4.22 Reading Directories
这里给出了几个函数,专注处理directroy本身。
1. 这几个函数之间有约定速成的一个结构体DIR 便于数据交换
2. opendir fopendir这里函数负责由一个给定的pathname传回DIR指针
3. 其余的5个函数根据DIR来执行各种操作(比如,迭代directory下面的每个元素)
这部分比较有价值的是给出了一个递归统计某个目录下各个类型的file的数量的代码,实现了简易版的ftw(3)函数。代码虽然比较长,但是值得仔细过一遍,可以学习很多细节。需要具体注意的点,都写在代码注释中了。
#include "apue.h" #include <dirent.h> #include <limits.h> #include <errno.h> /* If PATH_MAX is indeterminate, no guarantee this is adequate */ #define PATH_MAX_GUESS 1024 /*因为path不同于一般的变量 分配的长度是有讲究的 因此单拎出来一个函数 * 1. 返回分配好内存的首地址 也就是指针 * 2. 同时在sizep地址存放被分配的地址的长度*/ char *path_alloc(size_t *sizep) /* also return allocated size, if nonnull */ { #ifdef PATH_MAX long pathmax = PATH_MAX; #else long pathmax = 0; #endif char *ptr; size_t size; long posix_version = 0; long xsi_version = 0; /*系统配置相关*/ posix_version = sysconf(_SC_VERSION); xsi_version = sysconf(_SC_XOPEN_VERSION); /*这部分代码保证了pathmax在使用前是一个靠谱的非零值*/ if (pathmax == 0) { /* first time through */ errno = 0; if ((pathmax = pathconf("/", _PC_PATH_MAX)) < 0) { if (errno == 0) pathmax = PATH_MAX_GUESS; /* it's indeterminate */ else err_sys("pathconf error for _PC_PATH_MAX"); } else { pathmax++; /* add one since it's relative to root */ } } /* * Before POSIX.1-2001, we aren't guaranteed that PATH_MAX includes * the terminating null byte. Same goes for XPG3. */ /*这部分代码处理不同系统带来的size的差异性,最后一个结束字符到底是否计算入pathmax中*/ if ((posix_version < 200112L) && (xsi_version < 4)) size = pathmax + 1; else size = pathmax; if ((ptr = malloc(size)) == NULL) err_sys("malloc error for pathname"); if (sizep != NULL) *sizep = size; return(ptr); } typedef int Myfunc(const char *, const struct stat *, int); static Myfunc myfunc; static int myftw(char *, Myfunc *); static int dopath(Myfunc *); static long nreg, ndir, nblk, nchr, nfifo, nslink, nsock, ntot; #define FTW_F 1 /* file other than directory */ #define FTW_D 2 /* directory */ #define FTW_DNR 3 /* directory that can't be read */ #define FTW_NS 4 /* file that we can't stat */ static char *fullpath; /* contains full pathname for every file */ static size_t pathlen; static int myftw(char *pathname, Myfunc *func) { /* 1. 给fullpath分配内存 不能随意的malloc是因为文件路径的长度是有讲究的*/ fullpath = path_alloc(&pathlen); /* 2. 由于某些原因给fullpath分配长度pathlen不足 小于pathname的长度 因此就需要重新给fullpath分配内存*/ if (pathlen <= strlen(pathname)) { pathlen = strlen(pathname)*2; /*为什么是2倍 因为既要把pathname包含进去 又要把原来的pathlen包含进去 而pathlen是小于pathname的 所以2*pathname是最小代价的内存*/ if ((fullpath=realloc(fullpath, pathlen))==NULL) { err_sys("realloc failed"); } } /* 3. 把pathname复制到fullpath中*/ strcpy(fullpath, pathname); /* 4. 此时fullpath已经包含了目标原始pathname 则递归遍历*/ return(dopath(func)); } /* 总的来说, 这是一个典型的深度优先搜索的代码路子 * 这里只传递了一个函数指针 其实还有一个参数就完全路径 只不过这个参数以全局变量的形式出现了 * 终止条件: * 1. 如果无法获取fullpath对应的struct stat 则经过func函数处理后退出 * 2. 如果fullpath对应的不是目录 则经过func函数处理后退出 * 迭代fullpath路径下的各个元素 fullpath+各个元素 形成新的完整路径 再递归处理 * * 需要注意的是 fullpath是一个全局变量 保证返回到上一层递归的时候fullpath是干净的*/ static int dopath(Myfunc* func) { struct stat statbuf; struct dirent *dirp; DIR *dp; int ret, n; if (lstat(fullpath, &statbuf)<0) { /*stat error*/ return(func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_NS)); } if (S_ISDIR(statbuf.st_mode)==0) { /*not a directory*/ return(func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_F)); } /*it's a directory. * 1. first call func() for the directory, * 2. then address each filename in the directory * */ if ((ret=func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_D))!=0) { /*让'目录数量'这个全局变量累加*/ return(ret); } n = strlen(fullpath); /*如果初始分配的长度不够 要重新分配fullpath的占用内存大小*/ if (n+NAME_MAX+2>pathlen){ pathlen *= 2; if ((fullpath = realloc(fullpath, pathlen)) == NULL) { err_sys("realloc failed"); } } fullpath[n++] = '/'; printf("%s\n",fullpath); fullpath[n] = 0; /*本质的原因是malloc方法分配的内存is not cleared的 可以看man手册查询*/ /*opendir的作用是迭代遍历fullpath下的各个元素*/ if ((dp=opendir(fullpath))==NULL) { /*can't read directory*/ return(func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_DNR)); } /*readdir不断迭代DIR类型指针dp 直到迭代到头*/ while ((dirp=readdir(dp))!=NULL){ if(strcmp(dirp->d_name, ".")==0 || strcmp(dirp->d_name, "..")==0) continue; /*ignore dot and dot-dot*/ strcpy(&fullpath[n], dirp->d_name); /*补上d_name就形成了完整的路径信息*/ if((ret = dopath(func))!=0) /*recursive*/ break; /*这里的策略是一旦有一个子目录无法recursive了 整体就退出了*/ } fullpath[n-1] = 0; /*这样做是保证了回到上一层之前fullpath是干净的*/ if (closedir(dp)<0) err_ret("can't close directory %s", fullpath); return(ret); } /*统计各种类型的文件的数量*/ static int myfunc(const char *pathname, const struct stat *statptr, int type) { switch(type) { case FTW_F: switch (statptr->st_mode & S_IFMT) { case S_IFREG: nreg++; break; case S_IFBLK: nblk++; break; case S_IFCHR: nchr++; break; case S_IFIFO: nfifo++; break; case S_IFLNK: nslink++; break; case S_IFSOCK: nsock++; break; case S_IFDIR: err_dump("for S_IFDIR for %s", pathname); } break; ndir++; break; case FTW_D: ndir++; break; case FTW_DNR: err_ret("can't read directory %s", pathname); break; case FTW_NS: err_ret("stat error for %s", pathname); break; default: err_dump("unkown type %d for pathname %s", type, pathname); } return(0); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int ret; if (argc != 2) err_quit("usage: ftw <starting-pathname>"); ret = myftw(argv[1], myfunc); /* does it all */ ntot = nreg + ndir + nblk + nchr + nfifo + nslink + nsock; if (ntot == 0) ntot = 1; /* avoid divide by 0; print 0 for all counts */ printf("regular files = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nreg, nreg*100.0/ntot); printf("directories = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", ndir, ndir*100.0/ntot); printf("block special = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nblk, nblk*100.0/ntot); printf("char special = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nchr, nchr*100.0/ntot); printf("FIFOs = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nfifo, nfifo*100.0/ntot); printf("symbolic links = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nslink, nslink*100.0/ntot); printf("sockets = %7ld, %5.2f %%\n", nsock, nsock*100.0/ntot); exit(ret); }
再贴一个运行结果:
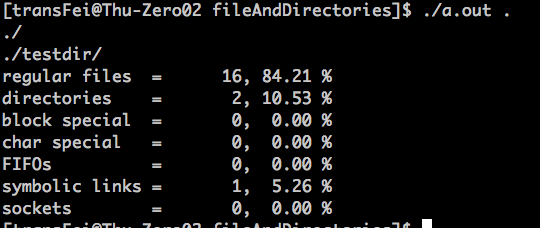
这里注意,输入给函数的参数是'.',在dopath中由lstat函数处理这个'.',间接证明了lstat是可以处理相对路径和绝对路径的。
还有需要注意是path_alloc函数是在APUE的第二张中提到的,我到原书第二章提供的源代码中找到了这个函数的实现,并加以修改。





















 739
739











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








