在传统编写 Web 自动化测试用例的过程中,基本都是需要测试工程师,根据功能测试用例转换为自动化测试的用例。市面上自动生成 Web 或 App 自动化测试用例的产品无非也都是通过录制的方式,获取操作人的行为操作,从而记录测试用例。整个过程类似于
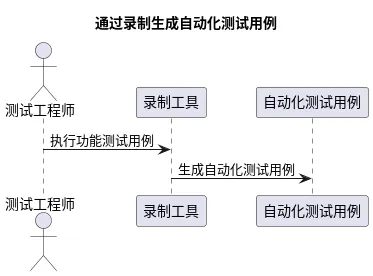
但是通常录制出来的用例可用性、可维护性都不强,而且依然需要人手工介入录制的过程。
在 LLM 问世之后,我们便在探索,是否有第二种可能性,由大模型执行功能测试用例,生成自动化测试用例?
应用价值
测试工程师在编写用例的过程中,将操作步骤明确的表达出来。即可通过大模型将功能测试用例可以直接转为 Web 自动化测试用例。极大的节省了人力与资源。
实践演练
实现原理
整个实现原理如下图所示:

实现思路
测试用例规范与要求
如果想要将功能用例转换为自动化测试用例,那么对功能测试用例则需要清晰,明确的表达出来每个操作步骤。如果测试用例本身就表达的含糊不清,那么自然大模型是无法识别它需要进行的具体的操作步骤的。
如下所示,为一个登录功能的测试步骤。在这些测试步骤中,具体打开哪些页面,输入哪些信息,点击哪些按钮都清晰的表达了出来。
通过 AGENT 执行功能测试用例。
大模型本身是不具备任何执行能力或生成能力的,它只会”思考“,但是通过 LangChain 的 Agent,可以将一些”工具”外挂到大模型身上。
那么如果要执行这些功能测试用例,大模型就需要具备执行用例的能力。而我们要做的事情,就是将 tools(工具包),外挂到大模型上面。
相关知识点: Agent、 tools
- 封装好 web 的底层工具
- 创建工具以及其说明,并且将工具绑定到工具包中
声明 Agent,并将tools传递过去:
执行 Agent:
记录执行步骤
在 Agent 的配置中,可以要求 agent 将所有的执行步骤记录下来。而执行记录会记录在返回结果中的intermediate_steps中。
而我们则需要将这些步骤取出来,按照我们的需求记录下来。
生成自动化测试用例。
拥有执行步骤之后,可以将执行步骤传递给大模型,然后让大模型根据执行步骤直接生成 web 自动化测试用例。
AGENT 结合 CHAIN
执行效果
最后,自动生成的 Web 自动化测试用例效果如下:
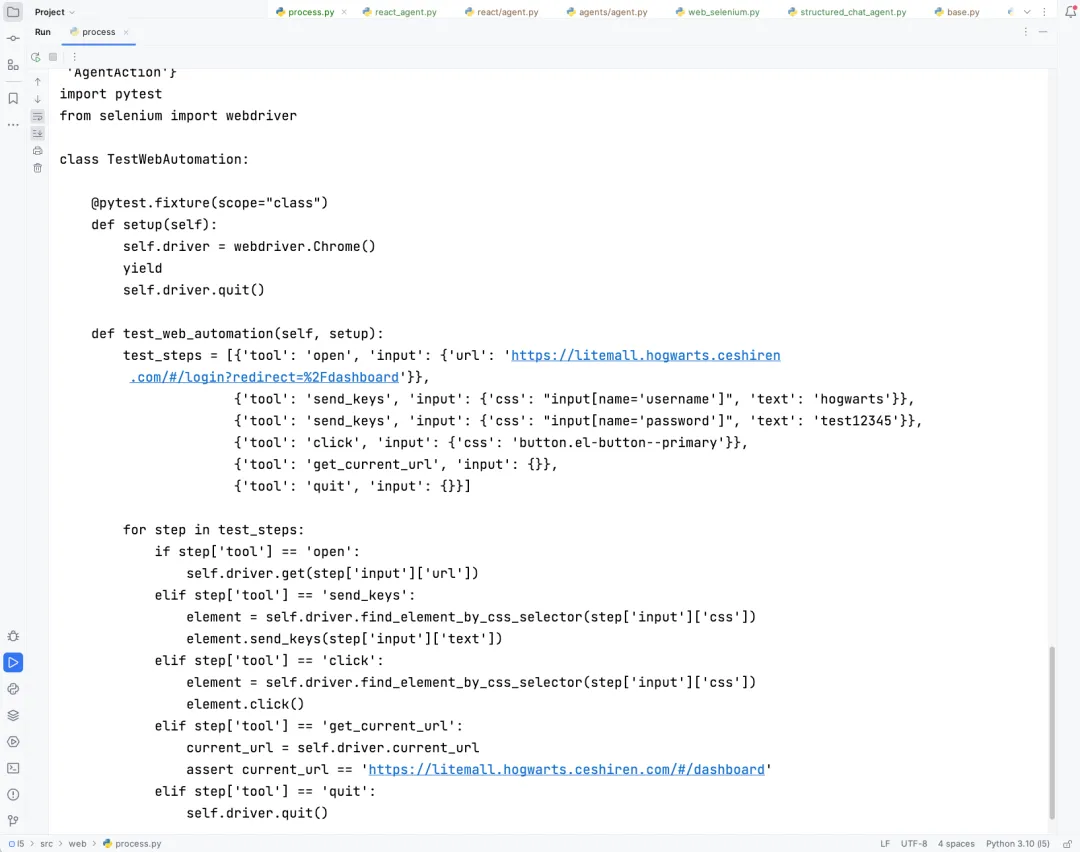
总结
- Web 自动化测试用例生成工具需求说明。
- 如何通过 LangChain 实现 Web 自动化测试用例生成工具。





















 1313
1313

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








