一、对比:
1.数组:
(1)优点
- 随机访问性强(通过下标进行快速定位)
- 查找速度快
(2) 缺点
- 插入和删除效率低(插入和删除需要移动数据 需要进行新老数组的替换问题)
- 可能浪费内存(因为是连续的,所以每次申请数组之前必须规定数组的大小,如果大小不合理,则可能会浪费内存)
- 内存空间要求高,必须有足够的连续内存空间。
- 数组大小固定,不能自动的动态拓展
2.链表:
(1) 优点:
- 插入删除速度快(根据index找到next的指针直接在指定位置进行新的替换)
- 内存利用率高,不会浪费内存(可以使用内存中细小的不连续空间(大于node节点的大小),并且在需要空间的时候才创建空间,即插入新的节点的时候只扩展了新节点的内存空间)
- 大小没有固定,只要内存允许,可以自由的拓展很灵活。
(2)缺点:
- 不能随机查找,必须从第一个头节点开始遍历直到发现指定的条件的节点,查找效率低
二、链表存储图示:
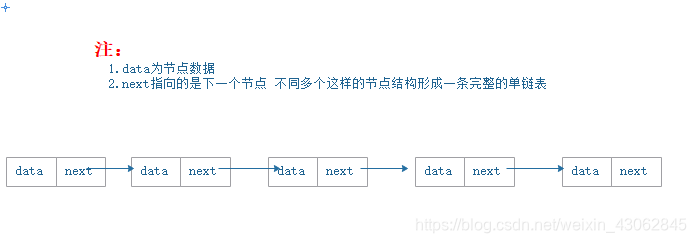
三、代码实现及注释说明:
(1)节点
public class Node {
/**
* 指针域
*/
protected Node next;
/**
* 数据域
*/
protected int data;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
/**
* 显示此节点
*/
public void display() {
System. out.print( data + " ");
}
}
(2)单链表
public class SingleLinkedList {
/**
* 头节点
*/
private Node first;
/**
* 节点的位置
*/
private int pos = 0;
public SingleLinkedList() {
this.first = null;
}
/**
* 头节点
*/
public void addFirstNode(int data) {
//创建一个节点
Node node = new Node(data);
//把头节点作为当前创建新节点的下一个节点
node.next = first;
/*
把当前新创建的节点作为新的头节点,而原头节点作为当前节点的下一个节点
依次类推,每次创建的新节点的下一节点就是原头节点,则每个节点都能互相关联起来形成一个单链链表式的数数据
*/
first = node;
}
/**
* 删除一个头节点,并返回头节点
*/
public Node deleteFirstNode() {
//获得当前的头节点
Node tempNode = first;
//根据当前头节点的下一节点赋值给当前头节点 实现了删除当前头节点
first = tempNode.next;
return tempNode;
}
/**
* 在任意位置插入节点,在index的后面插入
* current:现在
* previous:以前
*/
public void add(int index,int data) {
//创建要插入的数据的节点
Node node = new Node(data);
//把当前头节点赋值给临时变量
Node current = first;
Node previous = first;
/*
pos是插入的位置 默认为0;
如:你要插入1的位置新节点
则:你拿到的就是0位置的节点 作为以前的节点 然后再取0位置的下一个节点作为当前节点
这样你插入的时候就是 0位置节点的下一个节点是当前插入的, 而插入的位置的新节点的下一个节点就是之前取的赋值给当前节点的节点
这样就实现了定位插入。
而下边的while循环就是每次拿的都是指定插入位置的前一个节点 因为pos是从0开始 所以插入1位置
就是拿0位置的节点进行 添加新插入节点 新插入的节点的下一节点是原0位置的下一节点
依次类推 如果插入位置为100 则拿99位置的节点下一节点为新插入节点 新插入节点的下一节点为原99位置的下一节点
*/
while (pos != index) {
//取当前节点作为原几点
previous = current;
//取当前节点的下一节点为当前节点
current = current.next;
pos++;
}
//新插入的节点的下一 指向当前节点
node.next = current;
//把原节点的下一节点指向新节点 此时就实现了指定位置插入新节点并形成一条完整的新链表
previous.next = node;
pos = 0;
}
/**
* 删除任意位置节点
* current:现在
* previous:以前
*/
public Node deleteByPos(int index) {
//把当前头节点赋值给临时变量
Node current = first;
Node previous = first;
while (pos!=index) {
pos++;
//取当前节点作为原节点
previous = current;
//取删除节点即当前节点的下一节点
current = current.next;
}
//如果当前节点是头节点 则index=0 则pos=0 则头节点的下一节点作为头节点 实现删除
if (current==first) {
first = first.next;
}else {//原节点的下一节点指向当前删除的节点的下一节点 实现删除当前节点即指定节点
pos = 0;
previous.next = current.next;
}
//返回当前节点即删除的节点
return current;
}
/**
* 根据节点删除节点(仅仅删除第一个)
* current:现在
* previous:以前
* @param data
* @return
*/
public Node deleteByData(int data) {
//把头节点赋值给临时变量
Node current = first;
Node previous = first ;
//如果当前节点是指定删除的节点 不用进行while循环
while (current.data!=data) {
//如果当前节点的下一节点为空 则指定的节点在链表中不存在
if(current.next == null) {
return null;
}
//把当前节点作为原节点
previous = current;
//把当前节点的下一鞋垫作为当前节点
current = current.next;
}
//如果当前节点是头节点 则删除的是头节点
if(current == first ) {
first = first.next;
}else {
//原节点的下一节点指向当前节点的下一节点 实现删除当前节点即指定删除节点
previous.next = current.next;
}
//返回删除的节点
return current;
}
/**
* 显示出所有的节点信息
* current:现在
* previous:以前
*/
public void displayAllNodes() {
Node current = first;
while(current!=null) {
current.display();
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 根据位置查找节点信息
* current:现在
* previous:以前
* @param index
* @return
*/
public Node findByPos(int index) {
Node current = first;
if(pos !=index ) {
current = current.next;
pos++;
}
return current;
}
/**
* 根据数据查找节点
* current:现在
* previous:以前
* @param data
* @return
*/
public Node findByData(int data) {
Node current = first;
while (current.data!=data) {
if(current.next==null) {
return null;
}
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
}
(3)测试
public class SingleLinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
//插入后链表中的数据 87 33 56
singleLinkedList.addFirstNode(56);
singleLinkedList.addFirstNode(33);
singleLinkedList.addFirstNode(87);
//插入后 87 47 33 56
singleLinkedList.add(1, 47);
//插入后 87 47 23 33 56
singleLinkedList.add(2, 23);
//插入后 87 47 23 99 33 56
singleLinkedList.add(3, 99);
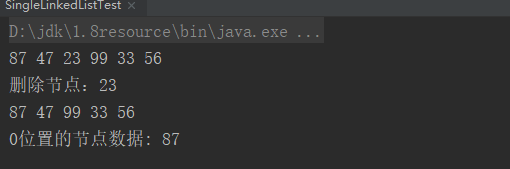
singleLinkedList.displayAllNodes();
//删除后 87 47 99 33 56
Node node = singleLinkedList.deleteByData(23);
System.out.println("删除节点:"+node.data);
singleLinkedList.displayAllNodes();
Node node1 = singleLinkedList.findByPos(0);
System.out.println("0位置的节点数据: " + node1.data);
}
}
测试结果:





















 1318
1318

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








