StateListDrawable
1、配合ImageView使用
- 比如向StateListDrawable对象中添加选中状态,以及选中状态所显示的Drawable
//定义常规和选中两种状态
int[] normal = StateSet.WILD_CARD;
int[] selected = new int[]{android.R.attr.state_selected};
//设置两种状态分别显示的Drawable
StateListDrawable stateListDrawable1 = new StateListDrawable();
stateListDrawable1.addState(selected,getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.ic_launcher_foreground));
stateListDrawable1.addState(normal,getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.ic_launcher_background));
- 给ImageView设置使用StateListDrawable
binding.iv1.setImageDrawable(stateListDrawable1);

- 设置ImageView为选中状态
binding.iv1.setSelected(true);
2、使用中遇到的问题
- 空状态(正常状态)必须在最后一个添加,不然设置选中会不生效
- StateListDrawable有个setState()方法,如果单独设置它的状态为选中状态,理论上就不用设置ImageView为选中状态了,但是实际效果却不生效
我主要好奇第二点为啥不生效,随后便开始了代码翻阅之旅,然后中途恰好翻到了第1点的原因
2.1 跟踪StateListDrawable的setState()源码
- 点击setState()方法进入到Drawable类中,判断当前是否是该状态,不是的话重新设置状态
//Drawable.java
public boolean setState(@NonNull final int[] stateSet) {
if (!Arrays.equals(mStateSet, stateSet)) {
mStateSet = stateSet;
return onStateChange(stateSet);
}
return false;
}
protected boolean onStateChange(int[] state) {
return false;
}
- 查看子类的实现,因为StateListDrawable是DrawableContainer的子类,DrawableContainer直接继承的Drawable,直接进入DrawableContainer.java
@Override
//DrawableContainer.java
protected boolean onStateChange(int[] state) {
//大概翻了下,和显隐动画相关的
if (mLastDrawable != null) {
return mLastDrawable.setState(state);
}
//设置当前显示的Drawable状态
if (mCurrDrawable != null) {
return mCurrDrawable.setState(state);
}
return false;
}
发现StateListDrawable也有实现,点进去查看代码,思路就是先根据设置的状态找到对应要显示的Drawable,然后设置一下
@Override
//StateListDrawable.java
protected boolean onStateChange(int[] stateSet) {
final boolean changed = super.onStateChange(stateSet);
//查找要设置状态的index
int idx = mStateListState.indexOfStateSet(stateSet);
if (DEBUG) {
android.util.Log.i(TAG, "onStateChange " + this + " states "
+ Arrays.toString(stateSet) + " found " + idx);
}
if (idx < 0) {
idx = mStateListState.indexOfStateSet(StateSet.WILD_CARD);
}
//设置当前的drawable
return selectDrawable(idx) || changed;
}
- 进入selectDrawable(int index)方法,核心代码就是绘制自身invalidateSelf()
//DrawableContanier.java
boolean selectDrawable(int index) {
if (index == mCurIndex) {
return false;
}
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (DEBUG) {
android.util.Log.i(TAG, toString() + " from " + mCurIndex + " to " + index
+ ": exit=" + mDrawableContainerState.mExitFadeDuration
+ " enter=" + mDrawableContainerState.mEnterFadeDuration);
}
if (mDrawableContainerState.mExitFadeDuration > 0) {
if (mLastDrawable != null) {
mLastDrawable.setVisible(false, false);
}
if (mCurrDrawable != null) {
mLastDrawable = mCurrDrawable;
mExitAnimationEnd = now + mDrawableContainerState.mExitFadeDuration;
} else {
mLastDrawable = null;
mExitAnimationEnd = 0;
}
} else if (mCurrDrawable != null) {
mCurrDrawable.setVisible(false, false);
}
if (index >= 0 && index < mDrawableContainerState.mNumChildren) {
final Drawable d = mDrawableContainerState.getChild(index);
mCurrDrawable = d;
mCurIndex = index;
if (d != null) {
if (mDrawableContainerState.mEnterFadeDuration > 0) {
mEnterAnimationEnd = now + mDrawableContainerState.mEnterFadeDuration;
}
initializeDrawableForDisplay(d);
}
} else {
mCurrDrawable = null;
mCurIndex = -1;
}
if (mEnterAnimationEnd != 0 || mExitAnimationEnd != 0) {
if (mAnimationRunnable == null) {
mAnimationRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
animate(true);
invalidateSelf();
}
};
} else {
unscheduleSelf(mAnimationRunnable);
}
// Compute first frame and schedule next animation.
animate(true);
}
invalidateSelf();
return true;
}
- 进入invalidateSelf,发现是获取callBack,然后调用callBack的invalidateDrawable()方法,这个callBack在ImageView里面,是在IamgeView.setImageDrawable()方法中调用了updateDrawable()设置的
// Drawable.java
public void invalidateSelf() {
final Callback callback = getCallback();
if (callback != null) {
callback.invalidateDrawable(this);
}
}
//ImageView.java
public void setImageDrawable(@Nullable Drawable drawable) {
if (mDrawable != drawable) {
mResource = 0;
mUri = null;
final int oldWidth = mDrawableWidth;
final int oldHeight = mDrawableHeight;
updateDrawable(drawable);
if (oldWidth != mDrawableWidth || oldHeight != mDrawableHeight) {
requestLayout();
}
invalidate();
}
}
private void updateDrawable(Drawable d) {
if (d != mRecycleableBitmapDrawable && mRecycleableBitmapDrawable != null) {
mRecycleableBitmapDrawable.setBitmap(null);
}
boolean sameDrawable = false;
if (mDrawable != null) {
sameDrawable = mDrawable == d;
mDrawable.setCallback(null);
unscheduleDrawable(mDrawable);
if (!sCompatDrawableVisibilityDispatch && !sameDrawable && isAttachedToWindow()) {
mDrawable.setVisible(false, false);
}
}
mDrawable = d;
if (d != null) {
//就是这句设置的callback
d.setCallback(this);
d.setLayoutDirection(getLayoutDirection());
if (d.isStateful()) {
d.setState(getDrawableState());
}
if (!sameDrawable || sCompatDrawableVisibilityDispatch) {
final boolean visible = sCompatDrawableVisibilityDispatch
? getVisibility() == VISIBLE
: isAttachedToWindow() && getWindowVisibility() == VISIBLE && isShown();
d.setVisible(visible, true);
}
d.setLevel(mLevel);
mDrawableWidth = d.getIntrinsicWidth();
mDrawableHeight = d.getIntrinsicHeight();
applyImageTint();
applyColorFilter();
applyAlpha();
applyXfermode();
configureBounds();
} else {
mDrawableWidth = mDrawableHeight = -1;
}
}
- 查看ImageView的invalidateDrawable()方法,发现就是重绘自身,
@Override
//ImageView.java
public void invalidateDrawable(@NonNull Drawable dr) {
//走第一个,因为是相同的Drawable
if (dr == mDrawable) {
if (dr != null) {
// update cached drawable dimensions if they've changed
final int w = dr.getIntrinsicWidth();
final int h = dr.getIntrinsicHeight();
if (w != mDrawableWidth || h != mDrawableHeight) {
mDrawableWidth = w;
mDrawableHeight = h;
// updates the matrix, which is dependent on the bounds
configureBounds();
}
}
/* we invalidate the whole view in this case because it's very
* hard to know where the drawable actually is. This is made
* complicated because of the offsets and transformations that
* can be applied. In theory we could get the drawable's bounds
* and run them through the transformation and offsets, but this
* is probably not worth the effort.
*/
invalidate();
} else {
super.invalidateDrawable(dr);
}
}
2.2 跟踪ImageView的setSelected()源码
- resizeFromDrawable()就是大小尺寸计算相关,无关,所以追踪父类的setSelected()方法
//ImageView.java
@Override
public void setSelected(boolean selected) {
super.setSelected(selected);
resizeFromDrawable();
}
private void resizeFromDrawable() {
final Drawable d = mDrawable;
if (d != null) {
int w = d.getIntrinsicWidth();
if (w < 0) w = mDrawableWidth;
int h = d.getIntrinsicHeight();
if (h < 0) h = mDrawableHeight;
if (w != mDrawableWidth || h != mDrawableHeight) {
mDrawableWidth = w;
mDrawableHeight = h;
requestLayout();
}
}
}
- 发现除了重绘本身invalidate(true),就是刷新Drawable的状态refreshDrawableState(),然后分发选中事件dispatchSetSelected(selected)(viewGroup才会分发,所以是个空实现,忽略)
//View.java
public void setSelected(boolean selected) {
//noinspection DoubleNegation
if (((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SELECTED) != 0) != selected) {
mPrivateFlags = (mPrivateFlags & ~PFLAG_SELECTED) | (selected ? PFLAG_SELECTED : 0);
if (!selected) resetPressedState();
invalidate(true);
refreshDrawableState();
dispatchSetSelected(selected);
if (selected) {
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_SELECTED);
} else {
notifyViewAccessibilityStateChangedIfNeeded(
AccessibilityEvent.CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_UNDEFINED);
}
}
}
- 进入refreshDrawableState()方法,点进drawableStateChanged()的方法,都没啥用,不过drawableStateChanged()被ImageView重写了
//View.java
public void refreshDrawableState() {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWABLE_STATE_DIRTY;
drawableStateChanged();
ViewParent parent = mParent;
if (parent != null) {
parent.childDrawableStateChanged(this);
}
}
//ImageView有这个方法的重写
protected void drawableStateChanged() {
final int[] state = getDrawableState();
boolean changed = false;
final Drawable bg = mBackground;
if (bg != null && bg.isStateful()) {
changed |= bg.setState(state);
}
final Drawable hl = mDefaultFocusHighlight;
if (hl != null && hl.isStateful()) {
changed |= hl.setState(state);
}
final Drawable fg = mForegroundInfo != null ? mForegroundInfo.mDrawable : null;
if (fg != null && fg.isStateful()) {
changed |= fg.setState(state);
}
if (mScrollCache != null) {
final Drawable scrollBar = mScrollCache.scrollBar;
if (scrollBar != null && scrollBar.isStateful()) {
changed |= scrollBar.setState(state)
&& mScrollCache.state != ScrollabilityCache.OFF;
}
}
if (mStateListAnimator != null) {
mStateListAnimator.setState(state);
}
if (!isAggregatedVisible()) {
// If we're not visible, skip any animated changes
jumpDrawablesToCurrentState();
}
if (changed) {
invalidate();
}
}
- 发现最终还是调用了Drawable的setState()方法,以及重新绘制drawable的invalidateDrawable()方法
//ImageView.java
@Override
protected void drawableStateChanged() {
super.drawableStateChanged();
final Drawable drawable = mDrawable;
if (drawable != null && drawable.isStateful()
&& drawable.setState(getDrawableState())) {
invalidateDrawable(drawable);
}
}
然后我就纳闷了,ImageView最终还是调用的Drawable的setState()方法,但是Drawable的setState()直接使用却不生效呢,随后我又重新翻阅了两边的逻辑,并没有找到所以然,当天已经凌晨1点,第二天要上班就暂时放弃了,第二天晚上回家又先走了一遍两边的流程,确定自己这边逻辑没有问题,然后便猜测是重绘的时候可能搞了点什么,然后我就在setState()方法里面进行断点调试。
随后对Drawable.setState()进行调试,发现这边一开始是设置的setState()状态,后来又被调用被改掉了,根据断点得到调用栈,发现是在View.dispatchAttachedToWindow()方法中会先将view的state标识为污染状态,让view里面的Drawable的状态和view的本身状态保持一致
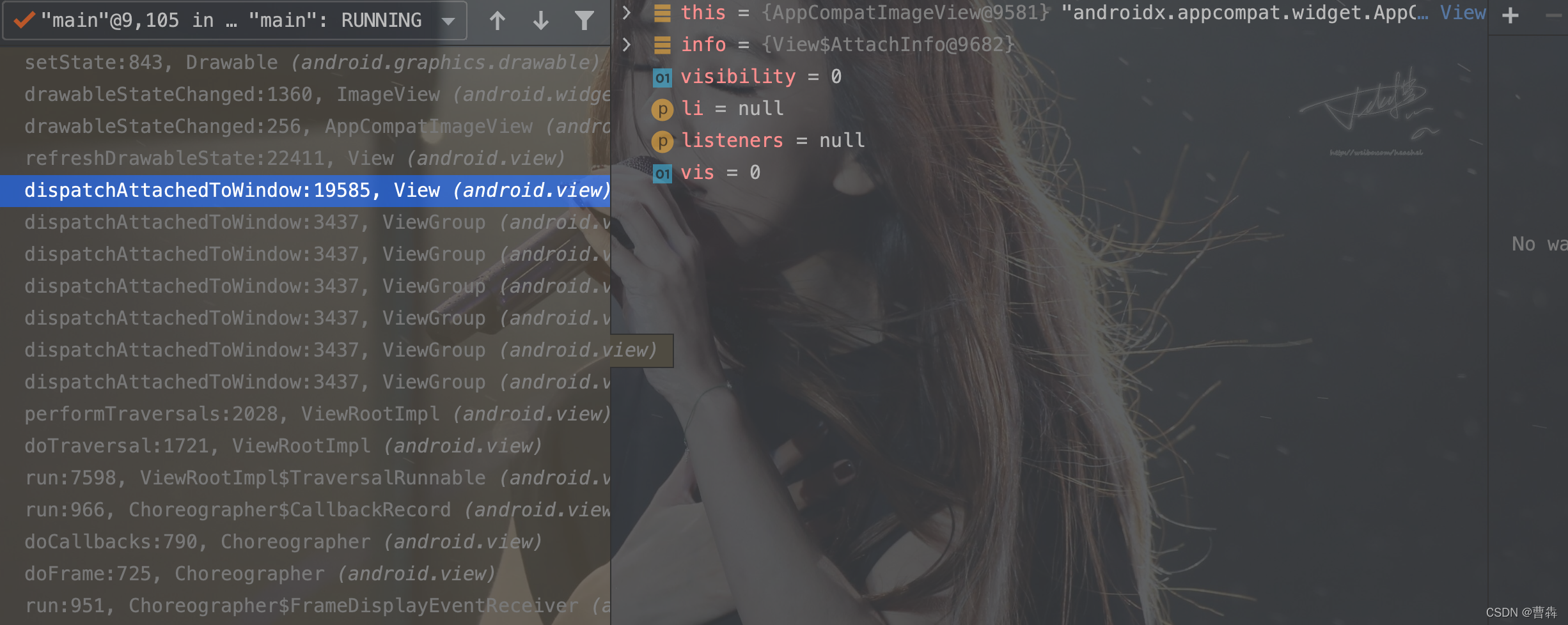
void dispatchAttachedToWindow(AttachInfo info, int visibility) {
mAttachInfo = info;
if (mOverlay != null) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchAttachedToWindow(info, visibility);
}
mWindowAttachCount++;
// We will need to evaluate the drawable state at least once.
//为了矫正Drawable的state,将标志标识为污染状态
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWABLE_STATE_DIRTY;
if (mFloatingTreeObserver != null) {
info.mTreeObserver.merge(mFloatingTreeObserver);
mFloatingTreeObserver = null;
}
registerPendingFrameMetricsObservers();
if ((mPrivateFlags&PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER) != 0) {
mAttachInfo.mScrollContainers.add(this);
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_SCROLL_CONTAINER_ADDED;
}
// Transfer all pending runnables.
if (mRunQueue != null) {
mRunQueue.executeActions(info.mHandler);
mRunQueue = null;
}
performCollectViewAttributes(mAttachInfo, visibility);
onAttachedToWindow();
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
final CopyOnWriteArrayList<OnAttachStateChangeListener> listeners =
li != null ? li.mOnAttachStateChangeListeners : null;
if (listeners != null && listeners.size() > 0) {
// NOTE: because of the use of CopyOnWriteArrayList, we *must* use an iterator to
// perform the dispatching. The iterator is a safe guard against listeners that
// could mutate the list by calling the various add/remove methods. This prevents
// the array from being modified while we iterate it.
for (OnAttachStateChangeListener listener : listeners) {
listener.onViewAttachedToWindow(this);
}
}
int vis = info.mWindowVisibility;
if (vis != GONE) {
onWindowVisibilityChanged(vis);
if (isShown()) {
// Calling onVisibilityAggregated directly here since the subtree will also
// receive dispatchAttachedToWindow and this same call
onVisibilityAggregated(vis == VISIBLE);
}
}
// Send onVisibilityChanged directly instead of dispatchVisibilityChanged.
// As all views in the subtree will already receive dispatchAttachedToWindow
// traversing the subtree again here is not desired.
onVisibilityChanged(this, visibility);
//重新设置Drawable的state
if ((mPrivateFlags&PFLAG_DRAWABLE_STATE_DIRTY) != 0) {
// If nobody has evaluated the drawable state yet, then do it now.
refreshDrawableState();
}
needGlobalAttributesUpdate(false);
notifyEnterOrExitForAutoFillIfNeeded(true);
notifyAppearedOrDisappearedForContentCaptureIfNeeded(true);
}
2.3 问题1的源码
在StateListDrawable的onStateChange()方法中调用了StateListState的indexOfStateSet()方法,他会遍历StateListState当前所有的状态集合,然后调用了StateSet的stateSetMatches()方法做比较,在该方法里面是遍历StateLIstState的里面取到的一个状态集合,然后在设置的状态中查找有没有是否都有满足该集合的状态,有的话就返回这个index了,所以要把选中的状态先设置,其实这也是我们xml布局文件中selector要把normal状态设置到最后的原因。
//StateListDrawable.java
@Override
protected boolean onStateChange(int[] stateSet) {
final boolean changed = super.onStateChange(stateSet);
//这一句
int idx = mStateListState.indexOfStateSet(stateSet);
if (DEBUG) android.util.Log.i(TAG, "onStateChange " + this + " states "
+ Arrays.toString(stateSet) + " found " + idx);
if (idx < 0) {
idx = mStateListState.indexOfStateSet(StateSet.WILD_CARD);
}
return selectDrawable(idx) || changed;
}
/**
* StateListState.java
*/
int indexOfStateSet(int[] stateSet) {
final int[][] stateSets = mStateSets;
final int N = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (StateSet.stateSetMatches(stateSets[i], stateSet)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* StateSet.java
*/
public static boolean stateSetMatches(int[] stateSpec, int[] stateSet) {
if (stateSet == null) {
return (stateSpec == null || isWildCard(stateSpec));
}
int stateSpecSize = stateSpec.length;
int stateSetSize = stateSet.length;
//遍历的是StateListState集合,然后去查看要设置的状态是否都有这些状态
for (int i = 0; i < stateSpecSize; i++) {
int stateSpecState = stateSpec[i];
if (stateSpecState == 0) {
// We've reached the end of the cases to match against.
return true;
}
final boolean mustMatch;
if (stateSpecState > 0) {
mustMatch = true;
} else {
// We use negative values to indicate must-NOT-match states.
mustMatch = false;
stateSpecState = -stateSpecState;
}
boolean found = false;
for (int j = 0; j < stateSetSize; j++) {
final int state = stateSet[j];
if (state == 0) {
// We've reached the end of states to match.
if (mustMatch) {
// We didn't find this must-match state.
return false;
} else {
// Continue checking other must-not-match states.
break;
}
}
if (state == stateSpecState) {
if (mustMatch) {
found = true;
// Continue checking other other must-match states.
break;
} else {
// Any match of a must-not-match state returns false.
return false;
}
}
}
if (mustMatch && !found) {
// We've reached the end of states to match and we didn't
// find a must-match state.
return false;
}
}
return true;
}







 本文深入探讨了StateListDrawable的工作原理,特别是如何与ImageView配合使用,以及在设置不同状态时遇到的具体问题。通过源码分析揭示了为何特定状态下某些操作无法生效。
本文深入探讨了StateListDrawable的工作原理,特别是如何与ImageView配合使用,以及在设置不同状态时遇到的具体问题。通过源码分析揭示了为何特定状态下某些操作无法生效。
















 4612
4612

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








