本文不讨论C/C++扩展python的方法,仅讨论用python脚本自定义的一些函数纳入python库的方法。
步骤如下:
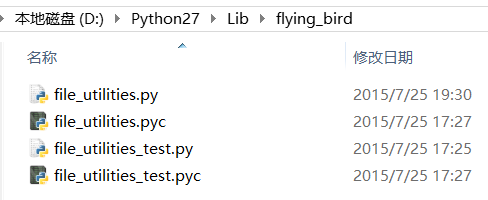
1. 在Python安装目录的Lib下面创建一个目录,放自己定义的python脚本;
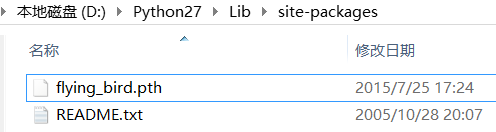
2. 在Lib/site-packages/目录下创建一个pth文本文件,把第一步对应的路径写在该文件中
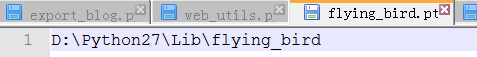
示例:
上述一切妥当之后,就和python自己的库一样使用了。
附 python帮助文档中的相关部分:
27.14. site — Site-specific configuration hook
This module is automatically imported during initialization. The automatic import can be suppressed using the interpreter’s -S option.
Importing this module will append site-specific paths to the module search path.
It starts by constructing up to four directories from a head and a tail part. For the head part, it uses sys.prefix and sys.exec_prefix; empty heads are skipped. For the tail part, it uses the empty string and then lib/site-packages (on Windows) or lib/python|version|/site-packages and then lib/site-python (on Unix and Macintosh). For each of the distinct head-tail combinations, it sees if it refers to an existing directory, and if so, adds it to sys.path and also inspects the newly added path for configuration files.
A path configuration file is a file whose name has the form package.pth and exists in one of the four directories mentioned above; its contents are additional items (one per line) to be added to sys.path. Non-existing items are never added to sys.path, but no check is made that the item refers to a directory (rather than a file). No item is added to sys.path more than once. Blank lines and lines beginning with # are skipped. Lines starting with import (followed by space or tab) are executed.
Changed in version 2.6: A space or tab is now required after the import keyword.
For example, suppose sys.prefix and sys.exec_prefix are set to /usr/local. The Python X.Y library is then installed in /usr/local/lib/pythonX.Y (where only the first three characters of sys.version are used to form the installation path name). Suppose this has a subdirectory /usr/local/lib/pythonX.Y/site-packages with three subsubdirectories, foo, bar and spam, and two path configuration files, foo.pth and bar.pth. Assume foo.pth contains the following:
# foo package configuration
foo
bar
bletch
and bar.pth contains:
# bar package configuration
bar
Then the following version-specific directories are added to sys.path, in this order:
/usr/local/lib/pythonX.Y/site-packages/bar
/usr/local/lib/pythonX.Y/site-packages/foo
Note that bletch is omitted because it doesn’t exist; the bar directory precedes the foo directory because bar.pth comes alphabetically before foo.pth; and spam is omitted because it is not mentioned in either path configuration file.
After these path manipulations, an attempt is made to import a module named sitecustomize, which can perform arbitrary site-specific customizations. If this import fails with an ImportError exception, it is silently ignored.
Note that for some non-Unix systems, sys.prefix and sys.exec_prefix are empty, and the path manipulations are skipped; however the import of sitecustomize is still attempted.




















 1281
1281

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








