前言
dataType 和 contentType 是前端开发中常见的两个概念,尤其在 AJAX 请求中经常用到。再谈contentType与dataType,它们的作用和区别如下:
1. contentType
定义:
contentType 是指发送给服务器的数据的格式(即请求头中的 Content-Type),告诉服务器客户端发送的数据是什么类型。
常见值:
- application/json:发送 JSON 格式的数据。
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded:发送 URL 编码的表单数据(默认值)。
- multipart/form-data:用于文件上传。
$.ajax({
url: "example.com/api",
method: "POST",
contentType: "application/json", // 告诉服务器发送的是 JSON 数据
data: JSON.stringify({ name: "John", age: 30 }),
success: function(response) {
console.log(response);
}
});
2. dataType
定义:
dataType 是指客户端期望从服务器返回的数据格式,告诉 jQuery 如何解析服务器返回的数据。
常见值:
-
json:期望返回 JSON 格式的数据,jQuery 会自动将其解析为 JavaScript 对象。
-
xml:期望返回 XML 格式的数据。
-
text:期望返回纯文本数据。
-
html:期望返回 HTML 片段。
$.ajax({
url: "example.com/api",
method: "GET",
dataType: "json", // 期望服务器返回 JSON 数据
success: function(response) {
console.log(response); // response 已经是 JavaScript 对象
}
});
3. 区别总结
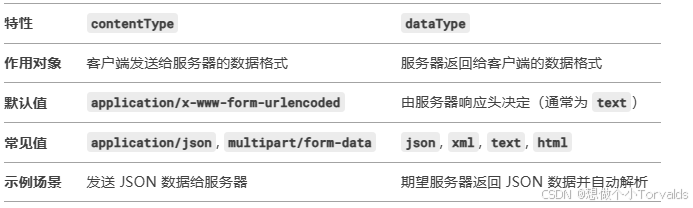
4. 实际应用场景
① 场景 1:发送 JSON 数据并期望返回 JSON
$.ajax({
url: "example.com/api",
method: "POST",
contentType: "application/json", // 发送 JSON 数据
dataType: "json", // 期望返回 JSON 数据
data: JSON.stringify({ name: "John", age: 30 }),
success: function(response) {
console.log(response); // response 是 JavaScript 对象
}
});
② 场景 2:发送表单数据并期望返回 HTML
$.ajax({
url: "example.com/api",
method: "POST",
contentType: "application/x-www-form-urlencoded", // 发送表单数据
dataType: "html", // 期望返回 HTML
data: { name: "John", age: 30 },
success: function(response) {
$("#result").html(response); // 将返回的 HTML 插入页面
}
});
- 注意事项
①contentType 不设置时: 默认值为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded,适合发送表单数据。
②dataType 不设置时: jQuery 会根据服务器返回的 Content-Type 自动推断数据类型,但建议显式指定以避免解析错误。
③JSON 数据格式: 如果 contentType 设置为 application/json,必须使用 JSON.stringify()将数据转换为 JSON 字符串。




















 434
434

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








