)
return "[]";
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
b.append('[');
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
b.append(getRaw(byteOffset(i)));
if (i == iMax)
return b.append(']').toString();
b.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
}



















 676
676











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








