
因本人技术水平和知识面有限, 内容如有纰漏或者需要修正的地方, 欢迎大家指正, 也欢迎大家提供一些其他好的调试工具以供收录, 鄙人在此谢谢啦
1 /proc/kallsyms显示value全部为0
今天一个同事问我 cat /proc/kallsyms 显示 value 全部为 0. 我在手机端试了一下, 果然如此.
切换到 root 用户运行, 依然是 0. 感到十分奇怪, 因为内核发生 crash 或者打开 trace 的时候, 都是调用的 sprint_ symbol 来打印的. 为啥内核可以, 用户态 cat 就不行呢?
后来发现是系统为了保护这些符号地址泄露, 而用的一种保护手段, 从而使除 root 用户外的普通用户不能直接查看符号地址.
2 kptr_restrict 介绍
原因在于内核文件 kallsyms.c 中的显示符号地址命令中做了如下限制.
seq_printf(m, "%pK %c %s
", (void *)iter->value, iter->type, iter->name);
只需要把其中的 %pK 换成 %p 就可以让普通用户查看符号地址了. 很多提权漏洞一般会用到此处的修改来获取符号地址
内核提供控制变量 /proc/sys/kernel/kptr_restrict 来进行修改. 从内核文档 Documentation/sysctl/kernel.txt 中可以看到 kptr_restrict 用于控制内核的一些输出打印.
Documentation/printk-formats.txt 有更加详细的描述, 除了我们平时遇到的一些打印格式之外, 还有一些比较特殊的格式(我以前没注意到).
==============================================================
kptr_restrict:
This toggle indicates whether restrictions are placed on
exposing kernel addresses via /proc and other interfaces.
When kptr_restrict is set to (0), the default, there are no restrictions.
When kptr_restrict is set to (1), kernel pointers printed using the %pK
format specifier will be replaced with 0's unless the user has CAP_SYSLOG and effective user and group ids are equal to the real ids. This is because %pK checks are done at read() time rather than open() time, so if permissions are elevated between the open() and the read() (e.g via a setuid binary) then %pK will not leak kernel pointers to unprivileged users. Note, this is a temporary solution only. The correct long-term solution is to do the permission checks at open() time. Consider removing world read permissions from files that use %pK, and using dmesg_restrict to protect against uses of %pK in dmesg(8) if leaking kernel pointer values to unprivileged users is a concern. When kptr_restrict is set to (2), kernel pointers printed using %pK will be replaced with 0's regardless of privileges.
==============================================================
kptr_restrict
权限描述
2
内核将符号地址打印为全0, root和普通用户都没有权限
1
root用户有权限读取, 普通用户没有权限
0
root和普通用户都可以读取
kptr_restrict 值为 2 时, 所有用户都无法读取内核符号地址.
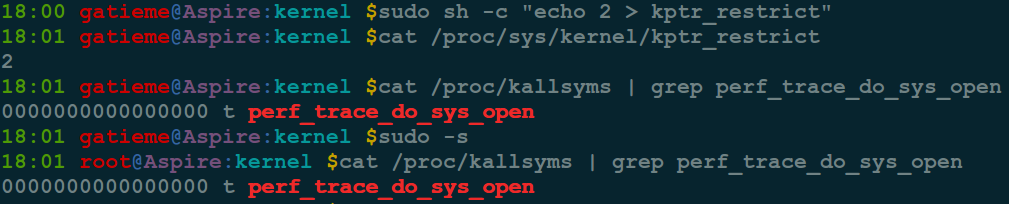
kptr_restrict 值为 1 时, 普通用户都无法读取内核符号地址, root 用户可以查看.

kptr_restrict 值为 0 时, 所有用户都可以读取内核地址.

注意 kptr_restrict 对内核中很多地址和符号表的信息导出都有影响, 比如 /proc/modules 等.
3 kptr_restrict的设计
#http://elixir.free-electrons.com/linux/v4.13.9/source/lib/vsprintf.c#L1708
case 'K':
switch (kptr_restrict) {
case 0:
/* Always print %pK values */
break;
case 1: {
const struct cred *cred;
/* * kptr_restrict==1 cannot be used in IRQ context * because its test for CAP_SYSLOG would be meaningless. */
if (in_irq() || in_serving_softirq() || in_nmi()) {
if (spec.field_width == -1)
spec.field_width = default_width;
return string(buf, end, "pK-error", spec);
}
/* * Only print the real pointer value if the current * process has CAP_SYSLOG and is running with the * same credentials it started with. This is because * access to files is checked at open() time, but %pK * checks permission at read() time. We don't want to * leak pointer values if a binary opens a file using * %pK and then elevates privileges before reading it. */
cred = current_cred();
if (!has_capability_noaudit(current, CAP_SYSLOG) ||
!uid_eq(cred->euid, cred->uid) ||
!gid_eq(cred->egid, cred->gid))
ptr = NULL;
break;
}
case 2:
default:
/* Always print 0's for %pK */
ptr = NULL;
break;
}
break;
4 参考





















 152
152











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








