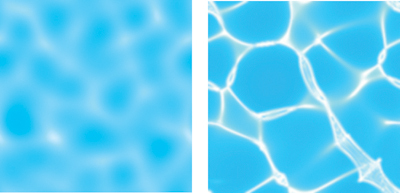
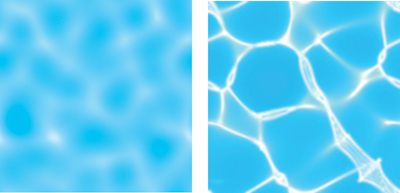
焦散原因:光线从曲面反射或折射从而在接受面上聚焦于某一区域
计算焦散
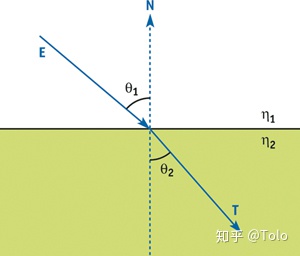
斯涅耳定律:(编程不友好)
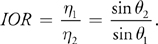
Foley公式:(编程友好,假设入射光线,传输光线和表面法线共面)
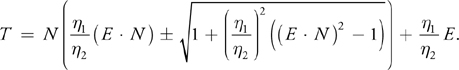
光线追踪方法:
- 前向光线追踪:大部分光线未到达水底造成计算浪费
- 逆向光线追踪:从水底出发按时间反向计算给定点的入射光总和,通过蒙特卡洛采样计算,从聚焦采样点的半球发射各个方向的光线,击中物体的光线丢弃,到达水面的光线使用逆向斯涅尔公式,计算光线是否为光源发出
实时方法:
- Jos Stam (Stam 1996):使用波理论计算动画焦散纹理
- Lasse Staff Jensen and Robert Golias (Jensen and Golias 2001):使用FFT来造型水体,从太阳向水面网格的每个顶点追踪光线,根据斯涅尔定律折射生成新的光线
本文方法
简化版的逆向蒙特卡洛光线追踪。
假设:
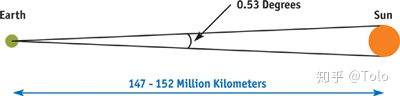
- 假设太阳在正上方,计算太阳覆盖的天空对应的角度为0.53度
- 假设照亮海面的光线发射于采样点的垂直上方,从水面到水底经过最短距离的光线最容易形成焦散,因此垂直光线最被考虑
算法:
- 在绘制完地面之后从海底开始计算,使用addictive混合
- 创建和波浪网格相同粒度的网格,根据焦散值逐顶点着色
- 将焦散网格的顶点垂直向上投影到波浪网格,通过有限差分计算投影点的法线
- 通过斯涅耳定律计算入射光并通过比较角度测试其发射自太阳的密度

OpenGL实现
多Pass实现:
- 第一个pass:渲染海底河床
- 第二个pass:使用焦散生成器逐顶点照亮河床的细分网格
- Send a vertical ray.
- Collide the ray with the ocean's mesh.
- Compute the refracted ray using Snell's Law in reverse.
- Use the refracted ray to compute texture coordinates for the "Sun" map.
- Apply texture coordinates to vertices in the finer mesh.
- 第三个pass:使用波浪渲染器渲染波浪
高级着色语言实现
逐像素计算焦散,使用偏导数计算发现而不是有限差分
方法:
- 在屏幕空间渲染程序化纹理,部分像素可见时节省开销,但是大量像素可见时会增加大量工作
- 在纹理空间渲染固定分辨率的render target,每帧的开销固定,但是难以估计适合当前场景的rt分辨率,依赖纹理过滤时若纹理像素比过低则可能引入双线性过滤交叉图案
优化:
观察到使用斯涅尔定律折射与根据沿波法线从水表面到地板表面的距离映射环境贴图存在很小的视觉差异,所以进行纹理采样,垂直光采中心区域,角度光进行衰减。该方法允许不平坦的河床,将深度写入顶点数据

波函数:
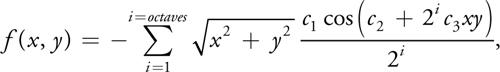
法线计算:
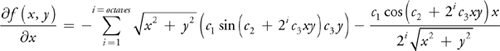
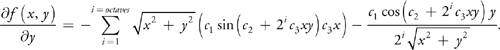
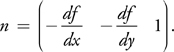
距离计算:
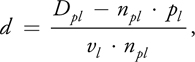
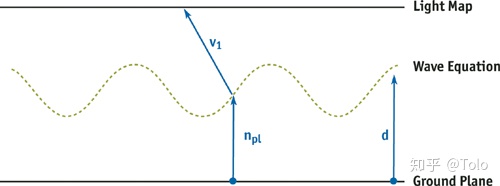
// Caustics
// Copyright (c) NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
//
// NOTE:
// This shader is based on the original work by Daniel Sanchez-Crespo
// of the Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, Spain.
#define VTXSIZE 0.01f // Amplitude
#define WAVESIZE 10.0f // Frequency
#define FACTOR 1.0f
#define SPEED 2.0f
#define OCTAVES 5
// Example of the same wave function used in the vertex engine
float wave(float x, float y, float timer)
{
float z = 0.0f;
float octaves = OCTAVES;
float factor = FACTOR;
float d = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
do {
z -= factor * cos(timer * SPEED + (1/factor) * x * y * WAVESIZE);
factor = factor/2;
octaves--;
} while (octaves > 0);
return 2 * VTXSIZE * d * z;
}
// This is a derivative of the above wave function.
// It returns the d(wave)/dx and d(wave)/dy partial derivatives.
float2 gradwave(float x, float y, float timer)
{
float dZx = 0.0f;
float dZy = 0.0f;
float octaves = OCTAVES;
float factor = FACTOR;
float d = sqrt(x * x + y * y);
do {
dZx += d * sin(timer * SPEED + (1/factor) * x * y * WAVESIZE) * y * WAVESIZE
- factor * cos(timer * SPEED + (1/factor) * x * y * WAVESIZE) * x/d;
dZy += d * sin(timer * SPEED + (1/factor) * x * y * WAVESIZE) * x * WAVESIZE
- factor * cos(timer * SPEED + (1/factor) * x * y * WAVESIZE) * y/d;
factor = factor/2;
octaves--;
} while (octaves > 0);
return float2(2 * VTXSIZE * dZx, 2 * VTXSIZE * dZy);
}
float3 line_plane_intercept(float3 lineP, float3 lineN, float3 planeN, float planeD)
{
// Unoptimized
// float distance = (planeD - dot(planeN, lineP)) /
// dot(lineN, planeN);
// Optimized (assumes planeN always points up)
float distance = (planeD - lineP.z) / lineN.z;
return lineP + lineN * distance;
}//使用结果进行lightmap采样
float4 main(VS_OUTPUT vert, uniform sampler2D LightMap : register(s0),
uniform sampler2D GroundMap : register(s1), uniform float Timer) : COLOR
{
// Generate a normal (line direction) from the gradient
// of the wave function and intercept with the water plane.
// We use screen-space z to attenuate the effect to avoid aliasing.
float2 dxdy = gradwave(vert.Position.x, vert.Position.y, Timer);
float3 intercept = line_plane_intercept( vert.Position.xyz, float3(dxdy, saturate(vert.Position.w)), float3(0, 0, 1), -0.8);
// OUTPUT
float4 colour;
colour.rgb = (float3)tex2D(LightMap, intercept.xy * 0.8);
colour.rgb += (float3)tex2D(GroundMap, vert.uv);
colour.a = 1;
return colour;
}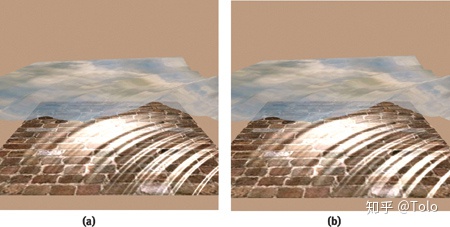
足够大的分辨率纹理具有与屏幕空间渲染一样好的质量,而在显示大量像素时不会影响性能。此外,在使用渲染目标纹理时,我们可以利用自动mipmap生成和各向异性过滤来减少焦散的混叠,这在渲染到屏幕空间时无法实现。




















 2724
2724

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








