// doRun() method logic in SocketProcessorif (handshake == 0) { SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN; // Process the request from this socket if (event == null) { state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ); } else { state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event); } if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) { poller.cancelledKey(key, socketWrapper); }} else if (handshake == -1 ) { poller.cancelledKey(key, socketWrapper);}- 对于 handshake 为 -1 表明握手有问题,调用 poller.cancelledKey() 方法来关闭原始 socket 不使用长连接。
握手正常,取决 ConnectionHandler.process() 返回的 SocketState 。如果状态为 CLOSED 则直接关闭原始 socket ,否则将不关闭保持长连接。
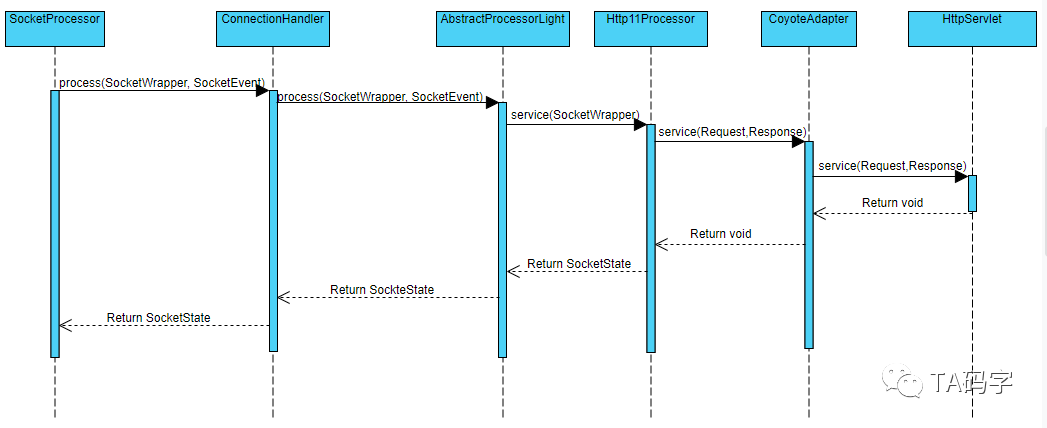
根据以前文章,ConnectionHandler 实例的 process() 方法会间接的调用Http11Processor 的 service() 方法来决定返回的 SocketState ,其核心逻辑如下:
// service() method in Http11Processorif (openSocket) { if (readComplete) { return SocketState.OPEN; } else { return SocketState.LONG; } } else { return SocketState.CLOSED; }由上可知 SocketState 由 openSocket 全局变量决定,为 false 的时候关闭连接,为 true 的时候不关闭连接。
openSocket 全局变量又会在 Http11Processor 的 service() 方法中通过调用 processSendfile() 方法改变,逻辑如下:
private SendfileState processSendfile(SocketWrapperBase> socketWrapper) { openSocket = keepAlive; //Other logic in processSendfile method return result;}- 由上述逻辑可知,openSokcet 又由全局变量 keepAlive 决定。keepAlive 的初始值为 true 。但是会有如下 items 改变其值:
-
- Http11Processor 中 service() 方法逻辑:
int maxKeepAliveRequests = protocol.getMaxKeepAliveRequests();if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) { keepAlive = false;} else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 && socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) { keepAlive = false;} - 由上面逻辑可知 keepAlive 由 tomcat 每个连接的 maxKeepLiveRequest 决定,其初始默认值为 100。即 server 端每个长连接可以支持 100 个请求,超过就会关闭连接。
- Http11Processor 中 prepareRequest() 方法逻辑:
if (protocolMB.equals(Constants.HTTP_10)) { http11 = false; keepAlive = false; protocolMB.setString(Constants.HTTP_10);}MessageBytes connectionValueMB = headers.getValue(Constants.CONNECTION);if (connectionValueMB != null) { ByteChunk connectionValueBC = connectionValueMB.getByteChunk();if (findBytes(connectionValueBC, Constants.CLOSE_BYTES) != -1) { keepAlive = false; } else if (findBytes(connectionValueBC, Constants.KEEPALIVE_BYTES) != -1) { keepAlive = true; }} - 如果是 http1.0 协议则 keepAlive 的值为 false ,关闭 socket 不用长连接,这也符合 http1.0 没有长连接的标准。
- 对于 http1.1 协议会根据 Connection 请求头的值决定,如果为 close 则表示关闭 socket 不用长连接,如果为 keep-alive 则表示使用长连接,这也符合 http1.1 对长连接定义的标准。
- Http11Processor 中 service() 方法逻辑:
除了以上在 tomcat io 线程中决定是否使用长连接之外,poller 线程也可以决定是否使用长连接。在 poller 的循环 run() 方法里会调用 timeout() 方法来决定是否关闭连接,核心逻辑如下:
if ((socketWrapper.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_READ) == SelectionKey.OP_READ || (socketWrapper.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) { boolean isTimedOut = false; boolean readTimeout = false; boolean writeTimeout = false; // Check for read timeout if ((socketWrapper.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_READ) == SelectionKey.OP_READ) { long delta = now - socketWrapper.getLastRead(); long timeout = socketWrapper.getReadTimeout(); isTimedOut = timeout > 0 && delta > timeout; readTimeout = true; } // Check for write timeout if (!isTimedOut && (socketWrapper.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) { long delta = now - socketWrapper.getLastWrite(); long timeout = socketWrapper.getWriteTimeout(); isTimedOut = timeout > 0 && delta > timeout; writeTimeout = true; } if (isTimedOut) { key.interestOps(0); // Avoid duplicate timeout calls socketWrapper.interestOps(0); socketWrapper.setError(new SocketTimeoutException()); if (readTimeout && socketWrapper.readOperation != null) { if (!socketWrapper.readOperation.process()) { cancelledKey(key, socketWrapper); } } else if (writeTimeout && socketWrapper.writeOperation != null) { if (!socketWrapper.writeOperation.process()) { cancelledKey(key, socketWrapper); } } else if (!processSocket(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.ERROR, true)) { cancelledKey(key, socketWrapper); } } }- 该方法会判断是否有读写超时,读写超时时间由 NioSocketWrapper 实例的 getReadTimeout() 和 getWriteTimeout() 决定,默认都为 1 分钟。
NioSocketWrapper 实例会有 getLastRead() 和 getLastWrite() 方法记录最近一次读写时间,根据上面超时时间判断是否超时(1分钟内没有读写操作)。
根据上述如果读写超时,一般情况会走 processSocket(socketWrapper,SocketEvent.ERROR, true) 调用,传递 SocketEvent.ERROR 作为 socket 事件。而对于 error 事件处理也是关闭 socket 。即使上面调用不成功也会调用 cancelledKey() 方法来关闭 socket ,从而不保持长连接。
根据以上分析对于 tomcat 长连接的总结如下:
- tomcat 默认就是开启长连接的。
- 对于 http1.0 协议不使用长连接。
- 如果请求头中 Connection 的值为 keep-alive 则使用长连接,为 close 则关闭 socket 不使用长连接。
- tomcat 每个长连接默认支持 100 个请求,如果超过则关闭 socket 停止当前长连接,不过在后续新的连接里还是继续支持长连接。
- 对于每个长连接 tomcat 会在以前文章介绍的 poller 线程中检查是否有读写超时,默认读写超时时间均为 1 分钟,如果 1 分钟之内没有读写操作,那么关闭 socket 停止当前长连接。
- 对于上面没有读写操作关闭长连接的情况不仅仅适用于 http 协议,还适用于其它基于 tcp 的协议,因为这个是基于原始 socket 的检测,例如 websocket 协议。 只是对于 websocket 协议来说服务器设置的默认读写超时时间为-1,即不会超时,所以实现了该协议的长连接。当然对于 websocket 协议来说本身也有 ping/pong 定义来实现 keeplive 。





















 752
752











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








