Linux的上下文切换
当程序运行的时候由于CPU当前寄存器中包含了当前时刻的所有信息,就好像是一部视频里面的一帧一样,假如我们此时记录下当前的cpu的状态信息保存下来,然后给cpu恢复数据到另外一个当时的cpu记录现场,那么理论上此时程序的执行状态就会沿着上一个程序状态执行,也就是程序跳到了另一个执行的上下文。听起来好像是可行的,其实确实可行,并且基于这种技术posix也提供了几个函数专门来实现这种超级goto的功能。
1. sigsetjmp和siglongjmp函数
C的标准库里面实现了自己sigsetjmp()和siglongjmp()这一对函数来实现跨栈的跳转功能。下面是使用sigsetjmp和siglongjmp的一个跳转例子:
/**
* Created by suli on 8/31/17.
*/
#include #include
jmp_buf g_jum_buf;//全局buff,用于记录当时上下文
void test()
{
printf("Enter test ...\n");
siglongjmp(g_jum_buf, 8);//如下代码不会被执行 printf("test::can't see");
}
int main()
{
int ret;
if(ret = sigsetjmp(g_jum_buf))
{
//后执行跳转过来 printf("Main: return after calling longjmp, ret = %d.\n", ret);
}
else
{
//先执行这句话 printf("Main: first time return from setjmp, ret = %d\n", ret);
test();
}
return 0;
}
sigsetjmp()这个函数比较重要首先的功能是记录当前的上下文到jmp_buf中去,然后它的返回值是0,而当运行到siglongjmp的时候就把jmp_buf中保存的上下文进行了恢复,然后就再次回到了sigsetjmp函数处,此时sigsetjmp有另外一个特性就是,从siglongjum跳转到sigsetjump时候函数返回值为非0,这时候程序就可以按着另一个分支走了。这个函数有几个问题,在多线程下不是很稳定。
2. ucontext函数簇
posix标准定义了一系列的上下文切换函数,其中ucontext函数簇中的函数很重要,一共有四个函数:
int getcontext(ucontext_t *ucp);
int setcontext(const ucontext_t *ucp);
void makecontext(ucontext_t *ucp, void (*func)(), int argc, ...);
int swapcontext(ucontext_t *oucp, ucontext_t *ucp);
一般的程序跳转只需要setcontext和getcontext两个就可以了,可以直接实现跳转。其中makecontext函数实现了ucp指向的上下文环境,swapcontext函数是保存当前上下文,并切换到新的上下文。使用setcontext和getcontext实现跳转和上面一个例子差不多,只不过不需要判断返回值就可以通过setcontext来直接跳转到记录的上下文处。
上下文切换的细节实现
上下文的具体切换的大体实现思路前面已经说了一下,但是实现的细节部分是需要具体分析的。我们就拿ucontext函数簇来进行分析,首先我们先获取到函数的实现,函数具体实现在glibc中glibc地址。其中getcontext.S文件是getcontext函数的具体实现。另外还有一个ucontext的头文件定义,ucontext的头文件代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
--
SIG_BLOCK
SIG_SETMASK
_NSIG8 (_NSIG / 8)
#define ucontext(member) offsetof (ucontext_t, member)
#define mcontext(member) ucontext (uc_mcontext.member)
#define mreg(reg) mcontext (gregs[REG_##reg])
oRBP mreg (RBP)
oRSP mreg (RSP)
oRBX mreg (RBX)
oR8 mreg (R8)
oR9 mreg (R9)
oR10 mreg (R10)
oR11 mreg (R11)
oR12 mreg (R12)
oR13 mreg (R13)
oR14 mreg (R14)
oR15 mreg (R15)
oRDI mreg (RDI)
oRSI mreg (RSI)
oRDX mreg (RDX)
oRAX mreg (RAX)
oRCX mreg (RCX)
oRIP mreg (RIP)
oEFL mreg (EFL)
oFPREGS mcontext (fpregs)
oSIGMASK ucontext (uc_sigmask)
oFPREGSMEM ucontext (__fpregs_mem)
oMXCSR ucontext (__fpregs_mem.mxcsr)
getcontext函数源代码:
/* Save current context.
Copyright (C) 2002-2017 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This file is part of the GNU C Library.
Contributed by Andreas Jaeger , 2002.
The GNU C Library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
The GNU C Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
Lesser General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
License along with the GNU C Library; if not, see
. */
#include
#include "ucontext_i.h"
/* int __getcontext (ucontext_t *ucp)
Saves the machine context in UCP such that when it is activated,
it appears as if __getcontext() returned again.
This implementation is intended to be used for *synchronous* context
switches only. Therefore, it does not have to save anything
other than the PRESERVED state. */
ENTRY(__getcontext)
/* Save the preserved registers, the registers used for passing
args, and the return address. */
movq%rbx, oRBX(%rdi)
movq%rbp, oRBP(%rdi)
movq%r12, oR12(%rdi)
movq%r13, oR13(%rdi)
movq%r14, oR14(%rdi)
movq%r15, oR15(%rdi)
movq%rdi, oRDI(%rdi)
movq%rsi, oRSI(%rdi)
movq%rdx, oRDX(%rdi)
movq%rcx, oRCX(%rdi)
movq%r8, oR8(%rdi)
movq%r9, oR9(%rdi)
movq(%rsp), %rcx
movq%rcx, oRIP(%rdi)
leaq8(%rsp), %rcx/* Exclude the return address. */
movq%rcx, oRSP(%rdi)
/* We have separate floating-point register content memory on the
stack. We use the __fpregs_mem block in the context. Set the
links up correctly. */
leaqoFPREGSMEM(%rdi), %rcx
movq%rcx, oFPREGS(%rdi)
/* Save the floating-point environment. */
fnstenv(%rcx)
fldenv(%rcx)
stmxcsr oMXCSR(%rdi)
/* Save the current signal mask with
rt_sigprocmask (SIG_BLOCK, NULL, set,_NSIG/8). */
leaqoSIGMASK(%rdi), %rdx
xorl%esi,%esi
#if SIG_BLOCK == 0xorl%edi, %edi
#elsemovl$SIG_BLOCK, %edi
#endifmovl$_NSIG8,%r10d
movl$__NR_rt_sigprocmask, %eax
syscall
cmpq$-4095, %rax/* Check %rax for error. */
jaeSYSCALL_ERROR_LABEL/* Jump to error handler if error. */
/* All done, return 0 for success. */
xorl%eax, %eax
ret
PSEUDO_END(__getcontext)
weak_alias (__getcontext, getcontext)
首先我们看这段程序,首先下面这句:
movq%rbx, oRBX(%rdi)
其中oRBX是在ucontext头文件中定义:
#define ucontext(member) offsetof (ucontext_t, member)
#define mcontext(member) ucontext (uc_mcontext.member)
#define mreg(reg) mcontext (gregs[REG_##reg])
oRBP mreg (RBP)
oRSP mreg (RSP)
oRBX mreg (RBX)
把所有的宏替换完后该指令的结果是下面的语句:
oRBP = offsetof(ucontext_t, un_mcontext.greps[REG_RBP])
offsetof函数是C语言里面用来获取一个结构体中的成员在结构体中的偏移量的函数。同时前一篇文章中讲过rdi寄存器一般存放的是函数的第一个参数,所以此时完全展开后就是上面那个ucontext_t结构体里面un_mcontext成员的REG_RBP字段,那我们现在看看un_mcontext这个结构体的样子:
#define_STRUCT_X86_THREAD_STATE64struct __darwin_x86_thread_state64
_STRUCT_X86_THREAD_STATE64
{
__uint64_t__rax;
__uint64_t__rbx;
__uint64_t__rcx;
__uint64_t__rdx;
__uint64_t__rdi;
__uint64_t__rsi;
__uint64_t__rbp;
__uint64_t__rsp;
__uint64_t__r8;
__uint64_t__r9;
__uint64_t__r10;
__uint64_t__r11;
__uint64_t__r12;
__uint64_t__r13;
__uint64_t__r14;
__uint64_t__r15;
__uint64_t__rip;
__uint64_t__rflags;
__uint64_t__cs;
__uint64_t__fs;
__uint64_t__gs;
};
这个代码是我mac里面_structs.h文件里面,Linux系统下会更标准一点但是我们可以用这个结构来详细说明一下这句话的含义。
movq%rbx, oRBX(%rdi)
通过movq语句将当前rbx中的值放到utcontext结构体内un_mcontext成员的__rbx字段中,后面的几句话同样是将当前的cpu寄存器的值记录保存。好了第一阶段的寄存器保存如下图所示。

下面这两句是将当前栈的RSP栈顶指针记录下来,存放在结构体的rip字段用来恢复上下文的时候读取该帧的地址,同时将rsp地址加上8字节来获取获取返回上一个栈帧的地址并且存取到RSP字段中。
movq(%rsp), %rcx
movq%rcx, oRIP(%rdi)
leaq8(%rsp), %rcx/* Exclude the return address. */
movq%rcx, oRSP(%rdi)
后面两句是开始记录浮点计数器,这部分比较复杂先不分析,后面代码是记录当前线程的信号屏蔽字。到这里大体知道了getcontext函数的主要功能。那当需要返回到上一个上下文的时候setcontext就派上用场了。先获取setcontext的代码,代码地址。
#include
#include "ucontext_i.h"
/* int __setcontext (const ucontext_t *ucp)
Restores the machine context in UCP and thereby resumes execution
in that context.
This implementation is intended to be used for *synchronous* context
switches only. Therefore, it does not have to restore anything
other than the PRESERVED state. */
ENTRY(__setcontext)
/* Save argument since syscall will destroy it. */
pushq%rdi
cfi_adjust_cfa_offset(8)
/* Set the signal mask with
rt_sigprocmask (SIG_SETMASK, mask, NULL, _NSIG/8). */
leaqoSIGMASK(%rdi), %rsi
xorl%edx, %edx
movl$SIG_SETMASK, %edi
movl$_NSIG8,%r10d
movl$__NR_rt_sigprocmask, %eax
syscall
popq%rdi/* Reload %rdi, adjust stack. */
cfi_adjust_cfa_offset(-8)
cmpq$-4095, %rax/* Check %rax for error. */
jaeSYSCALL_ERROR_LABEL/* Jump to error handler if error. */
/* Restore the floating-point context. Not the registers, only the
rest. */
movqoFPREGS(%rdi), %rcx
fldenv(%rcx)
ldmxcsr oMXCSR(%rdi)
/* Load the new stack pointer, the preserved registers and
registers used for passing args. */
cfi_def_cfa(%rdi, 0)
cfi_offset(%rbx,oRBX)
cfi_offset(%rbp,oRBP)
cfi_offset(%r12,oR12)
cfi_offset(%r13,oR13)
cfi_offset(%r14,oR14)
cfi_offset(%r15,oR15)
cfi_offset(%rsp,oRSP)
cfi_offset(%rip,oRIP)
movqoRSP(%rdi), %rsp
movqoRBX(%rdi), %rbx
movqoRBP(%rdi), %rbp
movqoR12(%rdi), %r12
movqoR13(%rdi), %r13
movqoR14(%rdi), %r14
movqoR15(%rdi), %r15
/* The following ret should return to the address set with
getcontext. Therefore push the address on the stack. */
movqoRIP(%rdi), %rcx
pushq%rcx
movqoRSI(%rdi), %rsi
movqoRDX(%rdi), %rdx
movqoRCX(%rdi), %rcx
movqoR8(%rdi), %r8
movqoR9(%rdi), %r9
/* Setup finally %rdi. */
movqoRDI(%rdi), %rdi
/* End FDE here, we fall into another context. */
cfi_endproc
cfi_startproc
/* Clear rax to indicate success. */
xorl%eax, %eax
ret
PSEUDO_END(__setcontext)
weak_alias (__setcontext, setcontext)
下面我们来看看函数堆栈恢复的过程:
pushq%rdi
cfi_adjust_cfa_offset(8)
首先记录传递过来的setcontext参数中的ucontext地址,cfi_adjust_cfa_offset(8)这句话是cfi指令,cfi是调用框架指令(Call Frame Instrctions)的简称,指令主要作用是记录程序运行堆栈的详细信息用于实现堆栈回绕或者异常处理,详细cfi文档地址,该条语句的意思该语句处距离函数栈帧的便宜量为8字节。
下面这段开始恢复当前线程的信号的屏蔽字:
leaqoSIGMASK(%rdi), %rsi
xorl%edx, %edx
movl$SIG_SETMASK, %edi
movl$_NSIG8,%r10d
movl$__NR_rt_sigprocmask, %eax
下面开始恢复浮点计数器状态:
movqoFPREGS(%rdi), %rcx
fldenv(%rcx)
ldmxcsr oMXCSR(%rdi)
其中fldenv和ldmxcsr是FPU浮点计数器的汇编指令,含义是加载数据到FPU寄存器中。
在运行到下面是恢复以下数据到寄存器:
movqoRSP(%rdi), %rsp
movqoRBX(%rdi), %rbx
movqoRBP(%rdi), %rbp
movqoR12(%rdi), %r12
movqoR13(%rdi), %r13
movqoR14(%rdi), %r14
movqoR15(%rdi), %r15
再往下运行是:
movqoRIP(%rdi), %rcx
pushq%rcx
这两句很重要,第一句首先将RIP中的值取出来,上面写道RIP中的值是放的记录上文中栈顶指针地址RSP指针,也就是当时记录栈帧的返回地址,所以下面需要把SP指针push到当前栈上,下面继续对寄存器信息进行恢复。
movqoRSI(%rdi), %rsi
movqoRDX(%rdi), %rdx
movqoRCX(%rdi), %rcx
movqoR8(%rdi), %r8
movqoR9(%rdi), %r9
/* Setup finally %rdi. */
movqoRDI(%rdi), %rdi
看一下最后一句,会发现最后才恢复了RDI寄存器中的内容,为什么?因为在记录堆栈信息的时候,是最后一个记录了当时上下文中函数的参数uccontext,此时需要恢复到上文状态。此时,CPU的运行状态已经恢复到了上一个断点的状态时刻。整个记录和恢复的过程如下图所示:
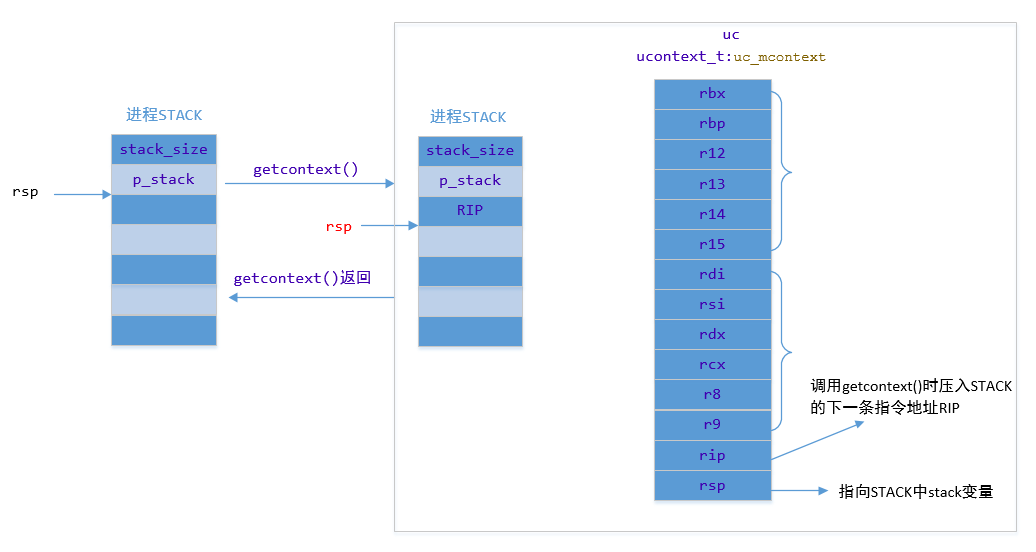
整个调用过程。
总结:
先总结了sigsetjmp和siglongjmp函数这两个函数的使用方法,以及一些基本原理。
再有就是详细介绍了ucontext函数簇中的两个函数setcontext和getcontext详细实现。那么这个函数簇剩下两个函数还没介绍makecontext(),swapcontext(),这两个函数可以实现更加有意思的技术就是协程技术。下次再写一个协程的小demo。




















 475
475











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








